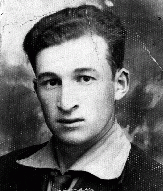You searched for: https://www.duybrand.com/brand-1-c0.html%20t%C3%BAi%20Dior%20sieu%20c?p%20nam%20,%20%C3%81o%20Dior%20sieu%20c?p?www.duybrand.com/brand-1-c0.html?%20Giay%20Dior%20sieu%20c?p%20,%20mu%20dior%20Dior,%20giay%20lu?i%20dior%20nam,%20T%C3%BAi%20c%C3%B4ng%20s?%20Dior%20Like%20Auth%20so%20mi%20dior%20nam
<< Previous | Displaying results 401-450 of 1747 for "https://www.duybrand.com/brand-1-c0.html%20t%C3%BAi%20Dior%20sieu%20c?p%20nam%20,%20%C3%81o%20Dior%20sieu%20c?p?www.duybrand.com/brand-1-c0.html?%20Giay%20Dior%20sieu%20c?p%20,%20mu%20dior%20Dior,%20giay%20lu?i%20dior%20nam,%20T%C3%BAi%20c%C3%B4ng%20s?%20Dior%20Like%20Auth%20so%20mi%20dior%20nam" | Next >>
-
Krakow Ghetto Established
Timeline EventMarch 3-20, 1941. During these dates, German authorities announced, established, and sealed the Krakow ghetto.

-
The 45th Infantry Division during World War II
ArticleThe 45th Infantry Division participated in major WWII campaigns and is recognized for liberating the Dachau concentration camp in 1945.
-
Charles E. Coughlin
ArticleCharles Coughlin, Catholic priest and populist leader, promoted antisemitic and pro-fascist views. In the 1930s, he was one of the most influential public figures in the US.

-
The Rescue Mission of Gilbert and Eleanor Kraus
ArticleIn the spring of 1939, Gilbert and Eleanor Kraus rescued 50 Jewish children from Vienna, Austria, by bringing them to the United States. Learn about their mission.

-
Halle
ArticleHalle an der Saale was a satellite camp of Buchenwald concentration camp. It was established by the Nazis in Saxony, Germany in 1941.
-
Flossenbürg
ArticleLearn about the Flossenbürg camp from its establishment until liberation in April 1945, including conditions, forced labor, subcamps, and death marches.

-
Mannschafts-Stammlager (Stalag) IX B
ArticleIn 1939, the Nazis established the Mannschafts-Stammlager (Stalag) IX B camp in Germany. Learn more about the camp’s history, prisoners, and liberation.
-
Sobibor
ArticleTo carry out the mass murder of Europe's Jews, the Nazis established killing centers that used assembly-line methods of murder. Sobibor was among these facilities.

-
Dawid Sierakowiak
ArticleYoung people's diaries capture some of the most heartbreaking experiences of the Holocaust. Learn about the diary and experiences of David Sierakowiak.

-
Jewish Communities of Prewar Germany
ArticleBefore the Nazi rise to power, Jews represented less than 1% of Germany's population. Learn more about Jewish communities in Germany before the Holocaust.

-
Odon Jerzy Wos
ID CardOdon was the third of four children born to Roman Catholic parents in Warsaw, Poland's capital. His father had worked for the Polish merchant marine before starting his own textile business in 1930. When Odon was 8, the family moved to a comfortable apartment located near the Royal Castle and Vistula River. In 1932 Odon began attending grade school. 1933-39: In September 1938 Odon began secondary school. Sensing growing danger from Germany, his father advised him to study German in addition to French. On…
-
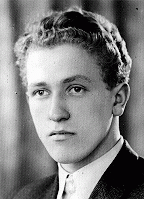
Mieczyslaw (Marek) Madejski
ID CardMieczyslaw was the eldest of three sons born to well-to-do Roman Catholic parents in Poland's capital of Warsaw. His father was a real estate developer and his mother was a housewife. Mieczyslaw, or Mieteck as he was nicknamed, began attending public elementary school in 1930 when he was 7 years old. 1933-39: Mieczyslaw's father urged him to study either German or Russian because he thought it was likely that there would be a German or Soviet invasion. Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. During…

-
Sobibor: Key Dates
ArticleExplore a timeline of key events in the history of the Sobibor killing center in the General Government, the German-administered territory of occupied Poland.

-
Ravensbrück
ArticleLearn about conditions and the treatment of prisoners in Ravensbrück, the largest concentration camp for women in the German Reich.

-
The German Churches and the Nazi State
ArticleHow did Christians and their churches in Germany respond to the Nazi regime and its laws, particularly to the persecution of the Jews? Learn more.

-
International Military Tribunal at Nuremberg
ArticleThe International Military Tribunal (IMT) opened in Nuremberg within months of Germany’s surrender. Learn about the judges, defendants, charges, and legacies.

-
What conditions, ideologies, and ideas made the Holocaust possible?
Discussion QuestionThe leaders of Nazi Germany, a modern, educated society, aimed to destroy millions of men, women, and children because of their Jewish identity. Understanding this process may help us to better understand the condit...

-
Siegfried Halbreich describes arrival at and brutality in the Gross-Rosen camp
Oral HistoryAfter Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939, Siegfried fled with a friend. They attempted to get papers allowing them to go to France, but were turned over to the Germans. Siegfried was jailed, taken to Berlin, and then transported to the Sachsenhausen camp near Berlin in October 1939. He was among the first Polish Jews imprisoned in Sachsenhausen. Inmates were mistreated and made to carry out forced labor. After two years, Siegfried was deported to the Gross-Rosen concentration camp, where he was…

-
Francis Akos describes experiences in the immediate aftermath of the Holocaust
Oral HistoryAfter the Germans occupied Hungary in March 1944, Francis was deported to Neuengamme, a concentration camp located on the outskirts of Hamburg, Germany. Later, as Allied forces advanced, Francis and other prisoners were transported from Neuengamme. They were placed on a cargo ship which sailed into Luebeck Bay, where the prisoners were crowded onto the "Cap Arcona." The "Cap Arcona" and other ships were bombed in early May 1945. Francis was rescued and came ashore in the German town of Neustadt, where…

-
Jacob Wiener
ArticleExplore Jacob Wiener’s biography and learn about his experiences during Kristallnacht in Würzburg, Germany.

-
SS: Decline, Disintegration, and Trials
ArticleIn 1945, the power and influence of the SS in Nazi Germany started to decline. Learn more about the subsequent disintegration and postwar trials.

-
Trawniki
ArticleFrom July 1941-May 1944, the SS camp at Trawniki had several purposes. It is best known as the training site for auxiliary police guards used in Nazi killing centers. Learn more.

-
Wagner-Rogers Bill
ArticleThe Wagner-Rogers Bill proposed admitting 20,000 refugee children to the US from the Greater German Reich in 1939–40, but did not become law. Learn more

-
Theresienstadt: Establishment
ArticleLearn about the establishment of the Theresienstadt camp/ghetto, which served multiple purposes from 1941-45 and had an important propaganda function for the Germans.

-
Wannsee Conference and the "Final Solution"
ArticleAt the Wannsee conference of January 1942, Nazi Party and German government officials gathered to coordinate implementation of the “Final Solution to the Jewish Question.”

-
Armband for "Foreign Pao Chia Vigilance Corps Pao"
ArtifactIdentifying armband worn by Pao Chia member. In 1942 the Japanese in Shanghai established self-policing units, Pao Chia, composed of all men, foreigners and Chinese, aged 20 to 45. In the designated area, male refugees served several hours weekly in rotating shifts as guards for buildings and ghetto entrances where they examined passes. Despite the Japanese use of the Pao Chia to help police the ghetto, it was relatively easy to leave the "designated area," which was not walled in. Individuals who did so,…

-
Einsatzgruppen in Liepaja, Latvia
FilmGerman Einsatzgruppen operated in German-occupied territories in eastern Europe during World War II. This rare footage shows a unit during a massacre in Liepaja, Latvia. The film was taken, contrary to orders, by a German soldier. Before the war, the Jewish population of Liepaja stood at more than 7,000 residents. Einsatzgruppen shot almost the entire Jewish population of the town. When the Soviet army liberated the city in 1945, just 20 to 30 Jews remained. Einsatzgruppen carried out various security…

-
Presenting the prosecution's case at the International Military Tribunal
PhotoUS Major Frank B. Wallis (standing center), a member of the trial legal staff, presents the prosecution's case to the International Military Tribunal at Nuremberg. A chart (top left) shows where the defendants (bottom left) fit into the organizational scheme of the Nazi Party. At right are lawyers for the four prosecuting countries. Nuremberg, Germany, November 22, 1945. The trials of leading German officials before the International Military Tribunal are the best known of the postwar war crimes trials.…

-
Battle of the Bulge
ArticleThe Battle of the Bulge was a failed German counter-offensive against the Allied armies. Learn more about the Battle of the Bulge and its impact on WWII.

-
Sachsenhausen: Liberation and Postwar Trials
ArticleLearn about the death march of prisoners from the Sachsenhausen camp, liberation of the remaining prisoners, and postwar trials of camp staff.

-
The Nuremberg Courtroom
ArticleThe International Military Tribunal took place in the Palace of Justice at Nuremberg, the only undamaged facility extensive enough to house the trials.

-
"Aryanization"
ArticleBy the process of "Aryanization" in Nazi Germany from 1933 to 1945, Jewish-owned businesses and property were transferred to non-Jews. Learn more.

-
UN Convention on the Prevention and Punishment of Genocide
Timeline EventJanuary 12, 1951. On this date, the United Nations Convention on the Prevention and Punishment of Genocide entered into force.

-
People crowded around an antisemitic "Pesti Ujság" newspaper display
PhotoVisitors view the exhibition of the Arrow Cross newspaper, Pesti Ujság, at the International Fair in Budapest. The headline reads: "For a Hungary without Jews." Budapest, Hungary, approximately 1941-1942. The Arrow Cross was Hungary's largest fascist political movement after 1935. In the 1939 parliamentary elections it won over 20% of the vote and had more than 250,000 members. Its ideology was ultra-nationalistic and fiercely antisemitic. The Arrow Cross viewed Jews as an "anti-national" "race"…

-
Historian Peter Black describes researching evidence for an OSI case
Oral HistoryIn the 1980s and 1990s, historian Peter Black worked for the US Department of Justice Office of Special Investigations, as part of a team tracking and prosecuting suspected war criminals. Black later served as the Senior Historian at the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum.

-
Sighet
ArticleLearn about the history of Sighet, birthplace of Elie Wiesel. The Jewish population of Sighet was deported to Auschwitz in May 1944. Most of the deportees were gassed on arrival.

-
Röhm Purge
ArticleThe Röhm Purge (the “Night of the Long Knives") was the murder of the leadership of the SA (Storm Troopers), the Nazi paramilitary formation led by Ernst Röhm. Learn more.
-
Ivo Herzer describes a roundup (from which he was released) of Jews by Croatian collaborators in 1941
Oral HistoryIvo grew up in a middle-class Jewish family in Zagreb. He experienced little overt antisemitism until the Germans and their allies invaded Yugoslavia in April 1941 and installed a fascist Ustasa government in Croatia. The Ustasa regime began killing Jews, Serbs, and Roma (Gypsies). Ivo's family escaped to Italian-occupied territory, where the Italians tried to protect Jewish refugees. Ivo lived in Italian internment camps, including the Rab island camp, before moving to mainland Italy in 1944. He worked…

-
Susan Bluman describes the German invasion of Poland
Oral HistorySusan was 19 years old when Germany invaded Poland in September 1939. Her boyfriend, Nathan, was in Lvov when the Soviet Union occupied eastern Poland. Nathan sent a guide to Warsaw to bring Susan to the Soviet zone of occupied Poland. Her parents reluctantly agreed after Susan promised to return to Warsaw within two weeks. Upon her arrival in Lvov, Susan married Nathan. The couple then fled across the Lithuanian border to Vilna, where they stayed for a year. They received a visa for transit through Japan…

-
Siegfried Halbreich describes conditions and forced labor in the Gross-Rosen camp
Oral HistoryAfter Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939, Siegfried fled with a friend. They attempted to get papers allowing them to go to France, but were turned over to the Germans. Siegfried was jailed, taken to Berlin, and then transported to the Sachsenhausen camp near Berlin in October 1939. He was among the first Polish Jews imprisoned in Sachsenhausen. Inmates were mistreated and made to carry out forced labor. After two years, Siegfried was deported to the Gross-Rosen concentration camp, where he was…

-
Auschwitz
ArticleThe Auschwitz camp system, located in German-occupied Poland, was a complex of 3 camps, including a killing center. Learn about the history of Auschwitz.

-
Plight of Jewish Children
ArticleDuring the Holocaust, some children went into hiding to escape Nazi persecution. They faced constant fear, dilemmas, and danger.

-
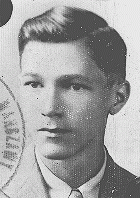
Pawel Zenon Wos
ID CardPawel was the oldest of four children born to Roman Catholic parents in Poland's capital of Warsaw. Pawel's father had worked for the Polish merchant marine before starting his own textile business in 1930. The family moved to a comfortable apartment near the Royal Castle and the Vistula River. Pawel excelled in sports, including basketball and tennis. His favorite sport was rowing. 1933-39: In May 1939 Pawel became an army reserve officer and went to training camp near Augustow. On the morning of…
-
Itka Wlos
ID CardItka was raised in a Yiddish-speaking, religious Jewish family in Sokolow Podlaski, a manufacturing town in central Poland with a large Jewish population of about 5,000. Itka came from a poor family. After completing her public schooling in Sokolow Podlaski at the age of 14, she began to work. 1933-39: Itka was a young woman, unmarried and living with her parents when war between Germany and Poland broke out on September 1, 1939. German aircraft bombed Sokolow Podlaski's market and other civilian targets…

-
Chaim Werzbe
ID CardChaim was raised in a Yiddish-speaking, religious Jewish family in Sokolow Podlaski, a manufacturing town in central Poland with a large Jewish community of about 5,000. The economic activities of most of the townspeople were closely tied to those of nearby Warsaw and surrounding farming communities. As a young man, Chaim liked to play chess and was active in a local Zionist organization. 1933-39: Chaim made a living in the grain business. After settling down, he married a widow who was older than he and…

-
Fela Perznianko
ID CardFela was the older of two children born to Jewish parents living in Zakroczym, a town on the Vistula River near Warsaw. Her father was a respected attorney. As a young woman, Fela worked as a hat designer in Warsaw, until she married Moshe Galek when she was in her late 20s. She moved to the nearby town of Sochocin, where her husband owned a pearl-button factory. Fela and Moshe raised four daughters. 1933-39: In 1936 the Galeks moved to Warsaw, attracted by the city's cultural life. When Germany invaded…

-
Mendel Rozenblit
ID CardMendel was one of six children born to a religious Jewish family. When Mendel was in his early 20s, he married and moved with his wife to her hometown of Wolomin, near Warsaw. One week after the Rozenblits' son, Avraham, was born, Mendel's wife died. Distraught after the death of his young wife and left to care for a baby, Mendel married his sister-in-law Perele. 1933-39: In Wolomin Mendel ran a lumber yard. In 1935 the Rozenblits had a daughter, Tovah. When Avraham and Tovah were school age, they began…

-
Schloma Wolf (Willy) Szapiro
ID CardBorn to a Jewish family, Willy left Poland at age 20 and emigrated to Palestine. He became active in the workers' organization to end the British mandate there. His activities led to his arrest on May 1, 1931. After serving a two-year prison sentence, Willy was expelled from Palestine. 1933-39: In 1933 Willy left Palestine for Austria, where he joined the ranks of the workers' movement. The economic depression in Austria gave momentum to the movement's cause, and Willy and his friends were closely watched…

-
Boria Lerner
ID CardBoria was born to a Jewish family living in the Bessarabian province when it was still a part of the Russian Empire. Following Romania's 1918 annexation of the province, life for Bessarabia's 200,000 Jews worsened. Subject to more widespread antisemitic laws and pogroms than while under Tsarist Russian rule, many Bessarabian Jews emigrated overseas or sought refuge back in Soviet villages. 1933-39: Boria became active in a local revolutionary communist group and was arrested and jailed many times. After…

-
Mendel Felman
ID CardOne of seven children, Mendel was raised in a Yiddish-speaking, religious Jewish home in Sokolow Podlaski, a manufacturing town in central Poland with a large Jewish population of about 5,000. Mendel's parents ran a grain business. As a teenager, Mendel liked to play chess, and he completed his public schooling in Sokolow Podlaski in 1931. 1933-39: After finishing middle school, Mendel went to work in his parents' business. When he was 18, he fell in love with Frieda Altman who was in the same Zionist…