You searched for: %EC%97%90%EB%B3%BC%EB%A3%A8%EC%85%98%20%EB%B0%94%EC%B9%B4%EB%9D%BC%20%EC%A1%B0%EC%9E%91%E2%97%87e49.top%E2%97%87%EC%98%A8%EB%9D%BC%EC%9D%B8%ED%99%80%EB%8D%A4%E2%97%87%ED%95%84%EB%A6%AC%ED%95%80%EC%B9%B4%EC%A7%80%EB%85%B8%20%EC%86%94%EB%A0%88%EC%96%B4%EC%B9%B4%EC%A7%80%EB%85%B8%20solaire%E2%97%87%EB%9D%BC%EC%9D%B4%EB%B8%8C%EB%B0%94%EC%B9%B4%EB%9D%BC%20%EC%A1%B0%EC%9E%91%E2%97%87oizi
<< Previous | Displaying results 201-250 of 549 for "%EC%97%90%EB%B3%BC%EB%A3%A8%EC%85%98%20%EB%B0%94%EC%B9%B4%EB%9D%BC%20%EC%A1%B0%EC%9E%91%E2%97%87e49.top%E2%97%87%EC%98%A8%EB%9D%BC%EC%9D%B8%ED%99%80%EB%8D%A4%E2%97%87%ED%95%84%EB%A6%AC%ED%95%80%EC%B9%B4%EC%A7%80%EB%85%B8%20%EC%86%94%EB%A0%88%EC%96%B4%EC%B9%B4%EC%A7%80%EB%85%B8%20solaire%E2%97%87%EB%9D%BC%EC%9D%B4%EB%B8%8C%EB%B0%94%EC%B9%B4%EB%9D%BC%20%EC%A1%B0%EC%9E%91%E2%97%87oizi" | Next >>
-
Flossenbürg
ArticleLearn about the Flossenbürg camp from its establishment until liberation in April 1945, including conditions, forced labor, subcamps, and death marches.

-
Jeno Muhlrad
ID CardJeno was the youngest of five children born to Jewish parents living in a suburb of Budapest. His father was a wholesale merchant who sold beer to restaurants and stores. After receiving a university diploma, Jeno became a pharmacist. He and his wife, Aranka, and their two children, Eva and Andras, shared a large old house in Ujpest with Jeno's father and other members of the extended family. 1933-39: Jeno's friends and family have helped him raise the large amount of money he needs to lease his own…

-
Dora Unger
ID CardDora, her parents, brother, aunt, uncle, and two cousins lived together in her grandfather's home in Essen, Germany. The Ungers were an observant Jewish family, and when Dora was 8, she began to regularly attend meetings of Brit HaNoar, a religious youth organization. 1933-39: In October 1938 a teacher, with tears in her eyes, came to Dora at the municipal pool, saying "Jews cannot swim here anymore." Just weeks later, on November 9, Jews were arrested and their property destroyed. A neighbor tried to…

-
Jeno Nemeth
ID CardJeno moved to Szentes from a tiny farming community near the city of Szolnok, where he and his two brothers had been born to Jewish parents. Jeno owned a store that carried groceries and hardware items. He lived in the southeast Hungarian town of Szentes. Jeno and his wife, Juliana, had two married daughters, Barbara and Margit. Their son, Desider, was a dentist in Szentes. 1933-39: Jeno and his wife work hard in their store. The Depression of the 1930s was devastating, but things are starting to get a…

-
Collaboration
ArticleTo perpetrate the Holocaust, Nazi Germany relied on the help of allies and collaborators from across Europe, including governments, institutions, and individuals.

-
Hidden Children: Hardships
ArticleParents, children, and rescuers faced daunting challenges once the decision was made for a child to go into hiding during the Holocaust.

-
Klaus Barbie: The Butcher of Lyon
ArticleKlaus Barbie, chief of the Gestapo in Lyon, France, was nicknamed the "Butcher of Lyon" for his brutal actions towards Jews and members of the French Resistance.
-
Brandenburg T4 Facility
ArticleBrandenburg was one of six killing centers the Nazis established to murder patients with disabilities under the so-called "euthanasia" program.
-
The Rescue Mission of Gilbert and Eleanor Kraus
ArticleIn the spring of 1939, Gilbert and Eleanor Kraus rescued 50 Jewish children from Vienna, Austria, by bringing them to the United States. Learn about their mission.

-
Kristallnacht
ArticleOn November 9–10, 1938, the Nazi regime coordinated a wave of antisemitic violence. This became known as Kristallnacht or the "Night of Broken Glass." Learn more

-
Book Burning
ArticleBook burning is the ritual destruction by fire of books or other written materials. The Nazi burning of books in May 1933 is perhaps the most famous in history. Learn more.

-
Eleanor Roosevelt
ArticleEleanor Roosevelt, longest serving First Lady in US history, used her social and political influence to intervene on behalf of refugees before and during WWII.

-
"Kristallnacht": nationwide pogrom
MapKristallnacht—literally, "Crystal Night"—is usually translated from German as the "Night of Broken Glass." It refers to the violent anti-Jewish pogrom of November 9 and 10, 1938. The pogrom occurred throughout Germany, which by then included both Austria and the Sudetenland region of Czechoslovakia. Hundreds of synagogues and Jewish institutions all over the German Reich were attacked, vandalized, looted, and destroyed. Many were set ablaze. Firemen were instructed to let the synagogues burn but to…
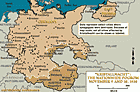
-
The Holocaust and World War II: Key Dates
ArticleRead a detailed timeline of the Holocaust and World War II. Learn about key dates and events from 1933-45 as Nazi antisemitic policies became more radical.

-
Erwin Rommel
ArticleErwin Rommel was commander of the German Afrika Korps in North Africa during WWII. Learn about Rommel's military career, death, and ongoing questions around his commitment to Nazism.

-
Genocide Timeline
ArticleKey dates in the use of the term genocide as part of the political, legal, and ethical vocabulary of responding to widespread threats of violence against groups.

-
Adolf Hitler: Key Dates
ArticleLearn about some key dates in the life of Adolf Hitler, one of Europe's most ruthless dictators, who led the Nazis from 1921 and Germany from 1933-45.

-
Subsequent Nuremberg Proceedings, Case #9, The Einsatzgruppen Case
ArticleThe Einsatzgruppen Case was Case #9 of 12 Subsequent Nuremberg Proceedings against leading German industrialists, military figures, SS perpetrators, and others.

-
Armband for "Foreign Pao Chia Vigilance Corps Pao"
ArtifactIdentifying armband worn by Pao Chia member. In 1942 the Japanese in Shanghai established self-policing units, Pao Chia, composed of all men, foreigners and Chinese, aged 20 to 45. In the designated area, male refugees served several hours weekly in rotating shifts as guards for buildings and ghetto entrances where they examined passes. Despite the Japanese use of the Pao Chia to help police the ghetto, it was relatively easy to leave the "designated area," which was not walled in. Individuals who did so,…

-
Einsatzgruppen in Liepaja, Latvia
FilmGerman Einsatzgruppen operated in German-occupied territories in eastern Europe during World War II. This rare footage shows a unit during a massacre in Liepaja, Latvia. The film was taken, contrary to orders, by a German soldier. Before the war, the Jewish population of Liepaja stood at more than 7,000 residents. Einsatzgruppen shot almost the entire Jewish population of the town. When the Soviet army liberated the city in 1945, just 20 to 30 Jews remained. Einsatzgruppen carried out various security…

-
Reinhard Heydrich: Key Dates
ArticleKey dates in the life of Reinhard Heydrich, chief of the Reich Security Main Office, the SS and police agency most directly concerned with implementing Final Solution.

-
German Railways and the Holocaust
ArticleThe European rail network played a crucial role in the implementation of the Final Solution. Millions were deported by rail to killing centers and other sites.

-
Battle of the Bulge
ArticleThe Battle of the Bulge was a failed German counter-offensive against the Allied armies. Learn more about the Battle of the Bulge and its impact on WWII.

-
The Wannsee Conference and the "Final Solution"
ArticleThe Wannsee Conference was a high-level meeting of Nazi Party and German State officials to coordinate “the Final Solution of the Jewish Question.” Learn more.

-
Ravensbrück: Key Dates
ArticleExplore a timeline of the history of the Ravensbrück camp in the Nazi camp system from its establishment in 1938 until the last of the Ravensbrück trials in 1966.

-
Sachsenhausen: Liberation and Postwar Trials
ArticleLearn about the death march of prisoners from the Sachsenhausen camp, liberation of the remaining prisoners, and postwar trials of camp staff.

-
The Nuremberg Courtroom
ArticleThe International Military Tribunal took place in the Palace of Justice at Nuremberg, the only undamaged facility extensive enough to house the trials.

-
Bayer
ArticleAs part of the IG Farben conglomerate, which strongly supported the Third Reich, the Bayer company was complicit in the crimes of Nazi Germany. Learn more.
-
Santa Maria di Bagni Displaced Persons Camp
ArticleAfter WWII, many Holocaust survivors, unable to return to their homes, lived in displaced persons camps in Germany, Austria, and Italy. Read about Santa Maria di Bagni DP camp.

-
"Aryanization"
ArticleBy the process of "Aryanization" in Nazi Germany from 1933 to 1945, Jewish-owned businesses and property were transferred to non-Jews. Learn more.

-
UN Convention on the Prevention and Punishment of Genocide
Timeline EventJanuary 12, 1951. On this date, the United Nations Convention on the Prevention and Punishment of Genocide entered into force.

-
People crowded around an antisemitic "Pesti Ujság" newspaper display
PhotoVisitors view the exhibition of the Arrow Cross newspaper, Pesti Ujság, at the International Fair in Budapest. The headline reads: "For a Hungary without Jews." Budapest, Hungary, approximately 1941-1942. The Arrow Cross was Hungary's largest fascist political movement after 1935. In the 1939 parliamentary elections it won over 20% of the vote and had more than 250,000 members. Its ideology was ultra-nationalistic and fiercely antisemitic. The Arrow Cross viewed Jews as an "anti-national" "race"…

-
The 11th Armored Division during World War II
ArticleThe 11th Armored Division participated in major WWII campaigns and is recognized for liberating Mauthausen and Gusen in 1945.

-
The 90th Infantry Division during World War II
ArticleThe 90th Infantry Division participated in major WWII campaigns and is recognized for liberating the Flossenbürg concentration camp in 1945.
-
Lackenbach (Roma internment and transit camp)
ArticleThe Lackenbach internment and transit camp for Roma, located in what had been eastern Austria, was a departure point for deportations to Lodz and Auschwitz.

-
Air war in Flanders: Western Campaign
FilmThe Junkers (Ju) 87, known as the "Stuka," spearheaded the Blitzkrieg ("lightning war") attacks that were decisive in the western campaign in 1940. Stuka dive-bombers closely supported German forces on the ground. They destroyed enemy strong points, aircraft, and airfields, and spread panic in rear areas. Although slow and easily shot down by Allied fighters, the Stukas proved devastatingly effective in the German invasions of Poland and western Europe, where Germany enjoyed air superiority. Stuka…

-
Soviet prisoners of war wait for rations
PhotoSoviet prisoners of war wait for food in Stalag (prison camp) 8C. More than 3 million Soviet soldiers died in German custody, mostly from malnutrition and exposure. Zagan, Poland, February 1942. Second only to the Jews, Soviet prisoners of war were the largest group of victims of Nazi racial policy.

-
Abdol Hossein Sardari (1895–1981)
ArticleIranian diplomat Abdol Hossein Sardari gave critical assistance to Iranian Jews in occupied France (1940-1944) to protect them from Nazi persecution.
-
Timeline of the German Military and the Nazi Regime
ArticleKey dates illustrating the relationship between Germany’s professional military elite and the Nazi state, and the German military’s role in the Holocaust.

-
1943: Key Dates
ArticleExplore a timeline of key events during 1943 in the history of Nazi Germany, World War II, and the Holocaust.

-
International Military Tribunal: The Defendants
ArticleListing of the 24 leading Nazi officials indicted at the International Military Tribunal at Nuremberg. Learn about the defendants and the charges against them.

-
Charles E. Coughlin
ArticleCharles Coughlin, Catholic priest and populist leader, promoted antisemitic and pro-fascist views. In the 1930s, he was one of the most influential public figures in the US.

-
Susan Bluman describes the German invasion of Poland
Oral HistorySusan was 19 years old when Germany invaded Poland in September 1939. Her boyfriend, Nathan, was in Lvov when the Soviet Union occupied eastern Poland. Nathan sent a guide to Warsaw to bring Susan to the Soviet zone of occupied Poland. Her parents reluctantly agreed after Susan promised to return to Warsaw within two weeks. Upon her arrival in Lvov, Susan married Nathan. The couple then fled across the Lithuanian border to Vilna, where they stayed for a year. They received a visa for transit through Japan…

-
Kristallnacht
Timeline EventNovember 9, 1938. On this date, the Nazi regime coordinated a wave of antisemitic violence in Nazi Germany. This became known as Kristallnacht or the "Night of Broken Glass."

-
Sam Itzkowitz describes the gas chambers in Auschwitz
Oral HistoryThe Germans invaded Poland in September 1939. When Makow was occupied, Sam fled to Soviet territory. He returned to Makow for provisions, but was forced to remain in the ghetto. In 1942, he was deported to Auschwitz. As the Soviet army advanced in 1944, Sam and other prisoners were sent to camps in Germany. The inmates were put on a death march early in 1945. American forces liberated Sam after he escaped during a bombing raid.

-
Janka Glueck Gruenberger
ID CardJanka was one of seven children raised in a Yiddish-and Hungarian-speaking household by religious Jewish parents in the city of Kosice. In 1918, when she was 20 years old, Kosice changed from Hungarian to Czechoslovak rule. Three years later, Janka married Ludovit Gruenberger, and their three children were born Czech citizens. 1933-39: Janka was an accomplished milliner, and she helped her husband run a tailoring business from their apartment. Like many Jews in Kosice, Janka and Ludovit were upset when…

-
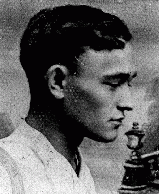
Mendel Grynberg
ID CardMendel was raised in a large, Yiddish-speaking, religious Jewish family in Sokolow Podlaski, a manufacturing town in central Poland with a large Jewish population of about 5,000. Upon completing school, Mendel worked as a shoemaker. He was also active in a local Zionist organization. 1933-39: Mendel was married and had a family when the Germans invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. Aircraft bombed the town's market and other civilian targets before victorious German troops marched into Sokolow Podlaski on…
-
Grietje Polak
ID CardGrietje was born to a large religious Jewish family in Amsterdam. When she was in her mid-20's, she married Frederik Polak, an accountant. The Polaks had a son, Jacob, and three daughters, Julia, Betty and Liesje. They lived in simple quarters on the second floor of a house. 1933-39: Creating an atmosphere of Jewish observance in the home was important to Grietje and her husband. They loved to celebrate the Sabbath and the Jewish holidays with their four children. Grietje taught shorthand and needlepoint…

-
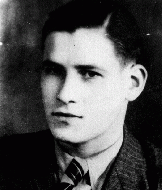
Wolfgang Kusserow
ID CardWhen Wolfgang was an infant, his parents became Jehovah's Witnesses. His father moved the family to the small Westphalian town of Bad Lippspringe when Wolfgang was 9. Their home became the headquarters of a new Jehovah's Witness congregation. Wolfgang and his ten brothers and sisters grew up studying the Bible daily. 1933-39: The Kusserows were under close scrutiny by the Nazi secret police because of their religion. As a Jehovah's Witness, Wolfgang believed that his highest allegiance was to God and His…
-
Gregor Wohlfahrt
ID CardGregor was the second of six children born to Catholic parents in a village in the part of Austria known as Carinthia. His father was a farmer and quarryman. Disillusioned with Catholicism, his parents became Jehovah's Witnesses and raised their children according to that religion. As a boy, Gregor loved mountain climbing and skiing. 1933-39: Gregor attended school and worked as a waiter. The situation for Jehovah's Witnesses worsened after Germany annexed Austria in March 1938; Witnesses refused to swear…

