You searched for: 竞彩比分3串1奖金封顶【杏彩官方qee9.com】福彩3d杀码图最准杀,,,0278UTWK3yVp
<< Previous | Displaying results 651-675 of 946 for "竞彩比分3串1奖金封顶【杏彩官方qee9.com】福彩3d杀码图最准杀,,,0278UTWK3yVp" | Next >>
-
Quakers
ArticleThe American Friends Service Committee, a Quaker relief organization, helped thousands of people before, during, and after World War II. Learn about its refugee aid work.

-
Gisha Galina Bursztyn: Maps
Media EssayBorn to Jewish parents in Poland, Gisha Galina Bursztyn moved to the city of Warsaw after she married. On September 1, 1939, Germany invaded Poland. Warsaw fell four weeks later, and a ghetto was set up in November 1940. During a massive roundup i...
-

-
Chiune Sugihara
Media EssayChiune (Sempo) Sugihara (January 1, 1900-1986) was the first Japanese diplomat posted to Lithu...

-
Hoess affidavit
ArtifactAffidavit signed by Rudolf Hoess attesting to the gassing of Jews while he was the commandant of the Auschwitz killing center. The German text reads: "I declare herewith under oath that in the years 1941 to 1943 during my tenure in office as commandant of Auschwitz Concentration Camp 2 million Jews were put to death by gassing and a 1/2 million by other means. Rudolf Hoess. May 14, 1946." The confession is also signed by Josef Maier of the US Chief of Counsel's office. A photoreproduction of the original…

-
Lodz ghetto model
ArtifactLeon Jakubowicz, a shoemaker by training and a native of Lodz, began constructing this model of the Lodz ghetto soon after his arrival there from a prisoner-of-war camp in April 1940. The case holds a scale (1:5000) model of the ghetto, including streets, painted houses, bridges, churches, synagogue ruins, factories, cemeteries, and barbed wire around the ghetto edges. The model pieces are made from scrap wood. The case cover interior is lined with a collection of official seals, a ration card, and paper…

-
Model of the Lodz ghetto
ArtifactLeon Jakubowicz, a shoemaker by training and a native of Lodz, began constructing this model of the Lodz ghetto soon after his arrival there from a prisoner-of-war camp in April 1940. The case holds a scale (1:5000) model of the ghetto, including streets, painted houses, bridges, churches, synagogue ruins, factories, cemeteries, and barbed wire around the ghetto edges. The model pieces are made from scrap wood. The case cover interior is lined with a collection of official seals, a ration card, and paper…

-
Diagram of the “Gypsy camp” in Hodonín u Kunštátu
DocumentDiagram of the Hodonín u Kunštátu (Hodonin bei Kunstadt) camp in the Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia (Czech Republic). Before it was converted into a Zigeunerlager (“Gypsy camp”) in 1942, it served as a penal labor camp. Translation of key: Scale 1:500 Sleeping quarters Sleeping quarters Mess-hall Infirmary Offices, prison Living quarters for guard staff Economic/Agricultural Building Latrine Well Mess-hall for guard staff Pens for guard dogs
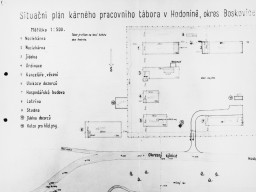
-
Scene during the opening of the 11th Summer Olympic Games
PhotoOn August 1, 1936, Hitler opened the 11th Summer Olympic Games. Inaugurating a new Olympic ritual, a lone runner arrived bearing a torch carried by relay from the site of the ancient Games in Olympia, Greece. This photograph shows an Olympic torch bearer running through Berlin, passing by the Brandenburg Gate, shortly before the opening ceremony. Berlin, Germany, July-August 1936.

-
SA members post anti-Jewish boycott signs
PhotoAn SA member instructs others where to post anti-Jewish boycott signs on a commercial street in Germany. A German civilian wearing a Nazi armband holds a sheaf of anti-Jewish boycott signs, while SA members paste them on a Jewish-owned business. Most of the signs read, "Germans defend yourselves against Jewish atrocity propaganda/Buy only at German stores." Germany, ca. April 1, 1933.

-
The Nazi Olympics Berlin 1936: Inauguration of the Olympic Torch Relay
ArticleThe 1936 Olympics were the first to employ the torch relay. Learn more about this new ritual, Nazi propaganda, and the Olympic Games in Berlin, Germany.

-
Siege (1940)
ArticleJulien Bryan’s ten-minute film Siege, first non-Nazi produced footage of the start of WWII, records horror and chaos in Warsaw following the German invasion.

-
Encircling the Ruhr
ArticleEncircling the Ruhr region was a key Allied military goal. Learn about the military campaign to capture the industrial center of western Germany in the last months of WWII.

-
The Doctors Trial: The Medical Case of the Subsequent Nuremberg Proceedings
ArticleThe Medical Case, or Doctors Trial, was Case #1 of 12 Subsequent Nuremberg Proceedings against leading German industrialists, military figures, SS perpetrators, and others.

-
Ben Hecht
ArticleAmerican-Jewish journalist and author Ben Hecht co-wrote the We Will Never Die pageant and advocated for the rescue of Jewish victims from Nazism. Learn more.
-

-
Prewar photo of the extended Kracowski family
PhotoThe Kracowski family was living in Bialystok when German Order Police Battalion 309 killed 2,000-3,000 Jews on June 27, 1941. Dr. Samuel Kracowski was among the hundreds of Jews locked in the Great Synagogue and burned alive. After the Germans ordered the establishment of a ghetto in Bialystok, Samuel's wife, Esther, and children, Ewa and Julek, were given a room in the ghetto clinic. Photo dated September 1, 1935. Samuel and Esther are seated in the center, with Julek seated in the front row on the…
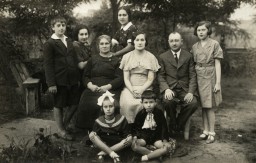
-
The Nazi Olympics Berlin 1936
ArticleThe 1936 Olympics in Berlin under Adolf Hitler's Nazi dictatorship were more than just a worldwide sporting event, they were also a show of Nazi propaganda.

-
Szlamach Radoszynski
ID CardSzlamach was one of six children born to Yiddish-speaking, religious Jewish parents. Szlamach's father was a peddler, and the Radoszynski family lived in a modest apartment in Warsaw's Praga section on the east bank of the Vistula River. After completing his schooling at the age of 16, Szlamach apprenticed to become a furrier. 1933-39: During the 1930s Szlamach owned a fur business. Despite the Depression, he was hoping the economy would turn around so that he could make enough money to move into his own…

-
Warsaw
ArticleIn October 1940, Nazi authorities established the Warsaw ghetto. Learn more about life in the ghetto, deportations, armed resistance, and liberation.

-
Irena Elzbieta Wos
ID CardIrena was the second of four children born to religious Roman Catholic parents in Poland's capital of Warsaw. Irena's father owned a successful textile business. When Irena was 10, her family moved to a comfortable apartment near the Royal Castle and the Vistula River. In 1930 Irena entered a private grade school. 1933-39: At 14 Irena began secondary school. She was a good student and wanted to be a doctor. On September 1, 1939, the day she was supposed to begin the new school year, the Germans attacked…
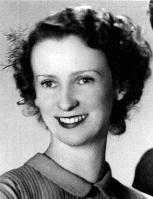
-
Mieczyslaw (Marek) Madejski
ID CardMieczyslaw was the eldest of three sons born to well-to-do Roman Catholic parents in Poland's capital of Warsaw. His father was a real estate developer and his mother was a housewife. Mieczyslaw, or Mieteck as he was nicknamed, began attending public elementary school in 1930 when he was 7 years old. 1933-39: Mieczyslaw's father urged him to study either German or Russian because he thought it was likely that there would be a German or Soviet invasion. Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. During…

-
Martin Niemöller: "First they came for..."
ArticleLearn about the origins and legacy of Pastor Martin Niemöller's famous postwar words, “First they came for the socialists, and I did not speak out…”

-
Mass Shootings at Babyn Yar (Babi Yar)
ArticleAt Babyn Yar in late September 1941, SS and German police units and their auxiliaries perpetrated one of the largest massacres of World War II.

-
Treblinka: Key Dates
ArticleExplore a timeline of key events during the history of the Treblinka killing center in German-occupied Poland.

