You searched for: used交易程序後臺源碼【tg���������@ek7676】平台包网搭建usd交易程序後臺源碼【tg���������@ek7676】平台包网搭建ivkcss1pgu
<< Previous | Displaying results 1451-1499 of 1782 for "used交易程序後臺源碼【tg���������@ek7676】平台包网搭建usd交易程序後臺源碼【tg���������@ek7676】平台包网搭建ivkcss1pgu" | Next >>
-
The Role of the German Police
ArticleTo implement their policies, the Nazis had help from individuals across Europe, including professionals in many fields. Learn about the role of the German police.

-
Eugenics
ArticleTheories of eugenics shaped many persecutory policies in Nazi Germany. Learn about the radicalization and deadly consequences of these theories and policies

-
Displaced Persons Camps in the Steiermark District
ArticleAfter WWII, many Holocaust survivors, unable to return to their homes, lived in displaced persons camps in Germany, Austria, and Italy. Read about Steiermark District DP camps.

-
Vittel
ArticleGerman authorities established the Vittel internment camp in occupied France in 1941. It belonged to the complex of POW camps designated Frontstalag 194.

-
Persecution of Roma (Gypsies) in Prewar Germany, 1933–1939
ArticleBeginning in 1933, the Nazis persecuted Roma (often pejoratively called “Gypsies”) based on underlying prejudices and racism. Learn how this harassment escalated to genocide.

-
Frieda Belinfante
Photo“For three months I was disguised as a man, and very successfully… I passed my mother several times … she never recognized me.” Frieda Belinfante, a half-Jewish lesbian, used this disguise to hide from Nazi authorities. In a later interview she said, “I really looked pretty good.” Her involvement in the resistance movement included planning the destruction of the Amsterdam Population Registry in March 1943, falsifying identity cards, and arranging hiding places for those who were sought by…

-

-
Raoul Wallenberg Arrives in Budapest
Timeline EventJuly 9, 1944. On this date, Raoul Wallenberg arrived in Budapest and began his wartime rescue efforts.

-
Hungarian Jewish Businessman Begins Issuing Papers to Jewish refugees
Timeline EventAugust 25, 1942. On this date, George Mandel-Mantello began issuing Salvadoran citizenship papers to Jewish refugees in Nazi-occupied Europe.

-
Page from Earl G. Harrison's Notebook
Timeline EventJune 4, 1945. On this date, Earl G. Harrison toured displaced persons camps and wrote of his impressions of Linz, Austria.

-
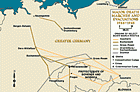
Evacuation of Prisoners from Sachsenhausen
Timeline EventApril 20-21, 1945. On this date, SS guards evacuated prisoners from the Sachsenausen concentration camp in Germany.
-
Anne Frank Born
Timeline EventJune 12, 1929. On this date, future diarist Anne Frank was born to Otto and Edith Frank. She would become a symbol for the children who died in the Holocaust.

-
Adolf Hitler Becomes Leader of the Reestablished Nazi Party
Timeline EventFebruary 27, 1925. On this date, Adolf Hitler declared the reformulation of the Nazi Party with himself as the leader.

-
Reichstag Speech
Timeline EventJanuary 30, 1939. On this date, Adolf Hitler declared that the outbreak of war would mean the end of European Jewry.

-
Occupation of Kyiv
Timeline EventSeptember 19, 1941. On this date, German forces entered Kyiv in Soviet Ukraine.

-
“Euthanasia” Killings
Timeline EventAugust 24, 1941. On this date, Adolf Hitler ordered the cessation of centrally coordinated "euthanasia" killings due to public protests.

-
Eden Dance Palace Shooting
Timeline EventNovember 22, 1930. On this date, Nazis attack a leftwing group at a dance hall in Berlin.
-
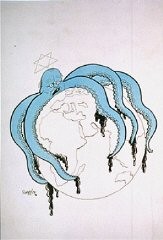
Nazi-era Antisemitic Propaganda Poster
PhotoNazi propaganda cartoon by Seppla (Josef Plank), a political cartoonist. Germany, date uncertain [probably during World War II]. Beginning in the 1920s, Nazi propagandists promoted the antisemitic myth that Jews were engaged in a massive conspiracy to take over the world. This false notion alleged that “international Jewry” used various people and groups as part of a plan for global conquest. At the time, an octopus extending its tentacles over the globe was a common visual metaphor for this…
-
Dr. Robert Ritter visits a "Gypsy camp"
PhotoDr. Robert Ritter talks to several residents in a Zigeunerlager ("Gypsy camp"). Hamburg, Germany, 1940. During the Nazi era, Dr. Robert Ritter was a leading authority on the racial classification of people pejoratively labeled “Zigeuner” (“Gypsies”). Ritter’s research was in a field called eugenics, or what the Nazis called “racial hygiene.” Ritter worked with a small team of racial hygienists. Among them were Eva Justin and Sophie Ehrhardt. Most of the people whom Ritter studied and…

-
Sophie Ehrhardt performs a racial examination on a Romani woman
PhotoSophie Ehrhardt, a German hygienist working with Dr. Robert Ritter, performs a racial examination on a Romani woman. Berlin, Germany, c. 1936-1940. During the Nazi era, Dr. Robert Ritter was a leading authority on the racial classification of people pejoratively labeled “Zigeuner” (“Gypsies”). Ritter’s research was in a field called eugenics, or what the Nazis called “racial hygiene.” Ritter worked with a small team of racial hygienists. Among them were Eva Justin and Sophie Ehrhardt. Most…

-
Eva Justin interviews a Romani woman interned in a "Gypsy camp"
PhotoA color photograph of Eva Justin interviewing a Romani woman interned in a "Gypsy camp." Vienna, Austria, 1940. During the Nazi era, Dr. Robert Ritter was a leading authority on the racial classification of people pejoratively labeled “Zigeuner” (“Gypsies”). Ritter’s research was in a field called eugenics, or what the Nazis called “racial hygiene.” Ritter worked with a small team of racial hygienists. Among them were Eva Justin and Sophie Ehrhardt. Most of the people whom Ritter studied and…

-
A family interned in a "Gypsy camp"
PhotoA family stands outside of their wagon while interned in a Zigeunerlager ("Gypsy camp"). In the background, children are crowded around Eva Justin. Justin worked for the Center for Research on Racial Hygiene and Demographic Biology. Schleswig-Holstein, Germany, 1938. During the Nazi era, Dr. Robert Ritter was a leading authority on the racial classification of people pejoratively labeled “Zigeuner” (“Gypsies”). Ritter’s research was in a field called eugenics, or what the Nazis called…

-
Introduction to the Holocaust
ArticleLearn about the Holocaust, the systematic, state-sponsored persecution and murder of six million Jews by the Nazi regime and its collaborators.

-
Benjamin (Beryl) Ferencz describes early war crimes investigations
Oral HistoryBen was born in a small village in the Carpathian Mountains of Transylvania in Romania. When he was an infant, his family moved to the United States. Ben attended Harvard University, where he studied criminal law. Ben graduated from Harvard University Law School in 1943. He joined a US anti-aircraft artillery battalion that was training in preparation for an Allied invasion of western Europe. At the end of World War II in Europe, Ben was transferred to the war crimes investigation branch of the US Army. He…

-
Magnus Hirschfeld
ArticleA leading researcher of sex, sexuality, and gender, German Jewish doctor Magnus Hirschfeld was forced to live in exile after the Nazi rise to power.

-
"Nuremberg: Its Lesson for Today"
FilmThis footage comes from "Nuremberg, Its Lesson for Today" a 1947 documentary film produced by the US military's Documentary Film Unit, Information Services Division. The film, directed by Pare Lorentz and Stuart Schulberg, shows footage from the trial of Nazi war criminals by the International Military Tribunal. It also intermixes historical footage depicting the founding of the Nazi state, the unleashing of World War II, and Nazi crimes against humanity. The sentencing sequence shown here illustrates the…

-
Isadore Helfing describes labor in the Treblinka camp
Oral HistoryIsadore was born to a Jewish family in Kielce, Poland. Germany invaded Poland in September 1939. Isadore and his family were forced into the Kielce ghetto, which was established in April 1941. When his parents were deported to the Treblinka killing center in 1942, Isadore went with them rather than remaining behind for forced labor. After arrival at the camp, Isadore hid in a pile of bodies. His parents were killed. Isadore survived by working in the camp. On August 2, 1943, prisoners at Treblinka revolted…

-
Tom Veres describes Wallenberg's rescue of members of the Swedish legation
Oral HistoryAfter the Germans occupied Hungary in 1944, Tom was ordered to work in labor camps and factories. He escaped after a few months and decided to contact the Swedish legation, where he met Raoul Wallenberg in October 1944. Tom stayed in Budapest and, using his training in photography, became active in Wallenberg's efforts to rescue the Jews of Budapest. He made copies of and took photographs for protective passes (Schutzpaesse), and documented deportations.

-
Charlene Schiff describes the Soviet occupation of Horochow after the outbreak of World War II
Oral HistoryBoth of Charlene's parents were local Jewish community leaders, and the family was active in community life. Charlene's father was a professor of philosophy at the State University of Lvov. World War II began with the German invasion of Poland on September 1, 1939. Charlene's town was in the part of eastern Poland occupied by the Soviet Union under the German-Soviet Pact of August 1939. Under the Soviet occupation, the family remained in its home and Charlene's father continued to teach. The Germans…

-
Leah Hammerstein Silverstein describes lack of burial of the corpses of people who died in the Warsaw ghetto
Oral HistoryLeah grew up in Praga, a suburb of Warsaw, Poland. She was active in the Ha-Shomer ha-Tsa'ir Zionist youth movement. Germany invaded Poland in September 1939. Jews were forced to live in the Warsaw ghetto, which the Germans sealed off in November 1940. In the ghetto, Leah lived with a group of Ha-Shomer ha-Tsa'ir members. In September 1941, she and other members of the youth group escaped from the ghetto to a Ha-Shomer ha-Tsa'ir farm in Zarki, near Czestochowa, Poland. In May 1942, Leah became a courier…

-
Irene Hizme and Rene Slotkin describe being separated from their mother upon arrival in the Auschwitz camp
Oral HistoryIrene and Rene were born Renate and Rene Guttmann. The family moved to Prague shortly after the twins' birth, where they were living when the Germans occupied Bohemia and Moravia in March 1939. A few months later, uniformed Germans arrested their father. Decades later, Irene and Rene learned that he was killed at the Auschwitz camp in December 1941. Irene, Rene, and their mother were deported to the Theresienstadt ghetto, and later to the Auschwitz camp. At Auschwitz, the twins were separated and subjected…

-
Wilek (William) Loew describes the Soviet occupation of Lvov in 1939
Oral HistoryWilek was the son of Jewish parents living in the southeastern Polish town of Lvov. His family owned and operated a winery that had been in family hands since 1870. Wilek's father died of a heart attack in 1929. Wilek entered secondary school in 1939. Soon after he began school, World War II began with the German invasion of Poland. Lvov was in the part of eastern Poland annexed by the Soviet Union. Although the Soviets took over Wilek's home and the family business, Wilek was able to continue his…

-
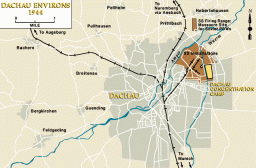
Dachau concentration camp
Animated MapView an animated map showing key events in the history of the Dachau concentration camp, which was established by the Nazi regime in 1933.
-
Killing Centers: In Depth
ArticleThe Nazis established killing centers in German-occupied Europe during WWII. They built these killing centers for the mass murder of human beings.

-
Children's Diaries during the Holocaust
ArticleOf the millions of children who suffered persecution at the hands of the Nazis and their Axis partners, a small number wrote diaries and journals that have survived.

-
Charlene Schiff describes escaping from the Horochow ghetto
Oral HistoryBoth of Charlene's parents were local Jewish community leaders, and the family was active in community life. Charlene's father was a professor of philosophy at the State University of Lvov. World War II began with the German invasion of Poland on September 1, 1939. Charlene's town was in the part of eastern Poland occupied by the Soviet Union under the German-Soviet Pact of August 1939. Under the Soviet occupation, the family remained in its home and Charlene's father continued to teach. The Germans…

-
Kazimiera Banach Justynowa
ID CardKazimiera was born to Roman Catholic parents in the town of Mierzen. After graduating from a teacher's college in Staniatki, she married Wincenty Justyna, a secondary school teacher. The couple settled in the small industrial city of Piotrkow Trybunalski and raised three children, Jerzy (a boy), Danuta and Maria. Kazimiera worked as a school teacher. 1933-39: With their combined incomes the Justynas were able to buy a plot of land and build a house. The Germans invaded Poland on September 1, 1939, and…

-
Abraham Malnik
ID CardAbraham was born to a Jewish family in Kovno, a city picturesquely situated at the confluence of two rivers. With an opera company, chic stores and lively nightclubs, it was often called "Little Paris." The city had a large Jewish community of 38,000 and was known for its extensive Hebrew school system. Abraham's father was a barber, and his mother was a beautician. 1933-39: When Abraham was a kid his family used to go to his grandparents' house for Sunday dinner. In the winter they would take a…

-
Abraham Bergman
ID CardAbraham was born to a Jewish family in Krasnik, a town in the Lublin district of Poland. The town had a large Jewish population. Abraham's father was a tailor. When Abraham was 2, his mother died and he was raised by his grandmother. At the age of 7, Abraham started public school. 1933-39: Abraham liked school but found it difficult. The Christian children often yelled at the Jews, "You killed our God." One year, on the day before Christmas break, some kids brought ropes tied to iron weights to school.…

-
Inge Berg
ID CardInge lived with her parents, grandparents, uncle, and younger sister, Gisella, in Lechenich, a small village outside Cologne. The Bergs were an observant Jewish family. Inge's grandfather was the president of the local synagogue association and her uncle was the cantor. Her father, Josef was a respected cattle dealer, who had many business and personal contacts with their Jewish and non-Jewish neighbors. 1933–39: In 1935, two years after the Nazis came to power, Inge was forced to leave public school in…

-
Gisella Renate Berg
ID CardGisella lived with her parents, grandparents, uncle, and older sister, Inge, in Lechenich, a small village outside of Cologne. The Bergs were an observant Jewish family. Gisella's grandfather was the president of the local synagogue association and her uncle was the cantor. Her father, Josef was a respected cattle dealer, who had many business and personal contacts with their Jewish and non-Jewish neighbors. 1933–39: Gisella was born several months after the Nazis came to power. Her parents feared for…

-
Martin Weiss
ID CardMartin was one of nine children born to orthodox Jewish parents in Veľká Poľana, a rural village in the Carpathian Mountains. His father owned a farm and a meat business, and his mother attended to the children and the home. Everyone in the family helped take care of the horses and cows. 1933–39: Martin attended the village's Czechoslovak schools, which were quite progressive. Like many of the other children, he looked forward to leaving the provincial life in Veľká Poľana. In 1938–1939, his…

-
Elizabeth Kaufmann
ID CardElizabeth's father was a journalist who covered financial and political subjects. In 1930, because of the economic crisis in Austria, her father relocated his family from Vienna to Berlin. 1933-39: In 1933 the Nazis blacklisted Elizabeth's father as an anti-fascist writer, so her family returned to Vienna. With fascism rising there, her father left, eventually making it to Paris. They were to join him, but the Reich's borders were closed to Jews. Finally, Elizabeth's mother used her jewelry to get French…

-
Catharina Soep
ID CardCatharina, called "Ina" by her family and friends, grew up in a religious Jewish household in Amsterdam. Ina's father, a successful diamond manufacturer, was president of the Amsterdam Jewish community. Ina had one brother, Benno, and a sister, Josette. 1933-39: On Sunday mornings and on Wednesdays after her classes at an Amsterdam Montessori school, Ina went to a private Jewish school where she studied Jewish history and Hebrew. Ina and her friends loved to meet in the evenings after they finished their…

-
Feige Schwarzfink
ID CardFeige was born to a religious Jewish family in the small village of Szydlowiec [in Poland]. She lived with her parents, six brothers and sisters, and elderly grandparents in a small house which, like many homes in the village, had no running water, indoor plumbing, or electricity. Feige's father was a shoemaker. 1933-39: In the afternoons after public school Feige studied at a Jewish religious school. Although her parents didn't know it, she attended meetings of the Bund, the Jewish Socialist party. Feige…

-
Claude Brunswic
ID CardClaude was one of five children born to Jewish parents in the university city of Heidelberg. His father, a physician specializing in internal medicine, had his practice on the first floor of the apartment building in which the family lived. Claude was an avid swimmer until November 1932, when local Nazi party edicts forbad Jews to use the city pool where he swam. 1933-39: In January 1933, just after Hitler became chancellor of Germany, hoodlums attacked Jewish-owned businesses in Heidelberg. They broke…

-
Welwel Kisielnicki
ID CardWelwel lived with his wife, Feiga, and their three children in the small, predominantly Jewish town of Kaluszyn, which was 35 miles east of Warsaw. The Kisielnickis were religious and spoke Yiddish in their home. Welwel was a merchant and often traveled, by horse and wagon, to Warsaw on business. 1933-39: The Kisielnicki family's hopes that the war wouldn't reach Kaluszyn have been shattered. Last week, a German plane flew over their town and dropped a bomb on people waiting in line outside a bakery.…

-
Ilona Karfunkel Kalman
ID CardOne of four children, Ilona was born to religious Jewish parents living in the village of Erdobenye in the highlands of northeastern Hungary. The Karfunkel's house, on the village outskirts, had a large garden in the back and fruit orchards. Ilona's parents had a small vineyard and a little grocery store. Ilona married Ferenc Kalman, and the couple moved to Hatvan, 36 miles northeast of Budapest. 1933-39: Ilona and Ferenc have always considered themselves Hungarians who happened to be Jewish, and they've…

-
Matvey Gredinger
ID CardMatvey was the youngest of three children born to a Jewish family. The Gredingers lived in the town of Vertujeni, which was located in Bessarabia, a region of Romania. His father was a kosher butcher, preparing meat, especially chicken, for sale in his kosher shop. Matvey attended a Jewish school where he studied Jewish history and Hebrew. 1933-39: The Gredingers heard stories from other towns about antisemitic groups, especially the League of National Christian Defense, harassing and sometimes attacking…

