<< Previous | Displaying results 451-500 of 1298 for "nazi germany" | Next >>
In Berlin, thousands of Party officials, Hitler Youth members, and Labor Service leaders take an oath of loyalty read by Rudolf Hess in Munich and broadcast across Germany. Berlin, Germany, February 25, 1934.

Bertolt Brecht (left), Marxist poet and dramatist, was a staunch opponent of the Nazis. He fled Germany shortly after Hitler's rise to power. Pictured here with his son, Stefan. Germany, 1931.

Authorities in Berlin, Germany, sent this notice to Barbara Wohlfahrt, informing her of her husband Gregor's execution on the morning of December 7, 1939. Although he was physically unfit to serve in the armed forces, the Nazis tried Wohlfahrt for his religious opposition to military service. As a Jehovah's Witness, Wohlfahrt believed that military service violated the biblical commandment not to kill. On November 8, 1939, a military court condemned Wohlfahrt to beheading, a sentence carried out one month…

In this German newsreel footage, Hitler addresses members of the SA and the SS in the Sportpalast, a sports arena in Berlin, Germany. He thanks them for their support and sacrifice during the Nazi struggle for power.

August 17, 1938. On this date, the German government issued the Executive Order on the Law on the Alteration of Family and Personal Names.

April 7, 1933. On this date, the German government issued the Law for the Restoration of the Professional Civil Service excluding Jews from civil service.

Erich Frost (1900–87), a musician and devout Jehovah's Witness, was active in the religious resistance to Hitler's authority. Caught smuggling pamphlets from Switzerland to Germany, he was imprisoned in the Sachsenhausen concentration camp near Berlin where he composed this song in 1942. Later deported to a labor camp at Alderney, Channel Islands, Frost survived the war and returned to Germany to serve the Watchtower Society. "Fest steht," reworked in English as "Forward, You Witnesses," is among the…
Following World War I, the Treaty of Versailles (1918) declared Danzig to be a free city administered by Poland and the League of Nations. Germany resented the loss of this largely German city. After invading Poland in September 1939, Nazi Germany annexed Danzig.
Adolf Hitler reviews SA troops celebrating the third anniversary of his assumption of power. Berlin, Germany, February 20, 1936.

Books and writings deemed "un-German" are burned at the Opernplatz (Opera Square). Berlin, Germany, May 10, 1933.

Dietrich Bonhoeffer, German Protestant theologian who was executed in the Flossenbürg concentration camp on April 9, 1945. Germany, date uncertain.

German forces enter Aachen, on the border with Belgium, following the remilitarization of the Rhineland. Aachen, Germany, March 18, 1936.

Wilhelm Keitel, head of the German Armed Forces High Command, who signed orders authorizing the shooting of Soviet prisoners of war. Germany, 1942.

The Holocaust (1933–1945) was the systematic, state-sponsored persecution and murder of six million European Jews by the Nazi German regime and its allies and collaborators. The Holocaust era began in January 1933 when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party came to power in Germany. It ended in May 1945, when the Allied Powers defeated Nazi Germany in World War II. The Holocaust was a German initiative that took place throughout German- and Axis-controlled Europe. It affected nearly all of Europe’s Jewish…
Parade of German police before Adolf Hitler in front of Hotel Deutsches Haus, at a Nazi Party Congress rally. Nuremberg, Germany, September 10, 1937.

Bertolt Brecht, author of the "Threepenny Opera" and a well-known leftist poet and dramatist, who emigrated from Germany in 1933. In exile, he co-edited an anti-Nazi magazine titled Das Wort. London, Great Britain, 1936.

Identification pictures of a bartender from Duisburg who was arrested under Paragraph 175. Duisburg, Germany, August 27, 1936.

Reich Labor Service battalions parade before Hitler during the Nazi Party Congress. Nuremberg, Germany, September 8, 1937.

Interior designer from Duesseldorf who was charged with homosexuality and imprisoned for 18 months. Duesseldorf, Germany, date uncertain.

Page from the antisemitic German children's book, "Trau Keinem Fuchs..." (Trust No Fox in the Green Meadow and No Jew on his Oath). Germany, 1936.

Page from the antisemitic German children's book, "Trau Keinem Fuchs..." (Trust No Fox in the Green Meadow and No Jew on his Oath). Germany, 1936.

Dr. Robert Ritter talks to several residents in a Zigeunerlager ("Gypsy camp"). Hamburg, Germany, 1940. During the Nazi era, Dr. Robert Ritter was a leading authority on the racial classification of people pejoratively labeled “Zigeuner” (“Gypsies”). Ritter’s research was in a field called eugenics, or what the Nazis called “racial hygiene.” Ritter worked with a small team of racial hygienists. Among them were Eva Justin and Sophie Ehrhardt. Most of the people whom Ritter studied and…

A family stands outside of their wagon while interned in a Zigeunerlager ("Gypsy camp"). In the background, children are crowded around Eva Justin. Justin worked for the Center for Research on Racial Hygiene and Demographic Biology. Schleswig-Holstein, Germany, 1938. During the Nazi era, Dr. Robert Ritter was a leading authority on the racial classification of people pejoratively labeled “Zigeuner” (“Gypsies”). Ritter’s research was in a field called eugenics, or what the Nazis called…

December 15, 1961. On this date, Adolf Eichmann was found guilty of crimes against the Jewish people and sentenced to death.

Germany annexed Austria in March 1938, bringing approximately 200,000 additional Jews under Nazi rule. The Nazi regime quickly extended anti-Jewish legislation to Austria. At the time, the majority of Austrian Jews...
Official identification tag (warrant badge) for the Criminal Police (Kriminalpolizei or Kripo), the detective police force of Nazi Germany. These badges were generally suspended from a chain and included the officer's identification number on the reverse.

Reverse of the official identification tag (warrant badge) for the Kriminalpolizei or Kripo, the detective police force of Nazi Germany. It reads Staatliche Kriminalpolizei (State Criminal Police) and identifies the officer's number as 8409.

Julius Streicher was one of the Nazi Party's earliest members. He founded the violently antisemitic newspaper, Der Stürmer. At its...
After liberation of the Bergen-Belsen camp, British soldiers forced German mayors from nearby towns to view mass graves. Bergen-Belsen, Germany, after April 15, 1945.

A crowd of saluting Germans surrounds Adolf Hitler's car as he leaves the Reich Chancellery following a meeting with President Paul von Hindenburg. Berlin, Germany, November 19, 1932.

Portrait of Robert T. Odeman, author and actor who was imprisoned in 1937 for 27 months for homosexuality. In 1942, he was deported to Sachsenhausen concentration camp where he was a prisoner for three years. Berlin, Germany, before 1937.

Nazi Germany’s semi-official and fiercely antisemitic newspaper Der Stuermer warned of a Jewish program for world domination in this 1934 issue. The article—titled “Who is the Enemy?”—blamed Jews for destroying social order and claimed that Jews wanted war, while the rest of the world wanted peace. Der Stuermer, July 1934.

Adolf Hitler (hand on rail) with Hermann Göring (second to left of Hitler) and Joseph Goebbels (third to left of Hitler) at the site of the fire that damaged the Reichstag (German parliament) building. Berlin, Germany, February 1933.

Recently appointed as German chancellor, Adolf Hitler greets President Paul von Hindenburg in Potsdam, Germany, on March 21, 1933. This pose was designed to project an image of Hitler as non-threatening to the established order. This particular image is from a popular postcard. The photo also appeared widely in both the German and international press. Hitler appears in civilian dress, bowing in deference to the heavily decorated von Hindenburg. The March 5, 1933, elections had conferred legitimacy on…

Dr. Robert Ritter and Eva Justin examine a young boy interned in a Zigeunerlager (“Gypsy camp”). Cologne, Germany, c. 1937-1940. During the Nazi era, Dr. Robert Ritter was a leading authority on the racial classification of people pejoratively labeled “Zigeuner” (“Gypsies”). Ritter’s research was in a field called eugenics, or what the Nazis called “racial hygiene.” Ritter worked with a small team of racial hygienists. Among them were Eva Justin and Sophie Ehrhardt. Most of the people…

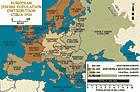
Jews have lived in Europe for more than two thousand years. The American Jewish Yearbook placed the total Jewish population of Europe at about 9.5 million in 1933. This number represented more than 60 percent of the world's Jewish population, which was estimated at 15.3 million. Most European Jews resided in eastern Europe, with about 5 1/2 million Jews living in Poland and the Soviet Union. Before the Nazi takeover of power in 1933, Europe had a dynamic and highly developed Jewish culture. In little more…
Scene during a visit by SS officer Theodor Eicke to the Lichtenburg camp in March 1936. Lichtenburg was one of the first concentration camps established in Germany were established soon after Hitler's appointment as chancellor in January 1933. When SS chief leader Heinrich Himmler centralized the administration of the concentration camps and formalized the camp system, he chose SS Lieutenant General Theodor Eicke for the task. Himmler appointed him Inspector of Concentration Camps, a new section of the…

Henny's parents met in Germany soon after her father emigrated from the Russian Empire. Henny was the first of the Jewish couple's three children. The family lived in Frankfurt am Main, an important center of commerce, banking, industry and the arts. 1933-39: After the Nazis came to power, they began to persecute Jews, Roma (Gypsies), men accused of homosexuality, people with disabilities, and political opponents. In 1938, as one way of identifying Jews, a Nazi ordinance decreed that "Sara" was to be…

Julius Streicher, Nazi leader and publisher of the antisemitic newspaper "Der Stuermer" (The Attacker), makes a speech accusing Jews of trying to control the world and living by the exploitation of non-Jews. According to Streicher, the only answer for Germany is to solve the "Jewish question."

A color photograph of Eva Justin interviewing a Romani woman interned in a "Gypsy camp." Vienna, Austria, 1940. During the Nazi era, Dr. Robert Ritter was a leading authority on the racial classification of people pejoratively labeled “Zigeuner” (“Gypsies”). Ritter’s research was in a field called eugenics, or what the Nazis called “racial hygiene.” Ritter worked with a small team of racial hygienists. Among them were Eva Justin and Sophie Ehrhardt. Most of the people whom Ritter studied and…

Musician Erich Frost was a devout Jehovah's Witness active in the religious resistance to Hitler's authority. Frost was caught smuggling pamphlets from Switzerland to Germany and was deported to the Sachsenhausen concentration camp near Berlin. There, he composed this song in 1942. Frost survived the war and died in 1987. This translation is taken from the Jehovah's Witness Songbook. Simone Arnold Liebster, who sings the English version of the song, was born in 1930 in Mulhouse, French Alsace. After the…
August 15, 1941. On this date, Heinrich Himmler inspected Soviet prisoners of war at a Nazi camp in Minsk, Belarus.

William Denson graduated from the US Military Academy at West Point in 1934 and attended Harvard Law School. He returned to West Point to teach law from 1942 until 1945. In January 1945, Denson accepted the position of Judge Advocate General (JAG) in Europe and was assigned to US Third Army headquarters in Germany. He took part in more than 90 trials against Germans who had committed atrocities against downed American pilots. In August 1945, Denson became chief prosecutor for the US government at the…

In Berlin, Germany, officials from Nazi Germany, Fascist Italy, and Imperial Japan sign the ten-year Tripartite Pact (the Three-Power Agreement), a military alliance. The pact sealed cooperation among the three nations (Axis powers) in waging World War II. This footage comes from "The Nazi Plan," a film produced and used by the United States in the prosecution at the Nuremberg trials.

Clip from George Stevens' "The Nazi Concentration Camps." This German film footage was compiled as evidence and used by the prosecution at the Nuremberg trials.

Former Nazi Party ideologist Alfred Rosenberg on trial at the International Military Tribunal war crimes trial. Nuremberg, Germany, April 15, 1946.

General Dwight D. Eisenhower and other American officers inspect conditions in the Ohrdruf concentration camp shortly after the liberation of the camp. As American forces had approached, SS camp guards shot the remaining prisoners before abandoning the camp. Confirmation of such atrocities prompted the US military to require Nazis and local German civilians to view the camps.

Members of the Hitler Youth march before their leader, Baldur von Schirach (at right, saluting), and other Nazi officials including Julius Streicher. Nuremberg, Germany, 1933.

Across Germany, students took books by truck, furniture van, even oxcart, and heaped them into pyres on public squares. This image shows members of the SA and students from the University of Frankfurt with oxen pulling manure carts loaded with books deemed "un-German." Frankfurt am Main, Germany, May 10, 1933.

Upon arrival in the Auschwitz camp, victims were forced to hand over all their belongings. Inmates' belongings were routinely packed and shipped to Germany for distribution to civilians or use by German industry. The Auschwitz camp was liberated in January 1945. This Soviet military footage shows civilians and Soviet soldiers sifting through possessions of people deported to the Auschwitz killing center.

We would like to thank Crown Family Philanthropies, Abe and Ida Cooper Foundation, the Claims Conference, EVZ, and BMF for supporting the ongoing work to create content and resources for the Holocaust Encyclopedia. View the list of donor acknowledgement.