You searched for: FACEBOOK代全世界推广开户【TG飞机:@bapingseo】谷歌seo网站推荐【TG电报:@bapingseo】尼日利亚做广告【Telegram:@bapingseo】128棋牌下载hi合乐888手机?20220707j5C1Wb.html
<< Previous | Displaying results 1251-1300 of 1613 for "FACEBOOK代全世界推广开户【TG飞机:@bapingseo】谷歌seo网站推荐【TG电报:@bapingseo】尼日利亚做广告【Telegram:@bapingseo】128棋牌下载hi合乐888手机?20220707j5C1Wb.html" | Next >>
-
The German Military and the Holocaust
ArticleThe German military played a vital role in the consolidation of Nazi power and persecution and mass murder of Jews and other groups. Learn more

-
Treblinka
ArticleTreblinka was one of three killing centers in Operation Reinhard, the SS plan to murder almost two million Jews living in the German-administered territory of occupied Poland.

-
Hodonín U Kunštátu (Hodonín bei Kunstadt) (Roma camp)
ArticleIn March 1942, the Hodonin camp was classified as a camp for Roma. It was a transfer station during deportation to Auschwitz-Birkenau. Learn about the camp and its history.

-
The United States: Isolation-Intervention
ArticleWhen WWII began, most Americans wanted the US to stay isolated from the war. From December 1941, the majority rallied in support of intervention to defeat the Axis powers.

-
Quakers
ArticleThe American Friends Service Committee, a Quaker relief organization, helped thousands of people before, during, and after World War II. Learn about its refugee aid work.

-
Stanisławów
ArticleLearn more about the history of Stanisławów during the Holocaust and World War II.
-
United States Immigration and Refugee Law, 1921–1980
ArticleUS immigration and refugee laws and policies evolved in response to World War I, the 1918 influenza pandemic, and World War II and the Holocaust. Learn more.

-
The Nazi Olympics Berlin 1936
ArticleThe 1936 Olympics in Berlin under Adolf Hitler's Nazi dictatorship were more than just a worldwide sporting event, they were also a show of Nazi propaganda.

-
President Truman attends Potsdam Conference
FilmAfter the sudden death of Franklin D. Roosevelt in April 1945, Vice President Harry S. Truman became president of the United States. Here, President Truman meets with the heads of state of the Soviet Union and Great Britain (Joseph Stalin, Winston S. Churchill, and later Clement Attlee) in Potsdam, near Berlin, to discuss the future of defeated Germany. The leaders agreed to the partition of Germany and Berlin, Germany's capital city, into four zones of occupation: British, French, American, and Soviet.…

-
Bella Jakubowicz Tovey describes a meeting between her father and the Jewish council leader in Sosnowiec
Oral HistoryBella was the oldest of four children born to a Jewish family in Sosnowiec. Her father owned a knitting factory. After the Germans invaded Poland in 1939, they took over the factory. The family's furniture was given to a German woman. Bella was forced to work in a factory in the Sosnowiec ghetto in 1941. At the end of 1942 the family was deported to the Bedzin ghetto. Bella was deported to the Graeben subcamp of Gross-Rosen in 1943 and to Bergen-Belsen in 1944. She was liberated in April 1945.

-
Max Karl Liebmann describes arrival at and conditions in the Gurs camp
Oral HistoryBecause he was Jewish, Max could not join the army when World War II began. Instead, he had to perform labor service. In October 1940, Max and his mother were deported to the Gurs camp in France. In Gurs, Max met his future wife, Hanne. In 1941, with the help of the Children's Aid Society (Oeuvre de Secours aux Enfants; OSE), Hanne left the camp. Max followed in July 1942. He escaped to Switzerland through the French Alps and was in internment and refugee camps throughout the war. Hanne reached Switzerland…

-
Ernest Koenig describes forced labor in the Laurahuette subcamp of the Auschwitz camp
Oral HistoryErnest was studying in Paris, France, until February 1939, when he returned to Brno, Czechoslovakia. The Germans occupied the latter region soon thereafter, but Ernest managed to return to France. He joined a Czech unit in the French army from October 1939 until the fall of France in May 1940. He made his way to unoccupied France, where he taught for a while. He then went to Grenoble, and again taught, but was arrested because he did not have the appropriate papers. Ernest was interned in Le Vernet camp…

-
Julian Noga describes conditions in Flossenbürg
Oral HistoryJulian's Catholic parents had settled in the United States, but his mother returned to Poland. In 1939, Julian was deported to Austria to do farm labor after he was caught for hiding a rifle. On the farm he met the landowner's daughter, Frieda, his future wife. He was arrested in 1941 because relationships between Austrians and Poles were considered illegal and in 1942 he was deported to the Flossenbürg camp in Germany. During a forced march in 1945, he was liberated by US forces. Julian and Freida…

-
Abraham Lewent recalls how, while ill with typhoid, he persuaded the Skarzysko doctor that he was fit to work
Oral HistoryLike other Jews, the Lewents were confined to the Warsaw ghetto. In 1942, as Abraham hid in a crawl space, the Germans seized his mother and sisters in a raid. They perished. He was deployed for forced labor nearby, but escaped to return to his father in the ghetto. In 1943, the two were deported to Majdanek, where Abraham's father died. Abraham later was sent to Skarzysko, Buchenwald, Schlieben, Bisingen, and Dachau. US troops liberated Abraham as the Germans evacuated prisoners.

-
Susan Bluman describes obtaining a transit visa from Chiune Sugihara
Oral HistorySusan was 19 years old when Germany invaded Poland in September 1939. Her boyfriend, Nathan, was in Lvov when the Soviet Union occupied eastern Poland. Nathan sent a guide to Warsaw to bring Susan to the Soviet zone of occupied Poland. Her parents reluctantly agreed after Susan promised to return to Warsaw within two weeks. Upon her arrival in Lvov, Susan married Nathan. The couple then fled across the Lithuanian border to Vilna, where they stayed for a year. They received a visa for transit through Japan…

-
Bart Stern describes the role of friendships in survival at Auschwitz
Oral HistoryFollowing the German occupation of Hungary in March 1944, Bart was forced into a ghetto established in his home town. From May to July 1944, the Germans deported Jews from Hungary to the Auschwitz killing center in occupied Poland. Bart was deported by cattle car to Auschwitz. At Auschwitz, he was selected to perform forced labor, drilling and digging in a coal mine. As Soviet forces advanced toward the Auschwitz camp in January 1945, the Germans forced most of the prisoners on a death march out of the…

-
Leo Melamed describes saying goodbye to father as he fled Bialystok
Oral HistoryLeo was seven years old when Germany invaded Poland in September 1939. Before the war, Leo's father was a mathematics teacher and member of the Bialystok City Council. Fearing arrest, Leo's father fled Bialystok for Vilna just before the German occupation. Leo and his mother eventually joined his father in Vilna. After the Soviets occupied Vilna, Leo's father obtained transit visas to Japan. The family left Vilna in December 1940, traveled across the Soviet Union on the Trans-Siberian Express, and arrived…

-
David (Dudi) Bergman describes being rescued by inmates before he could be taken to the Dachau crematorium
Oral HistoryThe Germans occupied David's town, previously annexed by Hungary, in 1944. David was deported to Auschwitz and, with his father, transported to Plaszow. David was sent to the Gross-Rosen camp and to Reichenbach. He was then among three of 150 in a cattle car who survived transportation to Dachau. He was liberated after a death march from Innsbruck toward the front line of combat between US and German troops.

-
Chaim Engel describes plans for the Sobibor uprising
Oral HistoryThe Germans captured Chaim, a soldier in the Polish army, as they invaded Poland in 1939. They first sent Chaim to Germany for forced labor, but as a Jewish prisoner of war, he was returned to Poland. Ultimately, Chaim was deported to the Sobibor camp, where the rest of his family died. In the 1943 Sobibor uprising, Chaim killed a guard. He escaped with his girlfriend, Selma, whom he later married. A farmer hid them until liberation in June 1944. In this clip, Chaim refers to [Gustav] Wagner, Sobibor's…

-
Thomas Buergenthal describes the charges brought at the International Military Tribunal at Nuremberg
Oral HistoryJudge Thomas Buergenthal was one of the youngest survivors of the Auschwitz and Sachsenhausen concentration camps. He immigrated to the United States at the age of 17. Judge Buergenthal devoted his life to international and human rights law. He served as chairman of the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum’s Committee on Conscience; was named the Lobingier Professor of Comparative Law and Jurisprudence at the George Washington University Law School; and served for a decade as the American judge at…

-
Thomas Buergenthal describes differing perspectives on international justice
Oral HistoryJudge Thomas Buergenthal was one of the youngest survivors of the Auschwitz and Sachsenhausen concentration camps. He immigrated to the United States at the age of 17. Judge Buergenthal devoted his life to international and human rights law. He served as chairman of the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum’s Committee on Conscience; was named the Lobingier Professor of Comparative Law and Jurisprudence at the George Washington University Law School; and served for a decade as the American judge at…

-
Thomas Buergenthal describes the plight of refugees today
Oral HistoryJudge Thomas Buergenthal was one of the youngest survivors of the Auschwitz and Sachsenhausen concentration camps. He immigrated to the United States at the age of 17. Judge Buergenthal devoted his life to international and human rights law. He served as chairman of the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum’s Committee on Conscience; was named the Lobingier Professor of Comparative Law and Jurisprudence at the George Washington University Law School; and served for a decade as the American judge at…

-
Gerda Haas describes postwar reunion with her father in the United States
Oral HistoryGerda was raised in a religious family in the small town of Ansbach, Germany, where her father was the Jewish butcher. She attended German schools until 1936, and then moved to Berlin to attend a Jewish school. She returned to her hometown after Kristallnacht in November 1938. Her family was then ordered to move to Munich, and in July 1939 her father left for England and then the United States. He was unable to arrange for the rest of his family to join him. Gerda moved to Berlin in 1939 to study nursing.…

-
Abraham Bomba describes the Treblinka gas chambers
Oral HistoryExcerpt from Holocaust survivor Abraham Bomba's oral history testimony describing gas chambers at the Treblinka killing center.

-
Peter Becker describes indoctrination and being in the Hitler Youth
Oral HistoryPeter was six years old when his mother enrolled him in a special Hitler boarding school for future Nazi Party officials in 1935. He studied traditional academic subjects, but was constantly exposed to Nazi ideas and prepared for a military life. Peter was also a member of the Hitler Youth. He came to believe in Hitler as the savior of Germany. Peter would later describe his indoctrination as a subtle process. It took two years after the war had ended for Peter to come to terms with the atrocities that the…

-
Emanuel (Manny) Mandel describes the "Kasztner train" journey to Bergen-Belsen
Oral HistoryEmanuel's father was a cantor who became, soon after Emanuel was born, one of the chief cantors in Budapest. Germany occupied Hungary in March 1944. Systematic deportations of Jews from Hungary to the Auschwitz camp in occupied Poland began in May 1944. Emanuel and his mother were part of the train, organized by Zionist activist Rezso Kasztner, of over 1,600 Hungarian Jews who were to be sent to neutral countries as part of an exchange program. The train arrived at the Bergen-Belsen camp, where the…

-
Wilek (William) Loew describes Budapest after he escaped from the Lvov ghetto and before the German occupation of Hungary
Oral HistoryWilek was the son of Jewish parents living in the southeastern Polish town of Lvov. His family owned and operated a winery that had been in family hands since 1870. Wilek's father died of a heart attack in 1929. Wilek entered secondary school in 1939. Soon after he began school, World War II began with the German invasion of Poland. Lvov was in the part of eastern Poland annexed by the Soviet Union. Although the Soviets took over Wilek's home and the family business, Wilek was able to continue his…

-
Wilek (William) Loew describes Jewish life in prewar Lvov, including restrictions on admission to schools
Oral HistoryWilek was the son of Jewish parents living in the southeastern Polish town of Lvov. His family owned and operated a winery that had been in family hands since 1870. Wilek's father died of a heart attack in 1929. Wilek entered secondary school in 1939. Soon after he began school, World War II began with the German invasion of Poland. Lvov was in the part of eastern Poland annexed by the Soviet Union. Although the Soviets took over Wilek's home and the family business, Wilek was able to continue his…

-
Wilek (William) Loew describes political prison in Budapest after the Germans arrested him as a Polish spy
Oral HistoryWilek was the son of Jewish parents living in the southeastern Polish town of Lvov. His family owned and operated a winery that had been in family hands since 1870. Wilek's father died of a heart attack in 1929. Wilek entered secondary school in 1939. Soon after he began school, World War II began with the German invasion of Poland. Lvov was in the part of eastern Poland annexed by the Soviet Union. Although the Soviets took over Wilek's home and the family business, Wilek was able to continue his…

-
The Weimar Republic
ArticleThe Weimar Republic was a liberal democratic republic founded in Germany in the aftermath of WWI. Learn about the era’s political and economic crises and social trends.

-
Chelmno
ArticleThe Chelmno killing center was the first stationary facility where poison gas was used for mass murder of Jews. Killing operations began there in December 1941.

-
Concentration Camps, 1933–39
ArticleLearn about early concentration camps the Nazi regime established in Germany, and the expansion of the camp system during the Holocaust and World War II.

-
Oradour-sur-Glane
ArticleIn 1944, Waffen-SS troops massacred residents of Oradour-sur-Glane, a small village in France. Learn about the German occupation and destruction of the village.

-
Sobibor
ArticleTo carry out the mass murder of Europe's Jews, the Nazis established killing centers that used assembly-line methods of murder. Sobibor was among these facilities.

-
Mannschafts-Stammlager (Stalag) IX B
ArticleIn 1939, the Nazis established the Mannschafts-Stammlager (Stalag) IX B camp in Germany. Learn more about the camp’s history, prisoners, and liberation.
-
Anti-Jewish Legislation in North Africa
ArticleThe Vichy regime introduced race laws to the North African territories in October of 1940. Learn about the impact of the laws on the region’s Jewish people.

-
Wagner-Rogers Bill
ArticleThe Wagner-Rogers Bill proposed admitting 20,000 refugee children to the US from the Greater German Reich in 1939–40, but did not become law. Learn more

-
Japanese American Relocation
ArticleLearn more about the forcible relocation of some 120,000 people of Japanese descent living in the US to “relocation centers.”

-
The Rescue Mission of Gilbert and Eleanor Kraus
ArticleIn the spring of 1939, Gilbert and Eleanor Kraus rescued 50 Jewish children from Vienna, Austria, by bringing them to the United States. Learn about their mission.

-
Lidice: The Annihilation of a Czech Town
ArticleGerman forces razed the town of Lidice in June 1942 in retaliation for the death of Nazi leader Reinhard Heydrich. Learn about the assassination and reprisal.

-
The Krakow (Cracow) Ghetto during the Holocaust
ArticleThe Krakow ghetto in German-occupied Poland held over 15,000 Jews. Learn more about Krakow and the ghetto’s history during the Holocaust and WWII.

-
Vita Rivkina
ID CardBecause both of her parents had died by the time Vita was 5 years old, she went to live with her cousins. At the age of 18, Vita married Iosif Rivkin, and the couple moved to Minsk where they raised three daughters--Hacia, Dora and Berta. 1933-39: By the early 1930s, the Rivkin family lived on Novomesnitskaya Street in central Minsk, near the Svisloch River. In the 1930s the girls attended Soviet state schools and were members of the Soviet youth organization, Young Pioneers. By the late 1930s Minsk was…

-
Joseph Gani
ID CardJoseph and his family lived in Preveza, a town with a Jewish population of 300 that was located on the Ionian seashore. Joseph's father had a small textile shop. The Ganis were of Romaniot descent, Jews whose ancestors had lived in Greece and the Balkans for more than a thousand years. 1933-39: Joseph attended Greek public school in Preveza. He also received a religious education; the local rabbi would come to the public school for several hours a week to give religious instruction to the Jewish students.…
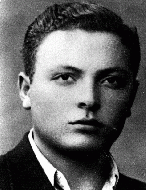
-
Betje Jakobs
ID CardBetje and her sister Saartje were born to Jewish parents in the town of Zwolle in the Netherlands' north central province of Overijssel. Betje was known affectionately as "Bep" to her friends. The Jakobs family owned a successful sporting goods store. 1933-39: As a young girl, Betje enjoyed playing the piano, knitting and tennis. At age 16, while still in secondary school, she began to date Maurits Wijnberg, a boy two years her senior, whose family owned Zwolle's Hotel Wijnberg. 1940-42: The Germans…
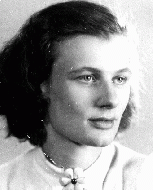
-
Robert Kulka
ID CardRobert was the son of Jewish parents, Leopold and Florentina Kulka, and was raised in the Moravian town of Olomouc. After completing secondary school, he attended a business school until 1909. He began a business in Olomouc and in 1933 he married Elsa Skutezka from the Moravian city of Brno. The couple made their home in Olomouc. 1933-39: The Kulkas' son, Tomas, was born a year and a day after they were married. In 1937 Elsa's father passed away and the Kulkas moved to Brno, where Elsa and her husband…

-
Alida Nathans Wijnberg
ID CardAlida was the oldest of eight children. Her parents, religious Jews, owned a textile business in the small town of Vries. As a teenager, Alida helped her family sell textiles to the local farmers, carrying the goods in a suitcase attached to the handlebars of her bicycle. She married Samuel Wijnberg, and the couple had three sons and a daughter. 1933-39: The Wijnbergs owned and lived in a kosher hotel in the town of Zwolle. It was the only kosher hotel in the region, so many Jewish businessmen and cattle…

-
Shlomo Reich
ID CardShlomo was one of seven children born in Lodz to the Reich family. The Reichs were a religious Jewish family, and Shlomo's Hasidic father wore earlocks and a traditional fur hat. After public school every day, Shlomo attended the Ostrovtze Yeshiva, a rabbinical academy where he studied Jewish holy texts. Shlomo's father owned a shoelace factory. 1933-39: The Germans invaded Lodz in September 1939 and began to institute anti-Jewish measures. Jews were not allowed to use public transportation, to leave the…

-
Grietje Polak
ID CardGrietje was born to a large religious Jewish family in Amsterdam. When she was in her mid-20's, she married Frederik Polak, an accountant. The Polaks had a son, Jacob, and three daughters, Julia, Betty and Liesje. They lived in simple quarters on the second floor of a house. 1933-39: Creating an atmosphere of Jewish observance in the home was important to Grietje and her husband. They loved to celebrate the Sabbath and the Jewish holidays with their four children. Grietje taught shorthand and needlepoint…

-
Daniel Judelowitz
ID CardDaniel was born to a Jewish family in the Latvian town of Aizpute. There, Daniel met and married Bella Hirschorn and together they opened a bakery-grocery in the town. In the 1920s they moved to Liepaja, on the Baltic coast, and opened a dry-goods store. The couple had 10 children, one of whom died in infancy. 1933-39: The Judelowitzes' store sold fabric, accessories and various clothing items from buttons to shirts and stockings. After Daniel and Bella retired, their daughters took over the business. In…

-
Notice of Gregor Wohlfahrt's execution
DocumentAuthorities in Berlin, Germany, sent this notice to Barbara Wohlfahrt, informing her of her husband Gregor's execution on the morning of December 7, 1939. Although he was physically unfit to serve in the armed forces, the Nazis tried Wohlfahrt for his religious opposition to military service. As a Jehovah's Witness, Wohlfahrt believed that military service violated the biblical commandment not to kill. On November 8, 1939, a military court condemned Wohlfahrt to beheading, a sentence carried out one month…

