You searched for: %EC%B9%B4%EC%A7%80%EB%85%B8%20%EB%B3%B4%EA%B3%A0%EC%84%9C%20zx444.top%20%EC%BD%94%EB%93%9C%206520%20%ED%94%8C%EB%A0%88%EC%9D%B4%20%EC%B9%B4%EC%A7%80%EB%85%B8%20%EC%A3%BC%EC%86%8C%20%EC%B9%B4%EC%A7%80%EB%85%B8%20%EA%B0%80%EC%9E%85%EC%BF%A0%ED%8F%B0%20%EC%A6%89%EC%8B%9C%EC%A7%80%EA%B8%89%20%EC%98%A4%EB%8A%98%EC%9D%98%ED%94%84%EB%A1%9C%EC%95%BC%EA%B5%AC%20ioq
<< Previous | Displaying results 401-450 of 505 for "%EC%B9%B4%EC%A7%80%EB%85%B8%20%EB%B3%B4%EA%B3%A0%EC%84%9C%20zx444.top%20%EC%BD%94%EB%93%9C%206520%20%ED%94%8C%EB%A0%88%EC%9D%B4%20%EC%B9%B4%EC%A7%80%EB%85%B8%20%EC%A3%BC%EC%86%8C%20%EC%B9%B4%EC%A7%80%EB%85%B8%20%EA%B0%80%EC%9E%85%EC%BF%A0%ED%8F%B0%20%EC%A6%89%EC%8B%9C%EC%A7%80%EA%B8%89%20%EC%98%A4%EB%8A%98%EC%9D%98%ED%94%84%EB%A1%9C%EC%95%BC%EA%B5%AC%20ioq" | Next >>
-
Beifeld album page with watercolors titled "Sports weeks" and "Quiet Don"
Artifact(top) "Watercolor entitled 'Sports weeks in Uryv, September 1942' in which a Russian tank attacks a Hungarian unit in Uryv."; (bottom) "Watercolor entitled 'Quiet Don: a detailed map of the Don River area' featuring images of dead soldiers, horses and spilled blood on a map of the Don River." [Photograph #58060]

-
Samuel Soltz's visa
DocumentThe back of Samuel Soltz's citizenship papers illustrates the vast array of bureaucratic stamps and visas needed to emigrate from Europe in 1940–41. The stamp in the top left, dated August 21, 1940, represents a visa from the Japanese consul to Lithuania, Chiune Sugihara. Sugihara issued thousands of visas to enable Jews to escape.

-
Renovating the courtroom to be used for the International Military Tribunal
PhotoRepairs and improvements are made to the courtroom where the International Military Tribunal trial of war criminals would be held. The holes in the walls at the top (when completed) housed radio commentators and public address operators. September 11, 1945.

-
Display from "Der ewige Jude," a Nazi antisemitic exhibit
PhotoDisplay from "Der ewige Jude" (The Eternal Jew), a Nazi antisemitic exhibit which claimed that Jews heavily dominated the German performing arts. A phrase at the top of the display states "Shameless Entertainment." Berlin, Germany, November 11, 1938.

-
Portrait of a preschool class in Copenhagen, Denmark
PhotoPortrait of a preschool class in Copenhagen. Gus Goldenburger (top row, second from left) was one of the few Jewish students in the class. His family moved to Denmark from Czechoslovakia, fearing the rising tide of Nazism. When the Nazis planned to deport Danish Jewry, the Goldenburgers managed to escape to Sweden, where they remained until the end of the war. After the war, the Goldenburgers returned to Copenhagen. Photograph taken in Copenhagen, Denmark, 1938–1939.

-
Portrait of a boarding school class in which a Jewish boy was hidden
PhotoClass photograph of students at the San Leone Magno Fratelli Maristi boarding school in Rome. Pictured in the top row at the far right is Zigmund Krauthamer, a Jewish child who was being hidden at the school. Rome, Italy, 1943–44.

-
Portrait of Norman Salsitz's family
PhotoIn this 1934 portrait of Norman Salsitz's family, Norman is seated in the front row (at left). In the top row, center, an image of one of Norman's brothers has been pasted into the photograph. This is seen by comparing the size of the brother's face with the others pictured. Pasting in images of family members who could not be present during family portraits was common practice and in some cases the resulting composite images are the only remaining visual records of family groups.

-
Werner Hegemann
ArticleWerner Hegemann was a city planner and author. The Nazis opposed his views of American architecture and German historical figures. His book was burned in 1933.
-
Gartenberg family portrait
PhotoFamily portrait of the Gartenberg family in Drohobycz, Poland. None of those pictured would survive the Holocaust. Photograph taken in 1930. Top row: Julius Gartenberg, Anna Fern, Bernard Klinger, Ona Fern and Izador Gartenberg. Lower row: Marcus Gartenberg, Hinda Gartenberg with her grandaughter Tony Schwartz on her lap, Sol Schwartz, and Ida Fern.
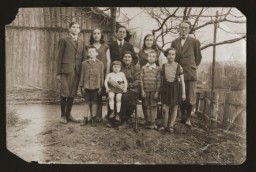
-
Poster for Nazi Party speech on Jewish Bolshevik threat
PhotoPoster for a meeting and speech about the Jewish Bolshevik threat against Germany sponsored by the local Nazi Party of East Hannover. Depicted is a silhouetted caricature of a Jewish man’s head in left profile, with a large, red Star of David beside him. The announcement at the top of the poster reads: "Victory over Bolshevism and plutocracy means being freed from the Jewish parasite!" Created ca. 1937–1940.

-
Warsaw Ghetto Sealed
Timeline EventNovember 15, 1940. On this date, German authorities ordered the Warsaw ghetto to be sealed.

-
Terez Goldberger Kalman
ID CardTerez came from a religious Jewish family. She and her husband, Samuel, raised eight children in Satoraljaujhely, in northeastern Hungary. The Kalmans lived on the outskirts of the city, and in the 1920s they ran a canteen for the soldiers who lived in the nearby barracks. The Kalmans were proud Hungarians; one of their sons had died in World War I. 1933-39: Since Samuel died a few years ago, Terez has been alone here in her house in Satoraljaujhely. Many of her children live nearby, though, so her home…

-
Buchenwald
ArticleThe Nazi regime established the Buchenwald camp in 1937. Learn about the camp’s prisoners, conditions there, forced labor, subcamps, medical experiments, and liberation.

-
Beifeld album page about events of August 28, 1942
Artifact(Top) A drawing dated October 1942 depicting the events of August 28 when Beifeld was wounded near the front lines. His caption reads: "I get wounded and manage to get away from the dangerous bend in the [Don] river]." (Bottom left) Skull of a Soviet soldier with the caption 'Keep Smiling.' (Bottom right) Map entitled 'Dangerous Curve' depicting the bend in the Don River where the Soviet army was threatening to break through. [Photograph # 58061]

-
Eugenio Gentili Tedeschi
ArticleRead the Jewish Partisan Educational Foundation's short biography of Eugenio Gentili Tedeschi.

-
Samuel Soltz's Visa
Timeline EventAugust 21, 1940. On this date, Samuel Soltz's visa was stamped by Chiune Sugihara, the Japanese consul to Lithuania.

-
Abraham Bomba describes the Treblinka gas chambers
Oral HistoryExcerpt from Holocaust survivor Abraham Bomba's oral history testimony describing gas chambers at the Treblinka killing center.

-
Léon Degrelle
ArticleLéon Degrelle was an extreme right-wing Belgian politician and Nazi collaborator. After the war, he continued to spread pro-Nazi propaganda for decades. Learn more.

-
David (Dudi) Bergman describes liberation by US Army in mountains near Innsbruck
Oral HistoryThe Germans occupied David's town, previously annexed by Hungary, in 1944. David was deported to Auschwitz and, with his father, transported to Plaszow. David was sent to the Gross-Rosen camp and to Reichenbach. He was then among three of 150 in a cattle car who survived transportation to Dachau. He was liberated after a death march from Innsbruck toward the front line of combat between US and German troops.

-
Selma Engel diary entry about life in hiding
ArtifactDiaries reveal some of the most intimate, heart-wrenching accounts of the Holocaust. They record in real time the feelings of loss, fear, and, sometimes, hope of those facing extraordinary peril. Selma Wijnberg and Chaim Engel met and fell in love in the Sobibor killing center. After the young couple made a daring escape during the camp uprising and fled into hiding, Selma began a diary to record their experiences. The diary was written in 1943-1944 while Selma was in hiding in German-occupied…

-
Anti-Masonic poster
ArtifactEugenics poster entitled "The relationship between Jews and Freemasons." The text at the top reads: "World politics World revolution." The text at the bottom reads, "Freemasonry is an international organization beholden to Jewry with the political goal of establishing Jewish domination through world-wide revolution." The map, decorated with Masonic symbols (temple, square, and apron), shows where revolutions took place in Europe from the French Revolution in 1789 through the German Revolution in 1919. This…

-
Beifeld album page titled "Mementos"
ArtifactCollage entitled: "Mementos from the Russian campaign," which includes a watercolor of Stalin with the caption: 'Russia a meeting place for foreigners 1942-43' (top); a commuter train ticket issued to military personnel who carried the special SAS [Hurry, Immediate, Urgent] draft notice (middle, right); a pseudo travel brochure cover entitled 'Spend your summer vacation in merry Russia' (bottom, left); and the original design for the cover of the labor company's journal entitled 'Hungarian Royal 109/13…

-
Former prisoners of the "little camp" in Buchenwald
PhotoFormer prisoners of the "little camp" in Buchenwald stare out from the wooden bunks in which they slept three to a "bed." Elie Wiesel is pictured in the second row of bunks, seventh from the left, next to the vertical beam. Abraham Hipler is pictured in the second row, fourth from the left. The man on the third bunk from the bottom, third from the left, is Ignacz (Isaac) Berkovicz. [He has also been identified as Abraham Baruch.] Michael Nikolas Gruner, originally from Hungary, is pictured on the bottom…

-
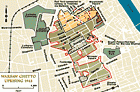
Warsaw ghetto uprising, 1943
MapThe city of Warsaw is the capital of Poland. Before World War II, Warsaw was the center of Jewish life and culture in Poland. Warsaw's prewar Jewish population of more than 350,000 constituted about 30 percent of the city's total population. The Warsaw Jewish community was the largest in both Poland and Europe, and was the second largest in the world, behind that of New York City. The Germans occupied Warsaw on September 29, 1939. In October 1940, the Germans ordered the establishment of a ghetto in…
-
Western Desert Campaign: Egypt and Libya
ArticleLearn more about the Western Desert campaign during World War II in Egypt and Libya between 1940-1943.

-
Ghettos in Occupied Poland
ArticleDuring World War II, the Nazis established ghettos, which were areas of a city where Jews were forced to live. Learn more about ghettos in occupied Poland.

-
Miriam Farcus Ingber describes witnessing a suicide attempt in the Stutthof camp
Oral HistoryMiriam was one of ten children born to a poor, religious Jewish family in Terava, Czechoslovakia. When Hungary took over the area in 1939, almost half the town's Jewish population was deported and sent to labor camps. Later, Miriam and her mother were forced into a ghetto. They were deported to the Auschwitz camp in 1944. After about three months, they were sent to the Stutthof camp. Toward the end of the war, Miriam and her mother were forced on a death march. They and others on the death march were…

-
Abraham Lewent describes hiding during a raid in which his mother and sisters were seized for deportation from Warsaw to Treblinka
Oral HistoryLike other Jews, the Lewents were confined to the Warsaw ghetto. In 1942, as Abraham hid in a crawl space, the Germans seized his mother and sisters in a raid. They perished. He was deployed for forced labor nearby, but escaped to return to his father in the ghetto. In 1943, the two were deported to Majdanek, where Abraham's father died. Abraham later was sent to Skarzysko, Buchenwald, Schlieben, Bisingen, and Dachau. US troops liberated Abraham as the Germans evacuated prisoners.

-
Peter Black describes the role of historians in researching war crimes cases for OSI
Oral HistoryIn the 1980s and 1990s, historian Peter Black worked for the US Department of Justice Office of Special Investigations, as part of a team tracking and prosecuting suspected war criminals. Black later served as the Senior Historian at the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum.

-
Frederick Dermer
ID CardFrederick was born to a Jewish family in the Austrian capital of Vienna. His father died when he was a baby, and he and his mother moved into an apartment with Frederick's widowed grandfather. As a young boy, Frederick attended a Viennese public school. 1933-39: Frederick was a rambunctious child. Once, when his grandfather was baby-sitting, Frederick used a silk lampshade as a "parachute," and jumped from the top of the wardrobe closet. That was the last time Frederick's grandfather would baby-sit.…

-
Killing Centers: An Overview
ArticleThe Nazis established killing centers in German-occupied Europe during WWII. They built these killing centers for the mass murder of human beings.

-
Beifeld album page outlining the labor service's roles in the war effort
ArtifactA page of drawings illustrating the contribution of Jewish Labor Servicemen to the war effort. At the top: "The different platoons work hard at the battle front and in the no man's land [between the armies]. They actively participate in the fighting. They carry ammunition to the Hungarian soldiers." In the middle: "They defuse land mines. They bury the dead, including those that had been left unburied from the winter campaign. They carry soldiers wounded on the front lines to safety." At the bottom: "For…

-
Sara Rachela Plagier
ArticleChildren's diaries bear witness to some of the most heartbreaking events of the Holocaust. Learn about the diary and experiences of Sara Rachela Plagier.

-
The SS
ArticleThe SS (Schutzstaffel) was the elite guard of the Nazi regime and a virtual state within the Third Reich.

-
Eduard Schulte
ArticleEduard Schulte was a prominent German industrialist and secret anti-Nazi who leaked the first report to the west that the Nazis intended to murder all Jews in Europe.
-
Life in the Ghettos
ArticleDuring the Holocaust, Jews were forced into ghettos with terrible living conditions, overcrowding, and starvation. Learn more about life in the Lodz ghetto.

-
The Warsaw Ghetto Uprising
ArticleThe Warsaw ghetto uprising was the largest uprising by Jews during World War II. 100s of ghetto fighters fought heavily armed and well-trained Germans for nearly a month.

-
Reich Security Main Office (RSHA)
ArticleThe Reich Security Main Office (RSHA), created by Heinrich Himmler, brutally coordinated and perpetrated many aspects of the Holocaust.

-
The SA
ArticleThe SA (Sturmabteilung) was a paramilitary organization integral to Hitler’s ascension to power. Learn more about the rise and fall of the SA.

-

-
Concentration Camp System: In Depth
ArticleThe Nazi regime's extensive camp system included concentration camps, forced-labor camps, prisoner-of-war camps, transit camps, and killing centers.

-
Felix Horn describes a hiding place in Warsaw
Oral HistoryFelix was born to an assimilated Jewish family in Lublin, Poland. His father was a locksmith and his mother was a singer. Following the German invasion of Poland on September 1, 1939, Felix fled east to Rovno and then to Soviet-occupied Lvov, where he was accepted at a medical school. After the German invasion of the Soviet Union in June 1941, Felix was taken to a labor camp. He escaped and returned to Lublin, and found that his family had been forced into the ghetto established there. After the…

-
Selma (Wijnberg) Engel describes deportation to Sobibor
Oral HistorySelma was the youngest of four children born to Jewish parents. When she was 7, Selma and her family moved to the town of Zwolle where her parents ran a small hotel. When the Germans invaded the Netherlands in 1940, they confiscated the hotel. The family had to live in a poor Jewish section of the town. Selma went into hiding but was betrayed and then sent to the Westerbork camp. In April 1943 she was deported to Sobibor, where she worked in the clothes sorting area. There, the prisoners tried to pocket…

-
Norbert Wollheim describes his experiences on a transport during deportation from Berlin
Oral HistoryNorbert studied law and was a social worker in Berlin. He worked on the Kindertransport (Children's Transport) program, arranging to send Jewish children from Europe to Great Britain. His parents, who also lived in Berlin, were deported in December 1942. Norbert, his wife, and their child were deported to Auschwitz in March 1943. He was separated from his wife and child, and sent to the Buna works near Auschwitz III (Monowitz) for forced labor. Norbert survived the Auschwitz camp, and was liberated by US…

-
Chaim Frenkiel
ID CardChaim was the third of seven boys born to religious Jewish parents. They lived in a town near Warsaw called Gabin, where Chaim's father worked as a cap maker. Gabin had one of Poland's oldest synagogues, built of wood in 1710. Like most of Gabin's Jews, Chaim's family lived close to the synagogue. The family of nine occupied a one-room apartment on the top floor of a three-story building. 1933-39: In September 1939, two months before Chaim was 12, Germany invaded Poland. In Gabin 10 people were shot in…

-
Jakob Frenkiel
ID CardJakob was one of seven boys in a religious Jewish family. They lived in a town 50 miles west of Warsaw called Gabin, where Jakob's father worked as a cap maker. Gabin had one of Poland's oldest synagogues, built of wood in 1710. Like most of Gabin's Jews, Jakob's family lived close to the synagogue. The family of nine occupied a one-room apartment on the top floor of a three-story building. 1933-39: On September 1, 1939, just a few months before Jakob turned 10, the Germans started a war with Poland.…

-
Andras Muhlrad
ID CardThe second of two children, Andras was born to Jewish parents living in a suburb of Budapest. His father was a pharmacist. The Muhlrads lived in a large house with Andras' grandfather and aunts. As a toddler, Andras often played with his older sister, Eva, and their cousins in the big yard behind their home. 1933-39: Andras was 4 when his family moved to their own apartment. It was 1936 when he began primary school and Hitler had already been in power in Nazi Germany for three years. At night his father…

-
David Bergman
ID CardDavid was born to religious Jewish parents in a small town in Ruthenia, Czechoslovakia's easternmost province, which had been ruled by Hungary until 1918. Located in the Carpathian Mountains, the town was so isolated that news from the rest of the country would arrive by a drummer who would read the news in the town's central square. David's father worked as a tailor and his mother was a seamstress. 1933-39: While David's parents worked, he would be at home having a good time. They had a beautiful home…

-
David J. Selznik
ID CardThe village in Lithuania where David grew up was located near the Latvian border. His father was a peddler. At age 6, David was sent to Ukmerge, a town known to Jews by its Russian name, Vilkomir, to study traditional Jewish texts at the rabbinical academy there. Six years later, David was called to return home to head the Selznik family because his father had died. 1933-39: David lost his job in 1933, so he left Lithuania and went to the United States and then Portugal. But in 1936 the Baltic states were…

-
Dezso Rozsa
ID CardDezso was from a Jewish family in Hungary's capital, Budapest. His father had been a violinist. Dezso earned a university degree in English, and became a language teacher. He wrote a number of high school grammar textbooks. In 1914 he married Iren Hajdu, who was a mathematician. The couple had two children; a daughter, Eva, born in 1918, and a son, Pal, born seven years later. 1933-39: Dezso fears for the worst now that the antisemitic Prime Minister Teleki has taken power again. Nineteen years ago, in…

