You searched for: 回国加速器【输入∶海归returnees加速器】海归returnees加速器app海归returnees加速器publishers海归returnees加速器top海归returnees加速器published海归returnees加速器apps海归returnees加速器and海归returnees加速器more海归returnees加速器in海归returnees加速器United海归returnees加速器States海归returnees加速器Google海归returnees加速器Play海归returnees加速器Store
<< Previous | Displaying results 2351-2400 of 2669 for "回国加速器【输入∶海归returnees加速器】海归returnees加速器app海归returnees加速器publishers海归returnees加速器top海归returnees加速器published海归returnees加速器apps海归returnees加速器and海归returnees加速器more海归returnees加速器in海归returnees加速器United海归returnees加速器States海归returnees加速器Google海归returnees加速器Play海归returnees加速器Store" | Next >>
-
Prewar portrait of Dorrith Oppenheim
PhotoDorrith was born in Kassel, Germany, in December 1938. Her parents were Hans and Trudi Oppenheim. Following increased anti-Jewish measures, Dorrith was among the children sent on Kindertransports to find refuge in the United Kingdom. She left Germany on July 24, 1939. She never saw her parents again. They were deported to Auschwitz, where they perished in October 1944.

-
Public Humiliation
ArticleThe Nazis used public humiliation tactics to degrade their victims and to reinforce Nazi racial ideology for German citizens and populations under Nazi occupation.

-
Theresienstadt
ArticleThe Theresienstadt camp/ghetto served multiple purposes during its existence from 1941-45 and had an important propaganda function for the Germans. Learn more.

-
German Wartime Expansion
ArticleBetween 1939-1942, Nazi Germany invaded multiple countries across Europe. Learn more about German expansion during World War II.

-
Resistance inside Germany
ArticleSome individuals and groups in Germany attempted to resist Nazism, despite the risk of being caught and facing punishment. Learn more about their efforts.

-
Ernest Koenig describes reaching the verge of death while in a subcamp of Auschwitz
Oral HistoryErnest was studying in Paris, France, until February 1939, when he returned to Brno, Czechoslovakia. The Germans occupied the latter region soon thereafter, but Ernest managed to return to France. He joined a Czech unit in the French army from October 1939 until the fall of France in May 1940. He made his way to unoccupied France, where he taught for a while. He then went to Grenoble, and again taught, but was arrested because he did not have the appropriate papers. Ernest was interned in Le Vernet camp…

-
Leah Hammerstein Silverstein describes lack of burial of the corpses of people who died in the Warsaw ghetto
Oral HistoryLeah grew up in Praga, a suburb of Warsaw, Poland. She was active in the Ha-Shomer ha-Tsa'ir Zionist youth movement. Germany invaded Poland in September 1939. Jews were forced to live in the Warsaw ghetto, which the Germans sealed off in November 1940. In the ghetto, Leah lived with a group of Ha-Shomer ha-Tsa'ir members. In September 1941, she and other members of the youth group escaped from the ghetto to a Ha-Shomer ha-Tsa'ir farm in Zarki, near Czestochowa, Poland. In May 1942, Leah became a courier…

-
Kripo warrant badge
Media EssayOfficial identification tag (warrant badge) used by the State Criminal Police (Kriminalpolizei or Kripo), after Heinrich Himmler centralized the police forces in the 1930s. These badges were generally suspended from a chain and included the individual officer's number on the reverse.
-
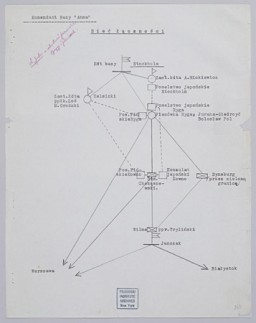
"Web of Communications" chart, July 1940
DocumentDiagram showing "the web of communications" between Japanese diplomats and members of the Polish resistance in the Baltic states and Scandinavia. The "Konsulat japonski Kowno" refers to Sugihara. Despite its ties with Nazi Germany, Japan pursued its own course in foreign policy. After the Germans occupied Poland and the Netherlands, Japan continued relations with both the Polish and Dutch governments-in-exile in London. July 1940.
-
Reverse of a Kripo warrant disc listing the officer's number
ArtifactReverse of the official identification tag (warrant badge) for the Kriminalpolizei or Kripo, the detective police force of Nazi Germany. It reads Staatliche Kriminalpolizei (State Criminal Police) and identifies the officer's number as 8409.

-
Courtroom Sketch of Elie Wiesel at the Trial of Klaus Barbie
ArtifactCourtroom sketch by artist David Rose of Nobel laureate and Holocaust survivor Elie Wiesel on the witness stand at the trial of Klaus Barbie. During his testimony, Wiesel stated that "The killer kills twice. First, by killing, and then by trying to wipe out the traces." June 2, 1987.

-
Sign excluding Jews from public places
ArtifactSigns excluding Jews, such as the sign shown here, were posted in public places (including parks, theaters, movie houses, and restaurants) throughout Nazi Germany. This sign states in German: "Jews are not wanted here."

-
Buchenwald trial document
ArtifactDocument from the Buchenwald trial stating that both the prosecution and the defense teams agree to waive their right to make closing statements. The document is signed by the US military prosecutors (including William Denson), the defense lawyers, and the defendants. Dachau, Germany, August 8, 1947.

-
Agreement Reached at Munich Conference
Film[This video is silent] An agreement signed at the Munich conference of September 1938 ceded the German-speaking Sudetenland region of Czechoslovakia to Germany. The agreement was reached between Germany, Italy, Britain, and France. Czechoslovakia was not permitted to attend the conference. In March 1939, six months after signing the Munich agreement, Hitler violated the agreement and destroyed the Czech state.

-
Albert Speer sworn in at Nuremberg
FilmDefendant Albert Speer is sworn in at the International Military Tribunal.

-
Interpreters at the International Military Tribunal
PhotoView of the interpreters' section in the courtroom during the International Military Tribunal. Nuremberg, Germany, March 29, 1946. The Nuremberg trials were an early experiment in simultaneous translation. The charter of the International Military Tribunal stated that the defendants had the right to a fair trial and that, accordingly, all proceedings be translated into a language that the defendants understood.

-
Jewish refugee ship Pan-York docks in Haifa
PhotoThe Jewish refugee ship Pan-York, carrying new citizens to the recently established state of Israel, docks at Haifa. The ship sailed from southern Europe to Israel, via Cyprus. Haifa, Israel, July 9, 1948.

-
Storm Troopers stand guard outside a defaced Jewish-owned business
PhotoShortly after the German annexation of Austria, Nazi Storm Troopers stand guard outside a Jewish-owned business. Graffiti painted on the window states: "You Jewish pig may your hands rot off!" Vienna, Austria, March 1938.

-
Antisemitism illustration from a Nazi film strip
PhotoAn antisemitic illustration from a Nazi film strip. The caption, translated from German, states: "As an alien race Jews had no civil rights in the middle ages. They had to reside in a restricted section of town, in a ghetto." Place and date uncertain.

-
Onlookers view the damaged Reichstag
PhotoOnlookers in front of the Reichstag (German parliament) building the day after it was damaged by fire. On this same day, the Nazis implemented the Decree of the Reich President for the Protection of the People and the State. It was one of a series of key decrees, legislative acts, and case law in the gradual process by which the Nazi leadership moved Germany from a democracy to a dictatorship. Berlin, Germany, February 28, 1933.

-
The White Rose Opposition Movement
ArticleThe White Rose, led by students including Hans and Sophie Scholl, was an anti-Nazi group during WWII. Its members spread leaflets denouncing the regime.

-

-
Balkan Campaign, Spring 1941
ArticleIn April 1941, Germany invaded and subdued the Balkan countries of Yugoslavia and Greece. These countries were then occupied and administered by Axis members. Read more.

-
Hermann Göring
ArticleBrief overview of the charges against Hermann Göring, highest ranking Nazi official tried during the International Military Tribunal at Nuremberg.

-
Santa Maria di Leuca Displaced Persons Camp
ArticleAfter WWII, many Holocaust survivors, unable to return to their homes, lived in displaced persons camps in Germany, Austria, and Italy. Read about Santa Maria di Leuca DP camp.
-
Hitler Abolishes the Office of President
Timeline EventAugust 19, 1934. On this date, Hitler abolished the office of President and declares himself as Führer, thus becoming the absolute dictator of Germany.

-
Jews in Prewar Germany
SeriesLearn about Jewish life in Germany and Europe before WWII, antisemitic laws, and Nazi violence and discrimination against the Jews of Germany.
-
Charlene Schiff describes being caught while trying to smuggle food into the Horochow ghetto
Oral HistoryBoth of Charlene's parents were local Jewish community leaders, and the family was active in community life. Charlene's father was a professor of philosophy at the State University of Lvov. World War II began with the German invasion of Poland on September 1, 1939. Charlene's town was in the part of eastern Poland occupied by the Soviet Union under the German-Soviet Pact of August 1939. Under the Soviet occupation, the family remained in its home and Charlene's father continued to teach. The Germans…

-
Bart Stern describes the role of friendships in survival at Auschwitz
Oral HistoryFollowing the German occupation of Hungary in March 1944, Bart was forced into a ghetto established in his home town. From May to July 1944, the Germans deported Jews from Hungary to the Auschwitz killing center in occupied Poland. Bart was deported by cattle car to Auschwitz. At Auschwitz, he was selected to perform forced labor, drilling and digging in a coal mine. As Soviet forces advanced toward the Auschwitz camp in January 1945, the Germans forced most of the prisoners on a death march out of the…

-
Cecilie Klein-Pollack describes survival with her sister in Auschwitz
Oral HistoryCecilie was the youngest of six children born to a religious, middle-class Jewish family. In 1939, Hungary occupied Cecilie's area of Czechoslovakia. Members of her family were imprisoned. The Germans occupied Hungary in 1944. Cecilie and her family had to move into a ghetto in Huszt and were later deported to Auschwitz. Cecilie and her sister were chosen for forced labor; the rest of her family was gassed upon arrival. Cecilie was transferred to several other camps, where she labored in factories. Allied…

-
Mieczyslaw Madejski describes battle during the Warsaw Polish uprising
Oral HistoryMieczyslaw and his family were not Jewish. When Germany invaded Poland, Mieczyslaw was working for an organization formed for self-defense against German bombings. Later, he worked for the Polish underground group ZWZ (Zwiazek Walki Zbrojnej; Union for Armed Struggle), which became the AK (Armia Krajowa; Home Army). In 1943, he was conscripted for forced labor at a BMW plant in Warsaw. He escaped, and participated in the Warsaw Polish uprising in August 1944. After the uprising, he left Warsaw and went…

-
Mieczyslaw Madejski describes underground organization and activities
Oral HistoryMieczyslaw and his family were not Jewish. When Germany invaded Poland, Mieczyslaw was working for an organization formed for self-defense against German bombings. Later, he worked for the Polish underground group ZWZ (Zwiazek Walki Zbrojnej; Union for Armed Struggle), which became the AK (Armia Krajowa; Home Army). In 1943, he was conscripted for forced labor at a BMW plant in Warsaw. He escaped, and participated in the Warsaw Polish uprising in August 1944. After the uprising, he left Warsaw and went…

-
Italy
ArticleItaly was home to one of the oldest Jewish communities in Europe. It was also a member of the Axis alliance with Nazi Germany. Learn about Italy during WWII and the Holocaust.

-
The Syrets Labor Education Camp
ArticleSyrets was a labor education camp established by the Germans outside of Kyiv. Learn more about Syrets prisoners and their daily life in the camp.
-
Leo Bretholz describes his escape from a train during deportation from the Drancy camp
Oral HistoryAfter the Germans annexed Austria in 1938, Leo attempted to flee. He eventually reached Belgium. In 1940 he was deported to the St.-Cyprien camp in France but escaped. In 1942 Leo was smuggled into Switzerland but was arrested and sent back to France, this time to the Rivesaltes and Drancy camps. He and a friend escaped from a train deporting them to Auschwitz in Poland. Leo joined the French underground in 1943. He arrived in the United States in 1947.

-
Estonian policemen stand trial for war crimes
FilmEstonian auxiliary forces assisted the German Einsatzgruppen (mobile killing units) in the mass killing of Jews and others during World War II. Ralf Gerrets and Jaan Viik were both members of the Estonian security police during the German occupation. This footage shows them during their trial, on charges of war crimes, in the Estonian Soviet Socialist Republic. The Estonian Supreme Court found both guilty and sentenced them to death in 1961.

-
Fall of Warsaw
FilmGerman troops reached parts of Warsaw on September 8 and 9, 1939. During the German siege of Warsaw, the city sustained heavy damage from air attacks and artillery shelling. Warsaw surrendered on September 28. Here, German troops occupy Warsaw. This footage comes from "Tale of a City," a film made by a Polish underground film unit.

-
Soviet military advance in Vitebsk
FilmThe Germans invaded the Soviet Union in June 1941 (Operation "Barbarossa"). German forces occupied Vitebsk in the northeastern region of Belorussia on July 11. Soviet forces seized the initiative from the Germans after the battle of Stalingrad in late 1942 and early 1943. The Soviet army liberated Vitebsk on June 26, 1944, during their summer 1944 offensive. This footage shows military units involved in the fighting and German soldiers captured during the campaign. By the end of the summer, the Soviet…

-
John Perry films US troops in Belgium
PhotoJohn Perry, a movie photographer with Unit 129, films GIs of the 290th Infantry Regiment, 75th Infantry Division, and 4th Cavalry Group ferreting out German snipers near Beffe, Belgium during the Battle of the Bulge. Twelve Germans were killed. The scene was photographed by Carmen Corrado of the 129th. January 7, 1945. US Army Signal Corps photograph taken by C.A. Corrado.

-
John Perry films US soldiers in Belgium
PhotoJohn Perry, a movie photographer with Unit 129, films GIs of the 290th Infantry Regiment, 75th Infantry Division, and 4th Cavalry Group ferreting out German snipers near Beffe, Belgium, in early January 1945. Twelve Germans were killed. The scene was photographed by Carmen Corrado of the 129th. January 7, 1945. US Army Signal Corps photograph taken by C.A. Corrado.

-
1934 Nazi Party propaganda poster
PhotoNazi propaganda constantly reinforced the notion that Hitler was the embodiment of the national will. Here, a determined looking Hitler in military dress stands with clenched fist, poised for action above the adoring crowd. The text on the poster says "Yes! Leader, We Follow You!" (Ja! Führer wir folgen Dir!) This poster, designed for a 1934 public referendum on uniting the posts of German chancellor and president, conveys unanimous popular support for Hitler.

-
Norway
ArticleGermany invaded Norway on April 9, 1940. Read more about this invasion, the collaborator Vidkun Quisling, and the tragic fate of Norway’s Jews.

-
Bernard Musmand
ArticleRead the Jewish Partisan Educational Foundation's short biography of Bernard Musmand.

-
Silvio Ortona
ArticleRead the Jewish Partisan Educational Foundation's short biography of Silvio Ortona.

-
Meir Porges
ArticleRead the Jewish Partisan Educational Foundation's short biography of Meir Porges.

-
Leon Senders
ArticleRead the Jewish Partisan Educational Foundation's short biography of Leon Senders.

-

-
Samuel Levi
ArticleRead the Jewish Partisan Educational Foundation's short biography of Samuel Levi.

-

-
Child survivors of Auschwitz
PhotoThis photograph is a still from Soviet film footage of the liberation of Auschwitz. The film was made by the film unit of the First Ukrainian Front. Relief workers and Soviet soldiers lead child survivors of Auschwitz through a narrow passage between two barbed-wire fences. Standing next to the nurse and behind them (wearing white hats) are two sets of twin sisters. During the camp's years of operation, many children in Auschwitz were subjected to medical experiments by Nazi physician Josef Mengele.

