You searched for: 竞彩比分3串1奖金封顶【杏彩官方qee9.com】福彩3d杀码图最准杀,,,0278UTWK3yVp
<< Previous | Displaying results 1-50 of 947 for "竞彩比分3串1奖金封顶【杏彩官方qee9.com】福彩3d杀码图最准杀,,,0278UTWK3yVp" | Next >>
-
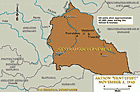
Subsequent Nuremberg Proceedings, Case #3: The Justice Case
ArticleThe Justice Case was Case #3 of 12 Subsequent Nuremberg Proceedings against leading German industrialists, military figures, SS perpetrators, and others.

-
-
Page 3 of International Military Tribunal program
ArtifactThird page of a list of defendants at the International Military Tribunal at Nuremberg. This material appears in a mimeographed program booklet distributed at the IMT. This page includes: Julius Streicher, Wilhelm Keitel, Walter Funk, and Hjalmar Schacht., along with brief biographical information for each.

-
D-Day
ArticleThe D-Day invasion was the largest amphibious attack in history. Read articles and browse photos and videos of Allied forces invading Normandy on June 6, 1944.

-
Page from volume 3 of a set of scrapbooks documenting the German occupation of Denmark
ArtifactPage from volume 3 of a set of scrapbooks compiled by Bjorn Sibbern, a Danish policeman and resistance member, documenting the German occupation of Denmark. Bjorn's wife Tove was also active in the Danish resistance. After World War II, Bjorn and Tove moved to Canada and later settled in California, where Bjorn compiled five scrapbooks dedicated to the Sibbern's daughter, Lisa. The books are fully annotated in English and contain photographs, documents and three-dimensional artifacts documenting all…

-
D-Day
Timeline EventJune 6, 1944. On this date, US, British, and Canadian troops land on the beaches of Normandy, France.

-
Canadian troops on D-Day
PhotoCanadian troops of the 'B' Company, North Shore (New Brunswick) Regiment take cover on June 6, 1944, or D-Day.

-
D-Day: Photographs
Media EssayExplore images related to the June 6, 1944, Allied invasion of Normandy—commonly known as “D-Day."

-
D-Day
FilmMassive Allied landings of air- and sea-borne forces on five Normandy beaches (codenamed Utah, Omaha, Gold, Juno, and Sword) began on June 6, 1944 (D-Day). The purpose of the invasion was to establish a bridgehead from which Allied forces could break out and liberate France. By the end of the operation's first day, some 150,000 troops were ashore in Normandy. This footage shows Allied forces landing on the Normandy beaches.

-
British troops land on D-Day
PhotoBritish troops land on the beaches of Normandy on D-Day, the beginning of the Allied invasion of France to establish a second front against German forces in Europe. Normandy, France, June 6, 1944.

-
D-Day bombings over France
FilmAllied air superiority over Germany was a decisive factor in the success of the D-Day (June 6, 1944) landings in France. This footage shows the Allied bombing of suspected German positions during the battle. Allied air attacks both supported Allied ground operations in Normandy and prevented German reinforcements from reaching the area. The Allies would liberate most of France by the end of August 1944.

-
D-Day: Historical Film Footage
Media EssayOn June 6, 1944, Allied troops landed on the beaches of Normandy, France. Commonly known as D-Day, the invasion was one of the most important Allied military operations during World War II.
-
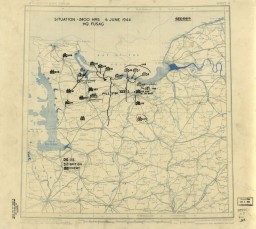
Twelfth Army Group Situation Map for D-Day
PhotoDated June 6, 1944, this US Twelfth Army Group situation map shows the presumed locations of Allied and Axis forces on D-Day, when Allied troops landed on the beaches of Normandy. Drafted during the war, the content in this historical map reflects the information that operational commander, General Omar N. Bradley, would have had on hand at the time.
-
Book burning in Berlin
PhotoCrowds gather at Berlin's Opernplatz (opera square) for the burning of books deemed "un-German." Berlin, Germany, May 10, 1933.

-
Liberation of Buchenwald
FilmThe US army filmed the weak and emaciated survivors of the Buchenwald concentration camp in Germany to document Nazi crimes against humanity. This film was shot shortly after the liberation of the camp in April 1945.

-
Matchbox cover with Japanese propaganda illustration
ArtifactDuring the war the Japanese flooded Shanghai with anti-American and anti-British propaganda, including this image from a matchbox cover. It depicts United States President Franklin D. Roosevelt--dressed in rags, on a raft in the ocean, and holding onto the U.S. flag--in the view of a Japanese submarine periscope. Shanghai, China, between 1943 and 1945. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

-
Troops approach Omaha Beach on D-Day
PhotoAssault troops in a landing craft approach Omaha Beach on D-Day. Normandy, France, June 6, 1944.

-
US troops landing at Normandy on D-Day
PhotoUS troops wade through the surf on their arrival at the Normandy beaches on D-Day. Normandy, France, June 6, 1944.

-
US troops pull the survivors ashore on D-Day
PhotoUS troops pull the survivors of a sunken craft on to the shores of the Normandy beaches on D-Day. Normandy, France, June 6, 1944.

-
The Normandy beach as it appeared after D-Day
PhotoThe Normandy beach as it appeared after D-Day. Landing craft on the beach unload troops and supplies transferred from transports offshore. Barrage balloons hover overhead to deter German aircraft. Normandy, France, undated (after June 6, 1944).

-
British troops land on the beaches of Normandy on D-Day
PhotoBritish troops land on the beaches of Normandy on D-Day, the beginning of the Allied invasion of France to establish a second front against German forces in Europe. Normandy, France, June 6, 1944.

-
US troops wade ashore at Normandy on D-Day
PhotoUS troops wade ashore at Normandy on D-Day, the beginning of the Allied invasion of France to establish a second front against German forces in Europe. Normandy, France, June 6, 1944.

-
The Times, August 17, 1921
ArtifactIn this London Times article, reporter Philip Graves compared passages from Maurice Joly’s Dialogue in Hell Between Machiavelli and Montesquieu (1864) side-by-side with the Protocols of the Elders of Zion in order to prove that the Protocols was plagiarized. Other investigations revealed that one chapter of a Prussian novel, Hermann Goedsche’s Biarritz (1868), also “inspired” the Protocols. Times (London), August 17, 1921.

-
Demonstrating the operation of the Dachau crematorium
PhotoSurvivors of the Dachau concentration camp demonstrate the operation of the crematorium by pushing a corpse into one of the ovens. Dachau, Germany, April 29–May 10, 1945. This image is among the commonly reproduced and distributed, and often extremely graphic, images of liberation. These photographs provided powerful documentation of the crimes of the Nazi era.

-
Deportation from the Warsaw ghetto
PhotoDeportation of Jews from the Warsaw ghetto during the uprising. This photo was taken secretly from a building adjacent to the ghetto by a Polish member of the resistance. Warsaw, Poland, April 1943.

-
Edward Vebell courtroom sketch
ArtifactCourtroom sketch drawn during the International Military Tribunal by American artist Edward Vebell. The drawing depicts defendants Rudolf Hess and Wilhelm Keitel, with this accompanying text: "Hess looked very hollow cheeked and thin necked. He seemed to ignore the proceedings and kept his head down, absorbed in a book. Keitel tried to retain a rigid military bearing and strike haughty poses." Nuremberg, Germany, 1945.

-
General Dwight D. Eisenhower with paratroopers of the 101st Airborne Division
PhotoGeneral Dwight D. Eisenhower visits with paratroopers of the 101st Airborne Division just hours before their jump into German-occupied France (D-Day). June 5, 1944.

-
President Franklin D. Roosevelt in the Oval office at the White House
PhotoPresident Franklin D. Roosevelt in the Oval office at the White House, shortly before delivering a speech accepting the Democratic Party's presidential nomination. Washington, DC, United States, July 24, 1940.

-
Construction of Oskar Schindler's armaments factory in Bruennlitz
PhotoView during the construction of Oskar Schindler's armaments factory in Bruennlitz. This photograph shows the construction of a rail line to the factory. Czechoslovakia, October 1944.

-
Gerda D. was sterilized after a disputed diagnosis of schizophrenia
PhotoOn July 14, 1933, the Nazi dictatorship enacted the Law for the Prevention of Offspring with Hereditary Diseases. Individuals who were subject to the law were those men and women who “suffered” from any of nine conditions listed in the law: hereditary feeblemindedness, schizophrenia, manic-depressive disorder, hereditary epilepsy, Huntington’s chorea (a rare and fatal degenerative disease), hereditary blindness, hereditary deafness, severe physical deformity, and chronic alcoholism. Gerda D., a…

-
Meeting between Franklin D. Roosevelt and Henry Morgenthau Jr.
Timeline EventJanuary 16, 1944. On this date, Franklin D. Roosevelt and Henry Morgenthau Jr. met to discuss the rescue of European Jews.

-
Blanka at about 1 year old
PhotoPhotograph showing Blanka when she was about 1 year old, ca. 1923. She received this photograph many years later, after she came to America, from her grandmother's half brother.

-
Aaron A. Eiferman Letter: Page 1
DocumentFirst page of a letter from a US soldier describing "the living dead" and conditions his unit encountered in a subcamp of Dachau in April 1945.

-
View of Rotterdam after German bombing in May 1940
PhotoView of Rotterdam after bombing by the German Luftwaffe in May 1940. Rotterdam, the Netherlands, 1940.

-
Page 1 of International Military Tribunal program
ArtifactFirst page of a list of defendants at the International Military Tribunal at Nuremberg. This material appears in a mimeographed program booklet distributed at the IMT. This page includes: Hermann Göring, Rudolf Hess, Joachim von Ribbentrop, and Alfred Rosenberg, along with brief biographical information for each.

-
General Dwight D. Eisenhower views the Ohrdruf camp
PhotoGeneral Dwight D. Eisenhower (center), Supreme Allied Commander, views the corpses of inmates who died at the Ohrdruf camp. Ohrdruf, Germany, April 12, 1945.

-
John D. Rastelli describes entering occupied Austria and burial of the dead in Mauthausen
Oral HistoryJohn D. Rastelli is a veteran of the 11th Armored Division. During the invasion of German-held Austria, in May 1945 the 11th Armored (the "Thunderbolt" division) overran two of the largest Nazi concentration camps in the country: Mauthausen and Gusen.

-
Page 1 of Letter from US Soldier Aaron Eiferman
Timeline EventApril 27, 1945. On this date, US soldier Aaron A. Eiferman wrote a letter to his wife describing conditions in Kaufering IV in Germany.

-
Page from volume 1 of a set of scrapbooks documenting the German occupation of Denmark
ArtifactPage from volume 1 of a set of scrapbooks compiled by Bjorn Sibbern, a Danish policeman and resistance member, documenting the German occupation of Denmark. Bjorn's wife Tove was also active in the Danish resistance. After World War II, Bjorn and Tove moved to Canada and later settled in California, where Bjorn compiled five scrapbooks dedicated to the Sibbern's daughter, Lisa. The books are fully annotated in English and contain photographs, documents and three-dimensional artifacts documenting all…

-
Franklin D. Roosevelt Elected President of the United States
Timeline EventNovember 8, 1932. On this date, Franklin D. Roosevelt was elected as the 32nd President of the United States.

-
Page from volume 1 of a set of scrapbooks documenting the German occupation of Denmark
ArtifactPage from volume 1 of a set of scrapbooks compiled by Bjorn Sibbern, a Danish policeman and resistance member, documenting the German occupation of Denmark. Bjorn's wife Tove was also active in the Danish resistance. After World War II, Bjorn and Tove moved to Canada and later settled in California, where Bjorn compiled five scrapbooks dedicated to the Sibbern's daughter, Lisa. The books are fully annotated in English and contain photographs, documents and three-dimensional artifacts documenting all…

-
Melk
ArticleLearn about the establishment of and conditions in Melk, a subcamp of the Mauthausen camp system in Austria.

-
World War II in Europe
ArticleWorld War II lasted from 1939 to 1945, when the Allies defeated the Axis powers. Learn about key invasions and events during WWII, also known as the Second World War.

-
Columbia-Haus
ArticleThe Columbia-Haus camp was one of the early camps established by the Nazi regime. It held primarily political detainees. Learn more about the history of the camp.
-
Communism
ArticleCommunist ideas spread rapidly in Europe during the 19th and 20th centuries, offering an alternative to both capitalism and far-right fascism and setting the stage for a political conflict with global repercussions.

-
Oranienburg
ArticleThe Oranienburg concentration camp was established as one of the first concentration camps in Nazi Germany on March 21, 1933. Learn more

-
Benito Mussolini
ArticleBenito Mussolini’s Fascist takeover of Italy was an inspiration and example for Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party in Germany. Learn more.

-
Auschwitz Camp Complex
ArticleAuschwitz was the largest camp established by the Germans. It was a complex of camps, including a concentration camp, killing center, and forced-labor camp.

-
Antisemitism
ArticleThroughout history Jews have faced prejudice and discrimination, known as antisemitism. Learn more about the long history of antisemitism.

-
Aryan
ArticleAdolf Hitler and the Nazi Party adapted, manipulated, and radicalized the unfounded belief in the existence of an "Aryan race." Learn about the term Aryan.

