<< Previous | Displaying results 151-175 of 981 for "" | Next >>
-
SS: Decline, Disintegration, and Trials
ArticleIn 1945, the power and influence of the SS in Nazi Germany started to decline. Learn more about the subsequent disintegration and postwar trials.

-
Waffen-SS
ArticleThe Waffen-SS was the military branch of the SS in Nazi Germany. During World War II, they took part in most military campaigns.

-
Reinhard Heydrich: In Depth
ArticleReinhard Heydrich, Reich Security Main Office chief, was one of the main architects of the “Final Solution," the Nazi plan to murder the Jews of Europe.

-
Leni Riefenstahl
ArticleLeni Riefenstahl was a German dancer, actress, and film director best known for her imposing propaganda films in support of the National Socialist (Nazi) Party.

-
Adolf Eichmann
ArticleCharged with managing the mass deportation of Jews to ghettos and killing centers, Adolf Eichmann was a key figure in the "Final Solution."

-
Adolf Eichmann: Key Dates
ArticleAdolf Eichmann was a key figure in implementing the “Final Solution,” the Nazi plan to kill Europe's Jews. Learn more through key dates and events.

-
Perpetrators
ArticleThe “Final Solution” was perpetrated by the SS along with other Nazi institutions and professionals. Learn more about key perpetrators of the Holocaust.

-
Adolf Hitler: Early Years, 1889–1913
ArticleUnder Adolf Hitler, the Nazi regime would be responsible for the murder of 6 million Jews and millions of other victims. Learn about Hitler's early years.

-
Adolf Hitler and World War I: 1913–1919
ArticleLearn about Adolf Hitler's experiences during World War I and his ideological development after the war.

-
Types of Ghettos
ArticleGhettos separating Jews from the rest of the population were part of the Nazi plan to destroy Europe's Jews. Learn about three types of ghettos: closed, open, and destruction.

-
The Nazi Olympics Berlin 1936: Inauguration of the Olympic Torch Relay
ArticleThe 1936 Olympics were the first to employ the torch relay. Learn more about this new ritual, Nazi propaganda, and the Olympic Games in Berlin, Germany.

-
Abdol Hossein Sardari (1895–1981)
ArticleIranian diplomat Abdol Hossein Sardari gave critical assistance to Iranian Jews in occupied France (1940-1944) to protect them from Nazi persecution.
-
Commissar Order
ArticleThe Commissar Order was issued by the German Armed Forces High Command on June 6, 1941. It ordered soldiers to shoot Soviet Communist Party officials taken prisoner.

-
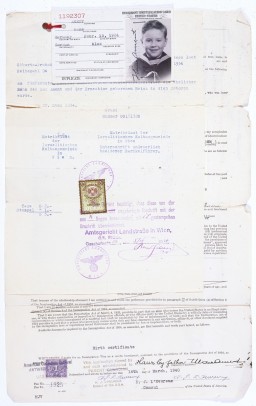
Documents Required to Obtain a Visa
ArticleGerman Jews trying to immigrate to the US in the late 1930s met extreme bureaucratic hurdles, including documentation that was often virtually impossible to obtain.
-
Victims of the Nazi Era: Nazi Racial Ideology
ArticleThe Nazis carried out genocide against Europe’s Jews and persecuted and murdered other groups based on racial theories. Learn about the history of these murderous ideas.

-
Krakow Ghetto: Key Dates
ArticleExplore a timeline of key events during the history of the Krakow ghetto in German-occupied Poland.

-
Theresienstadt: Key Dates
ArticleExplore key dates in the history of the Theresienstadt camp/ghetto, which served multiple purposes during its existence from 1941-45.

-
Theresienstadt: Cultural Life
ArticleDespite terrible living conditions and the constant threat of deportation, there was a highly developed cultural life in the Theresienstadt camp-ghetto. Learn more.

-
Theresienstadt: SS and Police Structure
ArticleLearn more about the unique SS and police structure of the Theresienstadt “camp-ghetto” during World War II.
-
Theresienstadt: Red Cross Visit
ArticleLearn more about the Danish Red Cross visit to Theresienstadt and the Nazi attempt to clean and hide the true conditions of the camp.

-
Theresienstadt: Transit Camp for Czech Jews
ArticleLearn more about Theresienstadt’s function as a transit camp and the deportation of Czech Jews during World War II.

-
Night and Fog Decree
ArticleThe "Nacht und Nebel" decree allowed German authorities to capture without trace ("by night and fog") and try individuals alleged to be "endangering German security."

-
Theresienstadt: "Retirement Settlement" for German and Austrian Jews
ArticleIn 1942, German authorities began to deport German and Austrian Jews to Theresienstadt. Learn about the administration of the camp-ghetto and Jews’ experiences.

-
Tehran Children
ArticleLearn about the “Tehran Children,” a group of Polish-Jewish refugees. In 1942, they were resettled from the Soviet Union to Palestine via Iran.

-

