You searched for: austria
<< Previous | Displaying results 401-450 of 505 for "austria" | Next >>
-
Josephine Kohn Dermer
ID CardJosephine, known affectionately as Pepi, and her brother and three sisters were raised in Vienna. Her father traded in furs and her mother was a homemaker. Only a few years after Pepi married, her husband died unexpectedly and she was left to care for their young son, Fred. She and her son moved in with her widowed father. 1933-39: Pepi spent much of her time with her sister Helene. Helene's husband was a Singer sewing machine representative, and in the summer of 1937 Pepi and Fred joined him and Helene…

-
Rubin Segalowicz
ID CardRubin was the second of four children born to a Jewish family in the northeastern Polish town of Ivenets, approximately 60 miles west of Minsk. His father was a butcher. Rubin attended Ivenets' public elementary school until the age of 10, when he transferred to the Mirar Yeshiva to study Jewish law. 1933-39: In 1936, after completing yeshiva, Rubin made his living as a house painter. In Ivenets people would stand in front of Jewish stores and drive customers away, telling them not to buy from Jews. In…

-
Dachau
ArticleDachau was the first and longest operating Nazi concentration camp. Learn about the camp's early years, prisoners, medical experiments, and liberation.

-
Lucien-Louis Bunel
ID CardLucien was the fourth of eight children born to poor Catholic parents in a small town in northwestern France. Lucien began his seminary studies in nearby Rouen at the age of 12. Following two years of military service, he resumed his religious studies in 1922 and was ordained as a priest three years later. He joined the Carmelite religious order in 1931, and became Father Jacques. 1933-39: In 1934 Father Jacques moved to the town of Avon, where he established a boys' school,…

-
Janos Geroe
ID CardJanos was the only child born to a Jewish family in the small agricultural city of Torokszentmiklos, about 65 miles southeast of Budapest. His father, who had a degree in pharmacology, joined his family's grain exporting business. 1933-39: In 1933, when Janos was 4 years old, his parents divorced. According to Hungarian law, Janos was to live with his mother until he was 7 and then return to his father. Janos moved with his mother to her hometown of Szentes, where he began studying at a religious primary…

-
Jeno Nemeth
ID CardJeno moved to Szentes from a tiny farming community near the city of Szolnok, where he and his two brothers had been born to Jewish parents. Jeno owned a store that carried groceries and hardware items. He lived in the southeast Hungarian town of Szentes. Jeno and his wife, Juliana, had two married daughters, Barbara and Margit. Their son, Desider, was a dentist in Szentes. 1933-39: Jeno and his wife work hard in their store. The Depression of the 1930s was devastating, but things are starting to get a…

-
Desider (Dezso) Nemeth
ID CardDesider and his sisters, Margit and Barbara, were born to a middle-class Jewish family. They lived in Szentes, a town in southeastern Hungary, located 30 miles from the city of Szeged. Desider had a dental practice in Szentes. He married Barbara Kertesz, who came from the neighboring town of Hodmezovasarhely. 1933-39: Desider and Barbara now have a baby daughter, Maria. Desider has a busy practice and his patients come from all walks of life. He is glad that he opened his practice in the town where he was…

-
Margit Morawetz
ID CardWhen Margit was a baby, her family moved from Austria to Prague, Czechoslovakia. Her father was a banker from a religious Jewish family in Bohemia and her mother came from a Viennese family of Jewish origin. Margit knew many languages: Czech, French, English and German, which she spoke with her family. 1933-39: In 1938, when Margit was 16, attacks on Jews in central Europe escalated and her parents decided she should leave. She left secondary school in Prague and went to Paris, where she studied…

-
Isachar Herszenhorn (Irving Horn)
ID CardIsachar was born to a Jewish family in the Polish city of Radom, approximately 75 miles south of Warsaw. The city was the center of Poland's leather-tanning industry. Isachar's father worked as a salesman for a nearby tanning factory. His father was a successful salesman and the family lived comfortably. 1933-39: During registration for Isachar's first-grade class in 1934, a Jewish boy was pushed down the stairs. When his mother confronted the principal about the incident, all he said was that the boy had…

-
Josel Gerszonowicz
ID CardThe oldest of eight children, Josel was born in Miechow, a small town in south central Poland. His father was a machinist and locksmith. As a boy, Josel spent long days learning Hebrew in the Jewish school and taking general subjects at the public school. He was 13 years old when he left school to work in his father's shop. 1933-39: Josel met his wife, Esther, through a matchmaker, and they settled in nearby Dzialoszyce, a town with a Jewish community of about 7,000, and a beautiful synagogue that had…

-
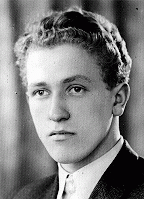
Odon Jerzy Wos
ID CardOdon was the third of four children born to Roman Catholic parents in Warsaw, Poland's capital. His father had worked for the Polish merchant marine before starting his own textile business in 1930. When Odon was 8, the family moved to a comfortable apartment located near the Royal Castle and Vistula River. In 1932 Odon began attending grade school. 1933-39: In September 1938 Odon began secondary school. Sensing growing danger from Germany, his father advised him to study German in addition to French. On…
-
Jozef Tiso
ArticleJozef Tiso was a Slovak politician and a Roman Catholic priest. From 1939 to 1945, he was the president of the Slovak Republic, one of Nazi Germany’s allies.

-
Leo Schneiderman describes routine at the Ebensee camp
Oral HistoryThe Germans invaded Poland in September 1939. Leo and his family were confined to a ghetto in Lodz. Leo was forced to work as a tailor in a uniform factory. The Lodz ghetto was liquidated in 1944, and Leo was deported to Auschwitz. He was then sent to the Gross-Rosen camp system for forced labor. As the Soviet army advanced, the prisoners were transferred to the Ebensee camp in Austria. The Ebensee camp was liberated in 1945.

-
Eva Rappoport Edmands describes packing to leave Vienna for France in 1938
Oral HistoryAfter the German annexation of Austria in March 1938, Eva's family decided to leave Vienna for Paris. Eva and her mother were later trapped in the occupied area of France while her father was in the unoccupied area after the French armistice with Germany in 1940. They were eventually reunited and together tried to find refuge in Switzerland, but were caught by the French police. They received help from a priest in Annecy and survived the war under his protection. After the liberation of France in August…

-
Colonel Richard R. Seibel describes US Army procedures for burial of the dead after liberation of Mauthausen
Oral HistoryIn June 1941, Richard was ordered to active duty in the US Army. After a period of training, he was sent to Europe. He entered Austria in April 1945. A patrol came upon the Mauthausen camp and Richard was appointed to take command of the camp. He organized those inmates who had survived in the camp until liberation in May 1945, and brought in two field hospitals. After 35 days in Mauthausen, he was transferred to a post in the Austrian Alps.

-
US veteran Raymond Buch describes forcing civilians to bury the dead
Oral HistoryAs a US Army sergeant, Raymond fought in the Battle of the Bulge. In May 1945, his unit was deployed to the Mauthausen camp in Austria to bulldoze mass graves for the victims. He watched as German civilians, on US orders, hauled bodies to the mass graves. He also saw stronger camp survivors pull clothes off their weaker counterparts to replace their own tattered uniforms. Raymond went on to Mauthausen's Ebensee camp and Gusen, guarding SS men.

-
Colonel Richard R. Seibel describes aid given to survivors after liberation in Mauthausen and their plans for emigration
Oral HistoryIn June 1941, Richard was ordered to active duty in the US Army. After a period of training, he was sent to Europe. He entered Austria in April 1945. A patrol came upon the Mauthausen camp and Richard was appointed to take command of the camp. He organized those inmates who had survived in the camp until liberation in May 1945, and brought in two field hospitals. After 35 days in Mauthausen, he was transferred to a post in the Austrian Alps.

-
Leo Bretholz describes arrival at the Drancy camp
Oral HistoryAfter the Germans annexed Austria in 1938, Leo attempted to flee. He eventually reached Belgium. In 1940 he was deported to the St.-Cyprien camp in France but escaped. In 1942 Leo was smuggled into Switzerland but was arrested and sent back to France, this time to the Rivesaltes and Drancy camps. He and a friend escaped from a train deporting them to Auschwitz in Poland. Leo joined the French underground in 1943. He arrived in the United States in 1947.

-
Leo Bretholz describes conditions in the Drancy camp
Oral HistoryAfter the Germans annexed Austria in 1938, Leo attempted to flee. He eventually reached Belgium. In 1940 he was deported to the St.-Cyprien camp in France but escaped. In 1942 Leo was smuggled into Switzerland but was arrested and sent back to France, this time to the Rivesaltes and Drancy camps. He and a friend escaped from a train deporting them to Auschwitz in Poland. Leo joined the French underground in 1943. He arrived in the United States in 1947.

-
US veteran Tarmo Holma describes encountering camp survivors
Oral HistoryTarmo Holma is a veteran of the 11th Armored Division. During the invasion of German-held Austria, in May 1945 the 11th Armored (the "Thunderbolt" division) overran two of the largest Nazi concentration camps in the country: Mauthausen and Gusen.

-
Charles Torluccio describes liberation and the role of medical staff
Oral HistoryCharles Torluccio is a veteran of the 11th Armored Division. During the invasion of German-held Austria, in May 1945 the 11th Armored (the "Thunderbolt" division) overran two of the largest Nazi concentration camps in the country: Mauthausen and Gusen.

-
Darrell Romjue describes how US troops encoutered camps such as Mauthausen
Oral HistoryDarrell Romjue is a veteran of the 11th Armored Division. During the invasion of German-held Austria, in May 1945 the 11th Armored (the "Thunderbolt" division) overran two of the largest Nazi concentration camps in the country: Mauthausen and Gusen.

-
Sophie Turner-Zaretsky describes her transition to living in London
Oral HistorySophie was born Selma Schwarzwald to parents Daniel and Laura in the industrial city of Lvov, two years before Germany invaded Poland. Daniel was a successful businessman who exported timber and Laura had studied economics. The Germans occupied Lvov in 1941. After her father's disappearance on her fifth birthday in 1941, Sophie and her mother procured false names and papers and moved to a small town called Busko-Zdroj. They became practicing Catholics to hide their identities. Sophie gradually forgot that…

-
Leo Schneiderman describes conditions in the Lodz ghetto
Oral HistoryThe Germans invaded Poland in September 1939. Leo and his family were confined to a ghetto in Lodz. Leo was forced to work as a tailor in a uniform factory. The Lodz ghetto was liquidated in 1944, and Leo was deported to Auschwitz. He was then sent to the Gross-Rosen camp system for forced labor. As the Soviet army advanced, the prisoners were transferred to the Ebensee camp in Austria. The Ebensee camp was liberated in 1945.

-
Hana Mueller Bruml recalls the occupation of Prague
Oral HistoryIn 1942, Hana was confined with other Jews to the Theresienstadt ghetto, where she worked as a nurse. There, amid epidemics and poverty, residents held operas, debates, and poetry readings. In 1944, she was deported to Auschwitz. After a month there, she was sent to Sackisch, a Gross-Rosen subcamp, where she made airplane parts at forced labor. She was liberated in May 1945.

-
Franz Wohlfahrt describes the trial and sentencing of his father
Oral HistoryFranz and his family were Jehovah's Witnesses. Germany annexed Austria in 1938. After World War II began, Franz's father was executed because, as a Witness, he opposed war. In 1940, Franz refused to participate in military training and would not salute the Nazi flag. He was imprisoned, interrogated by the Gestapo (German Secret State Police) in Graz, and sentenced to five years of hard labor in a camp in Germany. Franz was liberated by US forces in 1945.

-
Franz Wohlfahrt describes imprisonment in Graz
Oral HistoryFranz and his family were Jehovah's Witnesses. Germany annexed Austria in 1938. After World War II began, Franz's father was executed because, as a Witness, he opposed war. In 1940, Franz refused to participate in military training and would not salute the Nazi flag. He was imprisoned, interrogated by the Gestapo (German Secret State Police) in Graz, and sentenced to five years of hard labor in a camp in Germany. Franz was liberated by US forces in 1945.

-
Hans Heimann describes internment in Italy
Oral HistoryThe Germans annexed Austria in March 1938. In 1939, Hans fled first to Hungary and then to Italy. He and his parents were interned in various towns. Hans's father became ill and died in 1940. In 1943, Hans and his mother were warned of German plans to deport Jews from Italy to Poland. They moved to smaller towns until liberation by the British in August 1943. Hans worked as an interpreter for the Allies until 1945, when he worked for the American Jewish Joint Distribution Committee and helped resettle…

-
The Treatment of Soviet POWs: Starvation, Disease, and Shootings, June 1941–January 1942
ArticleThe Nazi treatment of Soviet prisoners of war (POWs) was determined by Nazi ideology. Cruel conditions included starvation, no medical care, and death.

-
Freemasonry
ArticleAdolf Hitler repeated the pre-existing claim that Jews used Freemasonry to achieve their political ends. Learn more about the history of Freemasonry.

-
Elie Wiesel Timeline and World Events: 1928–1951
ArticleSurvivor Elie Wiesel devoted his life to educating the world about the Holocaust. Learn about key events in the world and his life from 1928–1951.

-
Nazi Racism: In Depth
ArticleRacism, including racial antisemitism (prejudice against or hatred of Jews based on false biological theories), was an integral part of Nazism. Learn more
-
Glossary
ArticleAntisemitism: hostility toward or hatred of Jews as a religious or ethnic group, often accompanied by social, economic, or political discrimination. Appellplatz: German word for roll call square where prisoners were forced to assemble. Aryan: Term used in Nazi Germany to refer to non-Jewish and non-Roma (Gypsy) Caucasians. Northern Europeans with especially "Nordic" features such as blonde hair and blue eyes were considered by so-called race scientists to be the most superior of Aryans, members of a…
-
"Final Solution": In Depth
ArticleThe "Final Solution," the Nazi plan to kill the Jews of Europe, was a core goal of Adolf Hitler and the culmination of German policy under Nazi rule.

-
Fürstengrube
ArticleLearn about Fürstengrube subcamp of Auschwitz, including its establishment, administration, prisoner population, and forced labor and conditions in the camp.
-
Leni Riefenstahl
ArticleLeni Riefenstahl was a German dancer, actress, and film director best known for her imposing propaganda films in support of the National Socialist (Nazi) Party.

-
Theresienstadt: Key Dates
ArticleExplore key dates in the history of the Theresienstadt camp/ghetto, which served multiple purposes during its existence from 1941-45.

-
Theresienstadt: Concentration/Transit Camp for German and Austrian Jews
ArticleLearn about the role of Theresienstadt in the deportation of German and Austrian Jews to killing sites and killing centers in the east.

-
The Holocaust and World War II: Key Dates
ArticleRead a detailed timeline of the Holocaust and World War II. Learn about key dates and events from 1933-45 as Nazi antisemitic policies became more radical.

-
Political Prisoners
ArticleHitler's political opponents were the first victims of systematic Nazi persecution. They were incarcerated without trial and under conditions of great cruelty.

-
World War I
ArticleThe experiences of World War I and its aftermath would profoundly shape the attitudes and actions of leaders and ordinary people during the Holocaust.

-
Adolf Hitler
ArticleAdolf Hitler, leader of the Nazi Party, aimed to eliminate Europe's Jews and other perceived enemies of Nazi Germany. Learn more.

-
Nazi Camps
ArticleNazi Germany and its allies established over 44,000 concentration camps and incarceration sites during the Holocaust. Read about the Nazi camp system.

-
The Search for Perpetrators
ArticleThousands of Nazi criminals were never arrested. Learn more about the postwar efforts to bring Nazi perpetrators to justice.

-
Ardeatine Caves Massacre
ArticleNow a national memorial site, the Ardeatine Caves outside Rome were the site of a German reprisal for a bombing by Italian resistance operatives in March 1944.
-
German Jews during the Holocaust
ArticleBy September 1939, over half of German Jews had emigrated. WWII would accelerate the persecution, deportation, and later, mass murder, of the remainder of Germany's Jews.

-
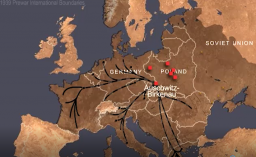
The Holocaust
Animated MapView an animated map showing key events of the Holocaust, the persecution and murder of 6 million Jews by the Nazi regime and its allies and collaborators.
-
Postwar Trials
ArticleEfforts to bring the perpetrators of Nazi-era crimes to justice continue into the 21st century. Learn more about postwar trials and their legacies.

-
Sobibor: Key Dates
ArticleExplore a timeline of key events in the history of the Sobibor killing center in the General Government, the German-administered territory of occupied Poland.

-
Blood Libel
ArticleBlood libels were false allegations that Jews used the blood of non-Jewish children in rituals. Nazi propagandists used this false charge in their antisemitic propaganda.

