<< Previous | Displaying results 6601-6650 of 6773 for "" | Next >>
The word antisemitism means prejudice against or hatred of Jews. The Holocaust is history’s most extreme example of antisemitism. In these oral histories, survivors......
This breakfast menu comes from the SS Exeter, an American ocean liner. The ship carried the Shadurs, a Jewish refugee family, to the United States in February-March 1941. The Shadurs were among the many Jewish refugees who journeyed on the SS Exeter from Lisbon, Portugal, to New York during World War II. Joseph Shadur was twelve years old at the time. He marveled at the ship’s bountiful meals, especially in light of the hunger his family had faced on their journey to the port of Lisbon. The course of…

This Olympic torch holder was used during the 1936 Berlin Olympics. It is engraved with the 1936 Olympics torch relay route from Olympia, Greece, to Berlin, Germany.

Racial antisemitism is the discriminatory idea that Jews are a separate and inferior race. This type of antisemitism dates back to the late 1800s.
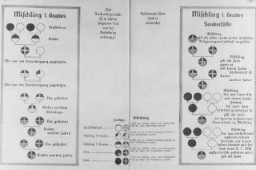
Eugenics poster entitled "The Nuremberg Law for the Protection of Blood and German Honor." The illustration is a stylized map of the borders of central Germany upon which is imposed a schematic of the forbidden degrees of marriage between Aryans and non-Aryans and the text of the Law for the Protection of German Blood. The German text at the bottom reads, "Maintaining the purity of blood insures the survival of the German people."
Explore a timeline of key events in the history of the Trawniki in German-occupied Poland.

Eugenics, or “racial hygiene” in the German context, was a scientific movement of the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. Eugenic theories provided the basis for the Nazi compulsory sterilization program and...


The Nazi Euthanasia Program, codenamed Aktion "T4," was the systematic murder of institutionalized people with disabilities. Read about Nazi “euthanasia.”

Martin was one of nine children born to orthodox Jewish parents in Veľká Poľana, a rural village in the Carpathian Mountains. His father owned a farm and a meat business, and his mother attended to the children and the home. Everyone in the family helped take care of the horses and cows. 1933–39: Martin attended the village's Czechoslovak schools, which were quite progressive. Like many of the other children, he looked forward to leaving the provincial life in Veľká Poľana. In 1938–1939, his…

Jews were the primary targets for mass murder by the Nazis and their collaborators. Nazi policies also led to the brutalization and persecution of millions of others.

Key dates in the life of Reinhard Heydrich, chief of the Reich Security Main Office, the SS and police agency most directly concerned with implementing Final Solution.

Prominent SS physician Josef Mengele, called the "angel of death" by his victims, conducted inhumane medical experiments on prisoners in the Auschwitz camp.

Adolf Hitler's Nazi aimed to purify the genetic makeup of the German population through measures known as racial hygiene or eugenics.

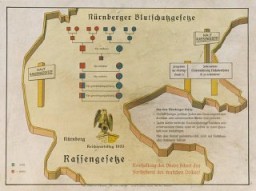
Learn more about the Reich Citizenship Law and the Law for the Protection of German Blood and German Honor, collectively known as the Nuremberg Race Laws.

Leah and her four brothers were raised in a religious Jewish family in the city of Lvov. After obtaining her high school diploma, Leah attended university for one year. In 1931 she married Joseph Rapaport, and the couple settled in Warsaw. 1933-39: The Rapaports lived in the suburbs, and Joseph worked as a banker. Their daughter Zofia was born in May 1933. Each year at the Jewish holiday of Passover, they returned to Lvov to visit Leah's parents. Two days after Joseph was mobilized for military duty in…

The 45th Infantry Division participated in major WWII campaigns and is recognized for liberating the Dachau concentration camp in 1945.

Josefa Boholle (Josefa van der Want after marrying her husband in 1943) sitting on the steps of a circus wagon with a bird on her shoulder. The photo was likely taken in Eisleben, Saxony-Anhalt, Germany, around 1936-1937. During World War II, Josefa and her Dutch husband were imprisoned in the Stutthof concentration camp. The official reason given for their arrest was for listening to foreign radio broadcasts. However, it is likely that the couple’s resistance activities and their interracial marriage…

Members of the German Africa Show (Deutsche Afrika-Schau), circa 1937 in Germany. Though these early shows were exploitative by nature, artists originally had the ability to shape their own performances and how they were represented. After the Nazis came to power in 1933, this agency began to disappear. During the Nazi era, working in such shows was an increasingly propaganda-driven, demoralizing, and unpleasant experience. Known persons in the photograph from left to right: Josef Boholle is the furthest…

After the Holocaust, the IMT charged the first case of “incitement to genocide.” Learn more about the crime and its application in modern genocide law.

Best friends Ejanga Egiomue (left) and Magdalene Garber (right) on an outing in Berlin, Germany during World War II (likely 1941-1942). Magdalene stayed in Germany, but Ejanga fled to Denmark in 1944. Both women survived the war and stayed in contact with each other, exchanging letters and correspondence well into the 1990s. Magdalene (“Leni”) Garber was born in January, 1919 in Germany. Her parents were Joseph Garber, a Togolese man, and Johanna Maychrzak, a white German woman. Magdalene grew up in…

Garber family photograph, likely taken in Zehlendorf, Berlin, circa 1946. Magdalene Garber and her husband Jack Goodwin (an African American GI) had a house in Zehlendorf. This photo was most likely taken in their garden. Standing left to right are Käthe Garber (‘an aunt’ according to the original caption), Magdalene, Joseph Garber, and Helga Naue (future wife of Hans Garber). The man kneeling is Hans Garber (Magdalene's brother). Joseph is wearing Jack Goodwin’s hat (Magdalene's…

Abraham was born to a Jewish family in the Polish capital of Warsaw. His grandfather owned a clothing factory and retail store, which his father managed. Abraham's family lived in a Jewish section of Warsaw and he attended a Jewish school. Warsaw's Jewish community was the largest in Europe, and made up nearly one-third of the population of the city. 1933-39: After the bombardment of Warsaw began on September 8, 1939, Abraham's family had little to eat. The stores had been reduced to rubble; they had no…

A group of female performers from the German Africa show (Deutsche Afrika-Schau) sitting on a circus wagon. This photo was likely taken in Eisleben, Saxony-Anhalt, Germany, around 1936-1937. Though early ethnographic shows like the Deutsche Afrika-Schau were exploitative by nature, artists originally had the ability to shape their own performances and how they were represented. After the Nazis came to power in 1933, this agency began to disappear. During the Nazi era, working in such shows was an…

Magdalene Garber with friends and family at the public beach in Wannsee, Berlin, around 1940-1941. There are Nazi flags visible in the background behind Magdalene. Magdalene (“Leni”) Garber was born in January, 1919 in Germany. Her parents were Joseph Garber, a Togolese man, and Johanna Maychrzak, a white German woman. Magdalene grew up in Berlin-Neukölln and worked as a performer from an early age. She was part of several ethnographic shows, including a variety of Mohamed ben Ahmed’s Afrika-Schau…

Party scene from the early 1940s in Germany. In the foreground is Deska Garber. Deska’s father was Joseph Garber, a Togolese man, and his mother was Johanna Maychrzak, a white German woman. The woman in the back left is Else Hummel, whom Deska would marry after the war. A small portrait of Adolf Hitler is visible on the wall in the background, something that would have been very common in German homes during the Nazi era.

A wartime photograph of Magdalene Garber in the 1940s, likely taken in Berlin, Germany. Magdalene (“Leni”) Garber was born to Joseph Garber, a Togolese man, and Johanna Maychrzak in January 1919 in Germany. Magdalene grew up in Berlin-Neukölln and worked as a performer from an early age. She was part of several ethnographic shows, including a variety of Mohamed ben Ahmed’s Afrika-Schau during the late 1920s through the early 1930s, and the German Africa Show (Deutsche Afrika-Schau) during the Nazi…

Standing in an open car, Adolf Hitler salutes a crowd in Hamburg, Germany. Photo dated August 17, 1934.

On November 9, 1938, the Nazis led a nationwide pogrom against Jews. During the pogrom, known as "Kristallnacht" (the "Night of Broken Glass"), bands of Storm Troopers (SA) destroyed thousands of Jewish-owned businesses and hundreds of synagogues. Almost 100 Jews were killed in the process. This footage shows scenes from a protest rally in New York City. Rabbi Stephen S. Wise voiced the outrage of the American Jewish community. As part of an official protest by the United States government against the…

Sir Horace Rumbold was the British ambassador to Germany from 1928 to 1933. Rumbold described for the British government the changes he saw in Germany once Hitler came to power in January 1933. In a dispatch dated April 26, 1933, he warned of the principles outlined in Hitler's Mein Kampf and wrote that "the outlook for Europe is far from peaceful." Undated photograph. Library of Congress, Prints & Photographs Division, LC-DIG-ggbain-36812

Explore Gideon Frieder’s biography and learn about his experiences as a child during the Holocaust in Slovakia.

Explore Estelle Laughlin’s biography and learn about her experiences during the Warsaw ghetto uprising.

Hitler inspects a German naval warship. On his left is Admiral Erich Raeder. Standing to the right of Hitler is most likely Captain Hermann von Fischel, commander of the Deutschland from April 1, 1933, to December 29, 1935. Bremerhaven, Germany, circa 1933–1935.

September 29-30, 1938. On this date, Germany, Italy, Great Britain, and France signed the Munich agreement, giving Germany the Sudetenland.

Portrait of British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain. London, England, 1937–1940.

Learn about the history of the Bergen-Belsen camp during WWII and the Holocaust until its liberation by British forces in April 1945.

Explore a timeline of key events during 1945 in the history of Nazi Germany, World War II, the Holocaust, and liberation and the aftermath of the Holocaust.

The liberation of concentration camps toward the end of the Holocaust revealed unspeakable conditions. Learn about liberators and what they confronted.

The first major Nazi camp was liberated by Allied troops in July, 1944. Learn more about liberation of camps towards the end of World War II.


November 18, 1919. On this date, Hindenburg spreads the “stab-in-the-back” myth in a testimony before a committee investigating Germany’s defeat in World War I.

April 15, 1945. On this date, the British army liberated approximately 60,000 prisoners at the Bergen-Belsen concentration camp.

As Allied forces approached Germany in late 1944 and early 1945, Bergen-Belsen became a collection camp for tens of thousands of prisoners evacuated from camps near the front. Thousands of these prisoners died due to overcrowding, poor sanitary conditions, and lack of adequate food and shelter. On April 15, 1945, British soldiers entered Bergen-Belsen. They found about 55,000 prisoners in the camp, most in a critical condition. This footage shows Allied cameramen filming the condition of the prisoners and…

Benito Mussolini’s Fascist takeover of Italy was an inspiration and example for Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party in Germany. Learn more.

A view of the Bergen-Belsen concentration camp after the liberation of the camp. Bergen-Belsen, after April 15, 1945. The 63rd Anti-tank Regiment and the 11th Armoured Division arrived at the Bergen-Belsen concentration camp on April 15, 1945. When British troops entered the camp, they were totally unprepared for what they found. Inside were about 55,000 prisoners, many of whom were emaciated and ill and in desperate need of medical attention. Thousands of corpses in various stages of decomposition lay…

The "Final Solution," the Nazi plan to kill the Jews of Europe, was a core goal of Adolf Hitler and the culmination of German policy under Nazi rule.

Soon after liberation, camp survivors cook in a field. Bergen-Belsen, Germany, after April 15, 1945. In the days before liberation, the prisoners had been left without food or water. More than 13,000 inmates died in the three months following liberation.

British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain and German Chancellor Adolf Hitler greet each other at the Munich conference. Munich, Germany, September 29–30, 1938.

March 11, 1941. On this date, the Lend-Lease Act passed in Congress, allowing the United States to send material aid to the Allies prior to entering World War II.

June 18, 1935. On this date, the United Kingdom and Germany signed an agreement allowing the German navy to expand beyond the terms of the Treaty of Versailles.

We would like to thank Crown Family Philanthropies, Abe and Ida Cooper Foundation, the Claims Conference, EVZ, and BMF for supporting the ongoing work to create content and resources for the Holocaust Encyclopedia. View the list of donor acknowledgement.