You searched for: 5G基站源码搭建定制开发【TG���������@EK7676】平台包网搭建5G基站源码搭建定制开发【TG���������@EK7676】平台包网搭建2S6C34nkOD
<< Previous | Displaying results 351-400 of 507 for "5G基站源码搭建定制开发【TG���������@EK7676】平台包网搭建5G基站源码搭建定制开发【TG���������@EK7676】平台包网搭建2S6C34nkOD" | Next >>
-
The Nazi Rise to Power
ArticleThe Nazi Party was one of a number of right-wing extremist political groups that emerged in Germany following World War I. Learn about the Nazi rise to power.

-
Kindertransport, 1938–40
ArticleKindertransport refers to a series of rescue efforts between 1938 and 1940 that brought thousands of refugee children to Great Britain from Nazi Germany.

-
Indoctrinating Youth
ArticleThe Nazi Party targeted German youth as a special audience for its propaganda messages. Read more about the indoctrination of youth.

-
Wannsee Conference and the "Final Solution"
ArticleAt the Wannsee conference of January 1942, Nazi Party and German government officials gathered to coordinate implementation of the “Final Solution to the Jewish Question.”

-
History of the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum
ArticleThe United States Holocaust Memorial Museum opened in April 1993. Explore the history of the nation's memorial to the millions murdered during the Holocaust.

-
Mobile Killing Squads
ArticleLearn more about Nazi mobile killing squads (Einsatzgruppen) killing activities in the Soviet Union during World War II.
-
Flossenbürg: Key Dates
ArticleExplore a timeline of the history of the Flossenbürg camp in the Nazi camp system from its establishment in 1938 until liberation in 1945.

-
Nicholas Winton and the Rescue of Children from Czechoslovakia, 1938–1939
ArticleNicholas Winton organized a rescue operation that brought hundreds of children, mostly Jewish, from Czechoslovakia to safety in Great Britain before the outbreak of WWII.

-
Wilhelm Keitel: Biography
ArticleField Marshal Wilhelm Keitel was commander of all German armed forces during World War II. Learn about his military career and postwar trial.

-
German Military Oaths
ArticleIn Nazi Germany, German military personnel swore an oath directly to Adolf Hitler. Learn about the oath and its impact.

-
Reich Security Main Office (RSHA)
ArticleThe Reich Security Main Office (RSHA), created by Heinrich Himmler, brutally coordinated and perpetrated many aspects of the Holocaust.

-
The Rwanda Genocide
ArticleFrom April to July 1994, extremist leaders of Rwanda’s Hutu majority directed a genocide against the country’s Tutsi minority. Learn more

-
First Kindertransport Arrives in Great Britain
Timeline EventDecember 2, 1938. On this date, the first Kindertransport of German Jewish children arrived in Great Britain.

-
Revision of Paragraph 175
Timeline EventJune 28, 1935. On this date, the German government revised Paragraphs 175 and 175a, facilitating the persecution of gay men and men accused of homosexuality.

-
Background: Jurists' Trial Verdict
ArticleThe Justice Case, or Jurists’ Trial, of the Subsequent Nuremberg Proceedings tried members of the German justice administration. Browse excerpts from the verdict.

-
Letter from Esther Lurie regarding lost art, 1945
DocumentThis document is one page of a letter from artist Esther Lurie, written after the war, asking for help in following down leads and locating the artwork she had created and hidden while imprisoned in the Kovno ghetto, Lithuania. She wrote, "The matter concerns a collection of 200 pen-and-ink drawings representing scenes of ghetto life which I made during my internment in the Kaunas Ghetto (Lithuania) in 1941-1944. I left the drawings buried in the earth as I felt that I had no hope of survival."

-
Ivo Herzer describes a roundup (from which he was released) of Jews by Croatian collaborators in 1941
Oral HistoryIvo grew up in a middle-class Jewish family in Zagreb. He experienced little overt antisemitism until the Germans and their allies invaded Yugoslavia in April 1941 and installed a fascist Ustasa government in Croatia. The Ustasa regime began killing Jews, Serbs, and Roma (Gypsies). Ivo's family escaped to Italian-occupied territory, where the Italians tried to protect Jewish refugees. Ivo lived in Italian internment camps, including the Rab island camp, before moving to mainland Italy in 1944. He worked…

-
Peter Somogyi
ID CardPeter and his twin brother, Thomas, were the youngest of three children born to an observant Jewish family. They lived in Pecs, an industrial center where goods such as bricks and ceramics were produced. Peter's father owned a prosperous business selling accessories and parts for cars, motorcycles and bicycles. He was also a regional sales representative for Ford automobiles. 1933-39: A German nanny took care of Peter, Thomas, and their older sister. She taught them German and they became quite fluent.…

-
Pinchas Galperin
ID CardPinchas was one of 16 children born to a Jewish family. Only nine of the Galperin children lived to adulthood. Pinchas' father worked as a typesetter for a Jewish newspaper and his mother ran a small grocery store. After World War I, Pinchas married Sara Bernstein and the couple moved to Siauliai, Lithuania, where they raised three children. 1933-39: Pinchas and Sara owned and ran a dairy store where they sold milk, butter and cheese that they bought from local farmers. Every morning they would rise early…

-
Wolfgang Lachman
ID CardWolfgang was the only son of observant Jewish parents living in Berlin. Though trained as a mechanical engineer, Wolfgang's father ran a wholesale kerchief and handkerchief business that he had taken over from his father-in-law. Wolfgang's family lived in an apartment above the business. They enjoyed vacationing at their country home in Neuenhagen, a suburb of Berlin. 1933-39: Wolfgang began school when he was 5; that year Hitler was named leader of Germany. Every morning they had to sing three songs: the…

-
Hanandel Drobiarz
ID CardHanandel was raised with his three brothers and sisters in the town of Kozlow, where his family sold grain and livestock. The family was religious, and they observed the Sabbath and all Jewish holidays and dietary laws. When Hanandel was 5, he began studying Hebrew, the Bible, prayers, and Jewish history. 1933-39: At age 14 Hanandel was apprenticed to his uncle in Sosnowiec as a tinsmith. He worked for his uncle during the day and attended trade school at night. When he graduated from trade school he…

-
Johannes M. Lublink
ID CardJohannes was born to Christian parents and had three brothers and three sisters. His father sold coal for heating systems. By 1933, Johannes was also a coal distributor. Like many other Dutch citizens, Johannes did not approve of Hitler's policies. He especially objected to Hitler's persecution of Jews and Jehovah's Witnesses. 1933-39: Hitler's coming to power in Germany was a threat to all of them. In 1936, Johannes became a Jehovah's Witness. His mother was also a Witness and, by 1938, one brother and…

-
Yosel Coller
ID CardOne of six children, Yosel was raised in a religious Jewish family in Lodz, an industrial city in western Poland. His father was a businessman. At the age of 6, Yosel began attending a Jewish day school. His two older sisters attended public school in the morning and religious school in the afternoon. Yosel spent much of his free time playing soccer with his brothers. 1933-39: Yosel's family lived in a modest house in the northern section of Lodz. He went to a Jewish day school and had many friends there.…

-
Machla Spicehandler Braun
ID CardRaised in Lowicz, Poland, in a religious Jewish family, Machla moved to Lodz when she married Jacob Braun. Her husband worked as a businessman and real estate investor. He became the landlord for an apartment building where he and his family also lived. Machla, a housewife, cared for their five children, who ranged in age from 5 to 15. 1933-39: Machla worked as a volunteer for the Zionist cause. The Brauns were a close family, and Machla's daughters Lena and Eva held their weddings in the Braun's large…

-
Helene Melanie Lebel
ID CardThe elder of two daughters born to a Jewish father and a Catholic mother, Helene was raised as a Catholic in Vienna. Her father died in action during World War I when Helene was just 5 years old, and her mother remarried when Helene was 15. Known affectionately as Helly, Helene loved to swim and go to the opera. After finishing her secondary education she entered law school. 1933-39: At 19 Helene first showed signs of mental illness. Her condition worsened during 1934, and by 1935 she had to give up her…
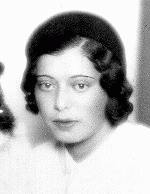
-
Chaim Engel
ID CardChaim's family came from a small town where his father owned a textile store. When antisemitic pogroms broke out in Brudzew, the Engels moved to the industrial city of Lodz. Chaim was then 5 years old. In Lodz he attended a Jewish school that also provided a secular education. After finishing middle school, Chaim went to work at his uncle's textile factory. 1933-39: Chaim's neighborhood in Lodz was predominantly Jewish, so most of his friends were Jews. As a young adult he began his compulsory army…

-
Maria Sava Moise
ID CardMaria was one of four children born to poor Roma ("Gypsy") parents in the capital of Moldavia in eastern Romania. The family lived in a mixed neighborhood that included Romanians and Roma. Maria grew up in a house with a yard where the family kept a pig and some chickens. Her father made a living by singing and by working at some of the many wineries that dotted the Moldavian countryside. 1933-39: Maria's parents couldn't afford to send her to school. To help make ends meet, Maria, her sister and older…

-
Ceija Stojka
ID CardCeija was the fifth of six children born to Roma ("Gypsy") parents who were Roman Catholic. The Stojka's family wagon traveled with a caravan that spent winters in the Austrian capital of Vienna and summers in the Austrian countryside. The Stojkas belonged to a tribe called the Lowara Roma, who made their living as itinerant horse traders. 1933-39: Ceija grew up used to freedom, travel and hard work. Once, her father made her a skirt out of some material from a broken sunshade. She was 5 years old and…

-
Johanna Niedermeier Buchner
ID CardJohanna was born in Vienna when it was still the capital of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. Her Christian family experienced the disruption resulting from the empire's collapse, as well as the instability of the Austrian republic. The depression of 1929 hit Vienna especially hard. In 1931 Johanna became a Jehovah's Witness. 1933-39: Johanna traveled constantly in and out of Austria distributing our Jehovah's Witness literature. In March 1938 Germany annexed Austria and her family was subjected to Nazi law;…

-
Monique Jackson
ID CardMonique's Jewish parents met in Paris. Her father had emigrated there from Russia to study engineering, and her mother had come from Poland as a young child. Monique's father did not have enough money to finish university, so he went to work as an upholsterer. He also shared a small business which sold his hand-tooled leather purses. 1933-39: Monique's mother was 20 when she gave birth to Monique in 1937. Two years later, Parisians were threatened by the possibility of bombing by the Germans, and French…

-
Nelly Adler
ID CardNelly was the youngest of three daughters born to Jewish parents in Liege, a French-speaking industrial city in eastern Belgium. Her Yiddish-speaking parents had moved there from Czechoslovakia a year before Nelly was born. The Adlers were one of only a few Jewish families in the largely Catholic city. Nelly grew up speaking French with her friends at school. 1933-39: The Adler's apartment was above a cafe and across the street from a Catholic church. Her parents ran a successful tailoring business from…

-
Sara Galperin
ID CardSara, born Sara Bernstein, was one of six children in a Jewish family in the Lithuanian village of Karchai. Her father was a farmer. Sara attended secondary school in Jonava and in 1920 she moved to Siauliai, where she met and married Pinchas Galperin. The couple owned and ran a dairy store, selling butter, milk and cheese. They had three children--two sons and a daughter. 1933-39: In addition to running the family store and rising early every morning to buy dairy products from the local farmers, Sara was…

-
Rachela Rottenberg
ID CardThe younger of two children born to Jewish parents, Rachela grew up in Radom, an industrial town located some 60 miles south of Warsaw. One-quarter of the city's 100,000 prewar population was Jewish. Rachela's father was a Zionist and was active in municipal affairs. Her mother did volunteer work. l933-39: Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. On September 5, with the Germans rapidly advancing, Rachela's family sought temporary safety with relatives in Warsaw. They got separated along the way.…

-
Jeno Gabor Braun
ID CardThe son of a rabbi, Jeno was raised in the town of Sighet in Transylvania. The region was multi-ethnic, and Jeno grew up in a family that knew Yiddish, Hungarian, Romanian, German and Hebrew. During World War I, when Sighet was near the front, Jeno's family fled to Hungary. There Jeno met Eszter Mendel, whom he married after the war. The couple settled in the town of Cristuru-Secuiesc in Romania. 1933-39: As a jeweler, Jeno is one of only two watchmakers in Cristuru-Secuiesc; the other is a German who…

-
Robert Gruber
ID CardRobert was raised by Hungarian-speaking parents in Kosice, a town in eastern Slovakia with a sizable Jewish community of 7,000. The Grubers were a traditional Jewish family and they observed the Jewish Sabbath, dietary laws, and holidays. Robert's father owned a small jewelry shop. 1933-39: When Robert was 5, Kosice was taken over by the Hungarians, who were led by a dictator named Horthy. He stood on the main street with his parents, watching the soldiers march into town in a victory parade. They were…
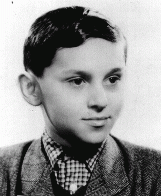
-
Bela Blau
ID CardBela's city of Bratislava, located on the banks of the Danube river, had an old and important Jewish community. Bela was the eighth child in his large Jewish family. His father was a furrier. At age 16 Bela began working as a salesman for a textile business. In 1930 he was called up for 18 months of army service. 1933-39: Bela and his wife moved to the Slovakian city of Zilina. Their son was born in November 1937. Bela worked for a German photographic company until 1938, when he lost his job because he…

-
Pearl Harbor
ArticleJapan’s aerial attack on Pearl Harbor changed many Americans' attitudes toward involvement in WWII. Learn more about the events, facts, and background info.

-
Ruth Gabriele Silten
ID CardGabriele was the only child of Jewish parents living in the German capital of Berlin. Her grandfather owned a pharmacy and a pharmaceuticals factory, where Gabriele's father also made his living. 1933-39: In 1938 the Nazis forced Ruth's grandfather to sell his factory and pharmacy for very little money to an "Aryan" German. After that, her father decided they should move to Amsterdam where it was safer for Jews. She was 5 years old and wanted to stay in Berlin. She didn't understand why she had to leave…

-
Ernst Silten
ID CardErnst was one of five sons born to a Jewish family in the Prussian city of Koenigsberg. He studied pharmacy and earned his doctorate in the late 1880s. Ernst spent several years as an apprentice before buying his own pharmacy in Berlin. Later, he also acquired a pharmaceuticals factory and supplied oxygen to hospitals. He married Marta Friedberg and the couple raised two sons. 1933-39: In Berlin, Ernst and his family lived in an apartment above their pharmacy and factory. In 1938 Ernst was forced to sell…

-
Erzsebet Markovics Katz
ID CardErzsebet was born to Jewish parents living in a town on the Bodrog River in northeastern Hungary. Sarospatak was a picturesque town with a ruined medieval fortress, the Windischgratz castle, and many wineries, flour mills, and brickworks. Erzsebet's father was a locksmith and sheet-metal worker. 1933-39: Erzsebet has married Jozsef Katz. It was a lovely, formal wedding. Jozsef comes from a large Jewish family. He's a joiner by trade and was working in Sarospatak when they met. Now they have moved here to…

-
Itzik Rosenblat
ID CardItzik, also known as Izak, was one of three sons born to Yiddish-speaking Jewish parents. When Itzik was a young child his family moved to the city of Radom. Itzik left school when he was 11 to apprentice as a women's tailor. After he apprenticed with several tailors in Radom and Warsaw, he went back to school and earned a tailor's license. 1933-39: In 1938 Itzik married Taube Fishman, the daughter of his first employer, after a 13-year courtship much opposed by her family. They lived in Radom, where…

-
Sandor (Shony) Alex Braun describes how music gave him the strength to survive while imprisoned in concentration camps
Oral HistoryShony was born to religious Jewish parents in a small Transylvanian city. He began to learn the violin at age 5. His town was occupied by Hungary in 1940 and by Germany in 1944. In May 1944, he was deported to the Auschwitz camp in Poland. He was transferred to the Natzweiler camp system in France and then to Dachau, where he was liberated by US troops in April 1945. In 1950, he immigrated to the United States, and became a composer and a professional violinist.

-
Sally Pitluk describes her removal from forced labor at Budy
Oral HistorySally Pitluk was born to Jewish parents in Płońsk, Poland in 1922. A few days after the German invasion of Poland in 1939, Płońsk was occupied. Sally and her family lived in a ghetto from 1940-1942. In October of 1942, Sally was transported to Auschwitz, where she was tattooed and moved into the subcamp Budy for forced labor. She stayed in the Auschwitz camp complex until the beginning of 1945 when she and other prisoners were death marched to several different camps. She was liberated in 1945 and…

-

-
The Holocaust and World War II: Key Dates
ArticleRead a detailed timeline of the Holocaust and World War II. Learn about key dates and events from 1933-45 as Nazi antisemitic policies became more radical.

-
Nazi Camps
ArticleNazi Germany and its allies established over 44,000 concentration camps and incarceration sites during the Holocaust. Read about the Nazi camp system.

-
Kovno
ArticleKovno had a rich and varied Jewish culture. Learn about the Soviet and German occupations of Kovno, ghettoization, secret archives, and resistance in Kovno during WWII and the Holocaust.

-
Law, Justice, and the Holocaust
ArticleLearn about the role of the legal profession as the Nazi leadership gradually moved Germany from a democracy to a dictatorship.

-
Glossary of Terms and Individuals in the Nazi Judicial System
ArticleLearn more about the Holocaust Encyclopedia’s key terms and individuals in the Nazi judicial system.
-
Hidden Children: Hardships
ArticleParents, children, and rescuers faced daunting challenges once the decision was made for a child to go into hiding during the Holocaust.

