You searched for: Concentration camps
<< Previous | Displaying results 751-799 of 1116 for "Concentration camps" | Next >>
-
Theodor Wolff
ArticleTheodor Wolff was an influential German journalist and vocal opponent of the Nazis. His work was burned during the Nazi book burnings of 1933. Learn more.
-
The Role of Academics and Teachers
ArticleTo implement their policies, the Nazis had help from individuals across Europe, including professionals in many fields. Learn about the role of academics and teachers.

-
Sigmund Freud
ArticleSigmund Freud was the founder of psychoanalysis. The Nazis abhorred his new science and Jewish heritage. His works were burned in Germany in 1933. Learn more.

-
Charred remains of victims at Maly Trostinets
PhotoView of the charred remains of Jewish victims burned by the Germans near the Maly Trostinets concentration camp. Photograph taken ca. 1944. In the fall of 1943, the Germans destroyed the Minsk ghetto. The SS deported some Jews from Minsk to the Sobibor killing center, and killed about 4,000 remaining Jews at Maly Trostinets.

-
Roundups of Norwegian Jews
Timeline EventOctober 26, 1942. On this date, German and Norwegian officials started rounding up and deporting Jews from Norway.

-
Flag graphic for US 20th Armored Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 20th Armored Division's flag. The US 20th Armored Division was occasionally known as the "Armoraiders" during World War II. They participared in the liberation of the Dachau concentration camp. The 20th Armored Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1985 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum (USHMM).

-
Flag graphic for US 6th Armored Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 6th Armored Division's flag. The US 6th Armored Division is also known as the "Super Sixth." During World War II, they were involved in the Battle of the Bulge and overran the Buchenwald concentration camp. The 6th Armored Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1985 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum (USHMM).

-
Grafeneck "euthanasia" killing center
PhotoSiegfried Graetschus (right) and an unidentified man stand in front of Grafeneck, the first killing center established under Aktion T4 (the Nazi Euthanasia Program). Before joining the T4 program, Graetschus worked at the Sachsenhausen concentration camp. Photo dated early 1940.

-
Aliyah Bet
ArticleLearn more about Aliyah Bet, the clandestine immigration of Jews to Palestine between 1920 and 1948, when Great Britain controlled the area.

-
Chaim Yelin
ArticleYiddish writer Chaim Yelin was a leader of the Kovno ghetto underground resistance movement again the Germans.

-
Hinda Chilewicz
ID CardHinda was the eldest of three children in a comfortable middle class Jewish family. Her father owned a textile business in Sosnowiec and her mother attended to the home. Sosnowiec in southwestern Poland had a growing Jewish community of almost 30,000 people. There was a Jewish hospital as well as religious schools. 1933–39: Hinda was just 13 years old when German troops invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. Three days later, they occupied Sosnowiec and terrorized the Jewish community, killing over a…

-
Aron Tabrys
ID CardAron was the second of six children born to Jewish parents in Vilna, a city known as a center of Jewish cultural life. He was called Arke by his friends and family. Aron's father supported his large family on the meager income of a chimney sweep. 1933-39: As a child Aron attended a Jewish day school, and then went on to attend a public secondary school. When he was 14 his father had an accident which rendered him blind, and Aron had to start working full-time to support the family. Aron belonged to an…

-
Warsaw
ArticleIn October 1940, Nazi authorities established the Warsaw ghetto. Learn more about life in the ghetto, deportations, armed resistance, and liberation.

-
Guta Blass Weintraub describes Starachowice ghetto cultural life
Oral HistoryGuta and her family fled to Starachowice, Poland. There, the Germans ordered them and other Jews into a ghetto and put them to work in forced-labor factories. As an act of resistance at the Majowka camp, Guta attacked a Nazi guard preparing to shoot her and other prisoners at a mass grave. A bullet grazed her, but Guta pretended to be fatally wounded. Days later, Guta was deported to Auschwitz, then Ravensbrueck, where she was liberated. Her mother died only weeks short of freedom.

-
SS and the Holocaust
ArticleLearn more about the SS and the organization’s involvement in perpetrating the Holocaust.

-
The Holocaust and World War II: Key Dates
ArticleRead a detailed timeline of the Holocaust and World War II. Learn about key dates and events from 1933-45 as Nazi antisemitic policies became more radical.

-
Warsaw Ghetto Uprising
ArticleThe Warsaw ghetto uprising was the largest, symbolically most important Jewish uprising, and first urban uprising in German-occupied Europe.

-
Melk
ArticleLearn about the establishment of and conditions in Melk, a subcamp of the Mauthausen camp system in Austria.

-
Nina Kaleska describes the formation of the ghettos in Grodno
Oral HistoryNina and her family were confined in a ghetto after the Germans entered Grodno in 1941. Her parents and then her sister perished after deportation to the Auschwitz concentration camp. Nina survived in the camp for two years. As the Soviet army advanced in 1945, Nina and other inmates from the camp were transferred first to the Ravensbrueck camp in Germany and then to the Retzof-am-Richlin camp. Nina was liberated in May 1945, during a forced march from the camp.

-
Rescue and Resistance
ArticleWhile some European Jews survived the Holocaust by hiding or escaping, others were rescued by non-Jews. Learn more about these acts of resistance.
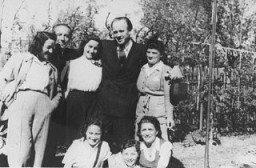
-
The War Refugee Board
ArticleThe War Refugee Board was formed in 1944 by executive order under President Roosevelt. It was tasked with the rescue and relief of victims of Nazi oppression.

-
Mass Shootings of Jews during the Holocaust
ArticleAlmost one third of the six million Holocaust victims were murdered in mass shootings.

-
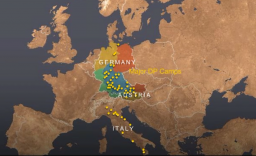
The Aftermath of the Holocaust
Animated MapView an animated map describing some of the challenges survivors faced in the aftermath of the Holocaust, when many feared returning to their former homes.
-
Sophie Ehrhardt performs a racial examination on a Romani woman
PhotoSophie Ehrhardt, a German hygienist working with Dr. Robert Ritter, performs a racial examination on a Romani woman. Berlin, Germany, c. 1936-1940. During the Nazi era, Dr. Robert Ritter was a leading authority on the racial classification of people pejoratively labeled “Zigeuner” (“Gypsies”). Ritter’s research was in a field called eugenics, or what the Nazis called “racial hygiene.” Ritter worked with a small team of racial hygienists. Among them were Eva Justin and Sophie Ehrhardt. Most…

-
Moniek Rozen
ID CardOne of 12 children, Moniek grew up in Dabrowa Gornicza, an industrial town in western Poland. His father, Jacob, owned a general store, which he was forced to close in 1938 as the result of a boycott by local antisemites. Moniek attended both public and Jewish schools, and his father hoped that one day he would become a rabbi. 1933–39: On September 1, 1939, Moniek was awakened by the sounds of airplanes flying overhead as German forces invaded Poland. As the war drew closer, Moniek fled eastward, but…

-
Susan Strauss
ID CardSusan grew up in Vacha, a small Thuringian town where her family had lived for more than 400 years. Her father, Herman, owned a general store and her mother, Bertha, took care of the home and children. Susan had a younger sister Brunhilde. The Strausses were one of about 25–30 Jewish families living in Vacha. 1933–39: Soon after the Nazis took power, many of Susan's friends stopped playing with her. In 1938 she was forced to leave the public school. That November, the Nazis unleashed a wave of pogroms…

-
David Bergman
ID CardDavid was born to religious Jewish parents in a small town in Ruthenia, Czechoslovakia's easternmost province, which had been ruled by Hungary until 1918. Located in the Carpathian Mountains, the town was so isolated that news from the rest of the country would arrive by a drummer who would read the news in the town's central square. David's father worked as a tailor and his mother was a seamstress. 1933-39: While David's parents worked, he would be at home having a good time. They had a beautiful home…

-
Morris Kornberg describes arrival at Auschwitz
Oral HistoryMorris grew up in a very religious Jewish household and was active in a Zionist sports league. When the Germans invaded Poland in September 1939, Morris's town was severely damaged. Morris's family was forced to live in a ghetto, and Morris was assigned to forced labor. After a period of imprisonment in Konskie, a town about 30 miles from Przedborz, Morris was deported to the Auschwitz camp. He was assigned to the Jawischowitz subcamp of Auschwitz. In January 1945, Morris was forced on a death march and…

-
Romania
ArticleEven before joining the Axis alliance in 1940, Romania had a history of antisemitic persecution. Learn more about Romania before and during World War II.

-
The Vélodrome d'Hiver (Vél d'Hiv) Roundup
ArticleThe Vélodrome d'Hiver (or Vél d'Hiv) roundup was the largest French deportation of Jews during the Holocaust. It took place in Paris on July 16–17, 1942.

-
Spanish Civil War
ArticleThe Spanish Civil War (1936–39) was the bloodiest conflict western Europe had experienced since the end of WWI in 1918. It was a breeding ground for mass atrocities.

-
An Overview of the Holocaust: Topics to Teach
ArticleRecommended resources, topics, context, rationale, and critical thinking questions if you have limited time to teach about the Holocaust.

-
Introduction to the Holocaust
ArticleLearn about the Holocaust, the systematic, state-sponsored persecution and murder of six million Jews by the Nazi regime and its collaborators.

-
Ghettos
ArticleGhettos separating Jews from the rest of the population were part of the Nazi plan to destroy Europe's Jews. Read about ghettoization during the Holocaust.

-
Richard Baer, Karl Höcker, and Dr. Enno Lolling
PhotoRichard Baer and Karl Höcker look over a document with SS-Standartenführer Dr. Enno Lolling, the director of the Office for Sanitation and Hygiene in the Inspectorate of Concentration Camps. From left to right: Lolling, Baer, Höcker. From Karl Höcker's photograph album, which includes both documentation of official visits and ceremonies at Auschwitz as well as more personal photographs depicting the many social activities that he and other members of the Auschwitz camp staff enjoyed.…

-
German Rule in Occupied Europe
ArticleThroughout the 1930s and 40s, Nazi Germany invaded much of Eastern and Western Europe. Learn more about German rule in occupied territories.

-
Office of Special Investigations
ArticleBeginning in 1979, the Office of Special Investigations (OSI) opened hundreds of investigations and initiated proceedings of Nazi war criminals. Learn more
-
Stand Fast
SongErich Frost (1900–87), a musician and devout Jehovah's Witness, was active in the religious resistance to Hitler's authority. Caught smuggling pamphlets from Switzerland to Germany, he was imprisoned in the Sachsenhausen concentration camp near Berlin where he composed this song in 1942. Later deported to a labor camp at Alderney, Channel Islands, Frost survived the war and returned to Germany to serve the Watchtower Society. "Fest steht," reworked in English as "Forward, You Witnesses," is among the…
-
Quakers
ArticleThe American Friends Service Committee, a Quaker relief organization, helped thousands of people before, during, and after World War II. Learn about its refugee aid work.

-
Nazi Propaganda
ArticleNazi propaganda had a key role in the persecution of Jews. Learn more about how Hitler and the Nazi Party used propaganda to facilitate war and genocide.

-
Vilna
ArticleDuring the Holocaust, the creation of ghettos was a key step in the Nazi process of ultimately destroying Europe's Jews. Learn about the Vilna ghetto.

-
Women in the Third Reich
ArticleDespite the Nazi Party's ideology of keeping women in the home, their roles expanded beyond wives and mothers.

-
Esther Lurie
ArticleArtist Esther Lurie documented life in the Kovno ghetto for its secret archives. Learn about her watercolors and sketches, the majority of which have never been found.

-
Hoess affidavit
ArtifactAffidavit signed by Rudolf Hoess attesting to the gassing of Jews while he was the commandant of the Auschwitz killing center. The German text reads: "I declare herewith under oath that in the years 1941 to 1943 during my tenure in office as commandant of Auschwitz Concentration Camp 2 million Jews were put to death by gassing and a 1/2 million by other means. Rudolf Hoess. May 14, 1946." The confession is also signed by Josef Maier of the US Chief of Counsel's office. A photoreproduction of the original…

-
Medical Case: US prosecutor details illegal experiments
FilmThe Medical Case was one of 12 war crimes trials held before an American tribunal as part of the Subsequent Nuremberg Proceedings. The trial dealt with doctors and nurses who had participated in the killing of physically and mentally impaired Germans and who had performed medical experiments on people imprisoned in concentration camps. Here, chief prosecutor Brigadier General Telford Taylor reads into evidence a July 1942 report detailing Nazi high-altitude experiments and outlines the prosecution's goals…

-
German civilians from Schwarzenfeld dig graves for the reburial victims of a death march
PhotoGerman civilians from Schwarzenfeld dig graves for the reburial of 140 Hungarian, Russian, and Polish Jews exhumed from a mass grave near the town. The victims died while on an evacuation transport from the Flossenbürg concentration camp. Schwarzenfeld, Germany, April 25, 1945. Following the discovery of death march victims, US Army officers forced local Germans to view the scene of the crime and ordered the townspeople to give the victims a proper burial.

-
American troops, including African American soldiers from the 183rd Engineer Combat Battalion
PhotoAmerican troops, including African American soldiers from the Headquarters and Service Company of the 183rd Engineer Combat Battalion, 8th Corps, US 3rd Army, view corpses stacked behind the crematorium during an inspection tour of the Buchenwald concentration camp. Among those pictured is Leon Bass (the soldier third from left). Buchenwald, Germany, April 17, 1945.

-
Père Jacques de Jésus (born Lucien Bunel)
PhotoPère Jacques de Jésus (born Lucien Bunel) was a Carmelite headmaster of a Catholic boys school in Avon, France. Angered at Nazi policies, he made his school a refuge for young men seeking to avoid forced labor and for Jews. On January 15, 1944, the Gestapo raided the school, seizing Père Jacques and three Jewish children. The boys were deported to Auschwitz and killed. Père Jacques, sent to various concentration camps, died shortly after liberation.

-
Chaim Benzion Cale
ArticleChildren's diaries bear witness to some of the most heartbreaking events of the Holocaust. Learn about the diary and experiences of Chaim Benzion Cale.

