You searched for: Ghettos
<< Previous | Displaying results 1001-1050 of 1236 for "Ghettos" | Next >>
-
Misuse of Holocaust Imagery Today: When Is It Antisemitism?
ArticleLearn more about the modern misuse of images and symbols from the Holocaust and how this distortion can lead to antisemitism.
-

-
Wartime Fate of the Passengers of the St. Louis
ArticleIn May 1939, the St. Louis set sail from Germany to Cuba. Most of the passengers, fleeing Nazi Germany, were denied entry. Learn more about their fates.

-
German Jewish Refugees, 1933–1939
ArticleLearn more about the plight of Jewish refugees who attempted to escape Germany between 1933 and 1939.

-
Wannsee Conference and the "Final Solution"
ArticleAt the Wannsee conference of January 1942, Nazi Party and German government officials gathered to coordinate implementation of the “Final Solution to the Jewish Question.”

-
Polish Jewish Refugees in Lithuania, 1939–40
ArticleLearn more about Polish Jewish refugees that relocated to Lithuania between 1939-1940.

-
History of the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum
ArticleThe United States Holocaust Memorial Museum opened in April 1993. Explore the history of the nation's memorial to the millions murdered during the Holocaust.

-
Mobile Killing Squads
ArticleLearn more about Nazi mobile killing squads (Einsatzgruppen) killing activities in the Soviet Union during World War II.
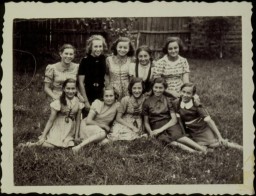
-
1945: Key Dates
ArticleExplore a timeline of key events during 1945 in the history of Nazi Germany, World War II, the Holocaust, and liberation and the aftermath of the Holocaust.

-
Sachsenhausen: Conditions in the Camp
ArticleLearn about conditions in the Sachsenhausen concentration camp system and the treatment of prisoners there, including medical experiments and forced labor.

-
Flossenbürg: Key Dates
ArticleExplore a timeline of the history of the Flossenbürg camp in the Nazi camp system from its establishment in 1938 until liberation in 1945.

-
Jewish Community of Kalisz: Youth, Culture, Religion
ArticleKalisz had a vibrant Jewish community between WWI and WWII. Learn about its youth movements, schools, cultural life, sports, and religious life.

-
Evidence from the Holocaust at the First Nuremberg Trial
ArticleProsecutors before the IMT based the case against 22 leading Nazi officials primarily on thousands of documents written by the Germans themselves. Learn more.

-
Belzec: Key Dates
ArticleExplore key events in the history of the Belzec killing center in the Nazi camp system. It was constructed for the sole purpose of murdering Jews.

-
The Role of the German Police
ArticleTo implement their policies, the Nazis had help from individuals across Europe, including professionals in many fields. Learn about the role of the German police.

-
King Christian X of Denmark
ArticleDid King Christian X of Denmark wear a yellow star in support of the Danish Jews? Read more about the historical truth behind the legend.
-
Helena Husserlova with her daughter, Zdenka
PhotoIn this portrait, Helena Husserlova, wearing a Jewish badge, poses with her daughter Zdenka who is holding a teddy bear. The photograph was taken shortly before they were deported to Theresienstadt. Zdenka was born in Prague on February 6, 1939. On October 10, 1941, when Zdenka was just two and a half years old, her father was deported to the Lodz ghetto. He died there almost a year later, on September 23, 1942. Following his deportation, Helena and Zdenka returned to Helena's hometown to live with…
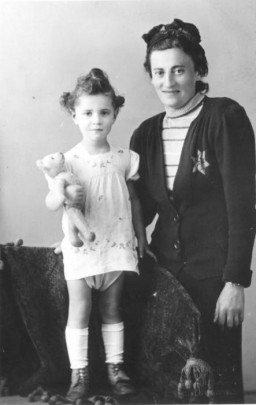
-
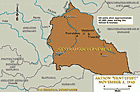
Operation Harvest Festival
Timeline EventNovember 3, 1943. On this date, SS and police units implemented "Operation Harvest Festival" (also known as Aktion Erntefest).
-
Dr. Robert Ritter visits a "Gypsy camp"
PhotoDr. Robert Ritter talks to several residents in a Zigeunerlager ("Gypsy camp"). Hamburg, Germany, 1940. During the Nazi era, Dr. Robert Ritter was a leading authority on the racial classification of people pejoratively labeled “Zigeuner” (“Gypsies”). Ritter’s research was in a field called eugenics, or what the Nazis called “racial hygiene.” Ritter worked with a small team of racial hygienists. Among them were Eva Justin and Sophie Ehrhardt. Most of the people whom Ritter studied and…

-
Sophie Ehrhardt performs a racial examination on a Romani woman
PhotoSophie Ehrhardt, a German hygienist working with Dr. Robert Ritter, performs a racial examination on a Romani woman. Berlin, Germany, c. 1936-1940. During the Nazi era, Dr. Robert Ritter was a leading authority on the racial classification of people pejoratively labeled “Zigeuner” (“Gypsies”). Ritter’s research was in a field called eugenics, or what the Nazis called “racial hygiene.” Ritter worked with a small team of racial hygienists. Among them were Eva Justin and Sophie Ehrhardt. Most…

-
Eva Justin interviews a Romani woman interned in a "Gypsy camp"
PhotoA color photograph of Eva Justin interviewing a Romani woman interned in a "Gypsy camp." Vienna, Austria, 1940. During the Nazi era, Dr. Robert Ritter was a leading authority on the racial classification of people pejoratively labeled “Zigeuner” (“Gypsies”). Ritter’s research was in a field called eugenics, or what the Nazis called “racial hygiene.” Ritter worked with a small team of racial hygienists. Among them were Eva Justin and Sophie Ehrhardt. Most of the people whom Ritter studied and…

-
A family interned in a "Gypsy camp"
PhotoA family stands outside of their wagon while interned in a Zigeunerlager ("Gypsy camp"). In the background, children are crowded around Eva Justin. Justin worked for the Center for Research on Racial Hygiene and Demographic Biology. Schleswig-Holstein, Germany, 1938. During the Nazi era, Dr. Robert Ritter was a leading authority on the racial classification of people pejoratively labeled “Zigeuner” (“Gypsies”). Ritter’s research was in a field called eugenics, or what the Nazis called…

-
Miriam Peleg explains why Żegota was important
Oral HistoryMiriam Peleg (1913–1996) was a member of the Council for Aid to Jews, codenamed “Żegota.” Żegota was a clandestine rescue organization of Poles and Jews in German-occupied Poland. Supported by the Polish government-in-exile, Żegota coordinated efforts to save Jews from Nazi persecution and murder. It operated from 1942 to 1945. Born Maria Hochberg, Miriam was from a Polish-Jewish family. She grew up in a small town about 70 miles east of Kraków. As early as the summer of 1940, Miriam obtained…

-
Reinhard Heydrich: In Depth
ArticleReinhard Heydrich, Reich Security Main Office chief, was one of the main architects of the “Final Solution," the Nazi plan to murder the Jews of Europe.

-
Blanka Rothschild describes returning to Lodz after the war to look for family members
Oral HistoryBlanka was an only child in a close-knit family in Lodz, Poland. Her father died in 1937. After the German invasion of Poland, Blanka and her mother remained in Lodz with Blanka's grandmother, who was unable to travel. Along with other relatives, they were forced into the Lodz ghetto in 1940. There, Blanka worked in a bakery. She and her mother later worked in a hospital in the Lodz ghetto, where they remained until late 1944 when they were deported to the Ravensbrueck camp in Germany. From Ravensbrueck,…

-
Madeline Deutsch describes adjusting to social and educational life after the war
Oral HistoryMadeline was born into a middle class family in an area of Czechoslovakia that was annexed by Hungary in 1938-1939. Her father worked out of their home and her mother was a homemaker. Madeline attended high school. In April 1944 her family was forced into a Hungarian ghetto. The family lived in the ghetto for two weeks before being transported to Auschwitz. Madeline and her mother were separated from her father and older brother. Neither her father nor brother survived the war. A week after arriving in…

-
Ludmilla Page recalls arriving in Auschwitz instead of Oskar Schindler's munitions factory in Brünnlitz
Oral HistoryLudmilla was born to an assimilated Jewish family in Kishinev, Romania. She and her mother, a physician, were living in Poland when the Germans invaded on September 1, 1939. They were taken to Krakow. Ludmilla was forced to live in the Krakow ghetto; her mother was sent to the Warsaw ghetto. Ludmilla worked in a factory at the Plaszow labor camp for a businessman who was a friend of the German industrialist Oskar Schindler. In October 1944, Schindler attempted to save some Jewish workers by relocating them…

-
Ludmilla Page describes leaving Auschwitz and arriving at the Bruennlitz munitions factory in the Sudetenland
Oral HistoryLudmilla was born to an assimilated Jewish family in Kishinev, Romania. She and her mother, a physician, were living in Poland when the Germans invaded on September 1, 1939. They were taken to Krakow. Ludmilla was forced to live in the Krakow ghetto; her mother was sent to the Warsaw ghetto. Ludmilla worked in a factory at the Plaszow labor camp for a businessman who was a friend of the German industrialist Oskar Schindler. In October 1944, Schindler attempted to save some Jewish workers by relocating them…

-
William (Bill) Lowenberg describes forced labor in the Kaufering subcamp of the Dachau concentration camp
Oral HistoryAs a boy, Bill attended school in Burgsteinfurt, a German town near the Dutch border. After the Nazis came to power in Germany in January 1933, Bill experienced increasing antisemitism and was once attacked on his way to Hebrew school by a boy who threw a knife at him. In 1936, he and his family left Germany for the Netherlands, where they had relatives and thought they would be safe. However, after Germany invaded the Netherlands in May 1940, antisemitic legislation--including the order to wear the Jewish…

-
Ludmilla Page describes arrival at the Brünnlitz munitions factory
Oral HistoryLudmilla was born to an assimilated Jewish family in Kishinev, Romania. She and her mother, a physician, were living in Poland when the Germans invaded on September 1, 1939. They were taken to Krakow. Ludmilla was forced to live in the Krakow ghetto; her mother was sent to the Warsaw ghetto. Ludmilla worked in a factory at the Plaszow labor camp for a businessman who was a friend of the German industrialist Oskar Schindler. In October 1944, Schindler attempted to save some Jewish workers by relocating them…

-
Charlene Schiff describes the Soviet occupation of Horochow after the outbreak of World War II
Oral HistoryBoth of Charlene's parents were local Jewish community leaders, and the family was active in community life. Charlene's father was a professor of philosophy at the State University of Lvov. World War II began with the German invasion of Poland on September 1, 1939. Charlene's town was in the part of eastern Poland occupied by the Soviet Union under the German-Soviet Pact of August 1939. Under the Soviet occupation, the family remained in its home and Charlene's father continued to teach. The Germans…

-
Charlene Schiff describes difficulties in gaining entry to the United States in the aftermath of the Holocaust
Oral HistoryBoth of Charlene's parents were local Jewish community leaders, and the family was active in community life. Charlene's father was a professor of philosophy at the State University of Lvov. World War II began with the German invasion of Poland on September 1, 1939. Charlene's town was in the part of eastern Poland occupied by the Soviet Union under the German-Soviet Pact of August 1939. Under the Soviet occupation, the family remained in its home and Charlene's father continued to teach. The Germans…

-
Barbara Marton Farkas describes punishment for spilling some food in the Auschwitz camp
Oral HistoryDescribes punishment for spilling some food in the Auschwitz camp

-
Killing Centers: In Depth
ArticleThe Nazis established killing centers in German-occupied Europe during WWII. They built these killing centers for the mass murder of human beings.

-
Börgermoor Camp
ArticleBörgermoor was part of the Nazi regime’s early system of concentration camps. It was located in the Emsland region of Prussia.
-
The United States and the Holocaust, 1942–45
ArticleWhy did the United States go to war? What did Americans know about the “Final Solution”? How did Americans respond to news about the Holocaust? Learn more.

-
The German Military and the Holocaust
ArticleThe German military played a vital role in the consolidation of Nazi power and persecution and mass murder of Jews and other groups. Learn more

-
Columbia-Haus
ArticleThe Columbia-Haus camp was one of the early camps established by the Nazi regime. It held primarily political detainees. Learn more about the history of the camp.
-
How did the Nazis and their collaborators implement the Holocaust?
Discussion QuestionWhen Nazi Party leader Adolf Hitler became German chancellor on January 30, 1933, no step-by-step blueprint for the genocide of Jews as a “race” existed. After the outbreak of World War II, millions of Jews came und...

-
Abraham Malnik
ID CardAbraham was born to a Jewish family in Kovno, a city picturesquely situated at the confluence of two rivers. With an opera company, chic stores and lively nightclubs, it was often called "Little Paris." The city had a large Jewish community of 38,000 and was known for its extensive Hebrew school system. Abraham's father was a barber, and his mother was a beautician. 1933-39: When Abraham was a kid his family used to go to his grandparents' house for Sunday dinner. In the winter they would take a…

-
Hinda Chilewicz
ID CardHinda was the eldest of three children in a comfortable middle class Jewish family. Her father owned a textile business in Sosnowiec and her mother attended to the home. Sosnowiec in southwestern Poland had a growing Jewish community of almost 30,000 people. There was a Jewish hospital as well as religious schools. 1933–39: Hinda was just 13 years old when German troops invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. Three days later, they occupied Sosnowiec and terrorized the Jewish community, killing over a…

-
Kurt Pauly
ID CardKurt was born to Jewish parents in the city of Aachen, where his mother's family had resided since the 18th century. His father, though trained as a chef, worked as a butcher and also managed several stores for his father-in-law. The Paulys lived over one of those shops in the nearby suburb of Eilendorf. Kurt enjoyed large family gatherings, where he would play with his cousins, Anne and Margot Frank. 1933–39: When the Nazis came to power in 1933, the situation drastically changed for the Paulys.…

-
Moniek Rozen
ID CardOne of 12 children, Moniek grew up in Dabrowa Gornicza, an industrial town in western Poland. His father, Jacob, owned a general store, which he was forced to close in 1938 as the result of a boycott by local antisemites. Moniek attended both public and Jewish schools, and his father hoped that one day he would become a rabbi. 1933–39: On September 1, 1939, Moniek was awakened by the sounds of airplanes flying overhead as German forces invaded Poland. As the war drew closer, Moniek fled eastward, but…

-
Elzbieta Lusthaus
ID CardElzbieta grew up in Iwonicz, a resort town in southwestern Poland noted for its mineral water. Her father, Edmund, was a respected physician and Helena, her mother, had studied pharmacology. At home, they spoke Polish and were among the few Jewish families who lived in Iwonicz. 1933–39: When German troops invaded Poland on September 1, 1939, Elzbieta's father was drafted into the Polish army. Seventeen days later, the Soviet army drove in from the east and Edmund was captured. He was transported to a…

-
Martin Weiss
ID CardMartin was one of nine children born to orthodox Jewish parents in Veľká Poľana, a rural village in the Carpathian Mountains. His father owned a farm and a meat business, and his mother attended to the children and the home. Everyone in the family helped take care of the horses and cows. 1933–39: Martin attended the village's Czechoslovak schools, which were quite progressive. Like many of the other children, he looked forward to leaving the provincial life in Veľká Poľana. In 1938–1939, his…

-
Aaron Lejzerowicz
ID CardAaron was one of four children born to a Jewish family in the northeastern Polish town of Zdzieciol. His father was a shoemaker and, along with a business partner, he also ran a shoe store in the town. Aaron attended a private Jewish school, where he studied the Polish language and history as well as Jewish history and Hebrew. 1933-39: On September 1, 1939, Germany invaded Poland. Three weeks later, Poland was partitioned between Germany and the Soviet Union [under the German-Soviet Pact]. Aaron and his…

-
Paula Wajcman
ID CardPaula was raised in a religious Jewish family in Kielce, a city in the southeast of Poland. Her family lived in a modern two-story apartment complex. Paula's father owned the only trucking company in the district. Her older brother, Herman, attended religious school, while Paula attended public kindergarten in the morning and religious school in the afternoon. 1933-39: Paula's school uniform was a navy blazer with a white blouse and pleated skirt. At age 9, she did the "Krakowiak" dance at school. Boys…
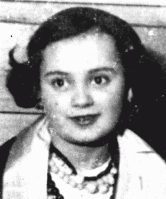
-
Fischel (Philip) Goldstein
ID CardFischel was the youngest of five children. He came from a Jewish family of artisans; his father was a tailor, his uncles were furriers, and his sister was a dressmaker. Fischel started his education at a Jewish parochial school at age 3, where he studied Hebrew and Yiddish. He continued his education at Jewish private schools until age 10, when he entered Polish public schools. 1933-39: After graduating from the Polish public school system at age 14, Fischel started an apprenticeship in his father's…

-
Judith Gabriel Dichter
ID CardJudith, nicknamed Julie, was one of five children born to religious Hungarian-Jewish parents in the Burgenland, the eastern province of Austria that was part of Hungary until 1921. She married Tobias Dichter, a traveling salesman from Vienna who had sold merchandise to her father. The Dichters moved to an apartment in Vienna's Jewish Leopoldstadt district, where they raised two children. 1933-39: The Germans have annexed Austria. One week after the annexation, Germans came to Julie's apartment to take her…
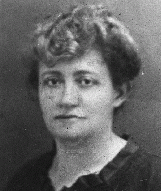
-
Alice Edelstein-Friedmann
ID CardAlice, born Alice Edelstein, was the youngest of two children raised in a Jewish family in the Bohemian village of Hostoun, near Prague. Shortly after Alice was born, her father moved the family to Vienna. There, Alice's father owned a wholesale shoe business. As a child, Alice attended public school and also received a religious education. 1933-39: After graduating from business school, Alice had a hard time finding a job because of the economic depression in Austria. In 1936 her father let her work in…

