<< Previous | Displaying results 151-200 of 6720 for "" | Next >>
-
Kyiv (Kiev) and Babyn Yar (Babi Yar) - maps
Media EssayIn late September 1941, SS and German police units and their auxiliaries perpetrated one of the largest massacres of World War II. It took place at a ravine called Babyn Yar (Babi Yar) just outside the Ukrainian capital city of Kyiv (Kiev).
-
Lutz Haase
ID CardLutz was one of two children born to religious Jewish parents living in Wrzesnia when it was still part of Germany. After World War I, Wrzesnia became part of Polish territory. Preferring to remain as German citizens, Lutz's family moved to Nuremberg. There, his father opened a kosher butcher shop. In 1926 the Haases relocated to Berlin and reestablished their butcher shop there. 1933-39: Like many of Berlin's Jews, Lutz was assigned by the Gestapo to a work detail in 1937. He laid electrical cable for…

-
Dr. Johan Hendrik Weidner
ID CardJohan was the eldest of four children born to Dutch parents. His father was a minister in the Seventh-Day Adventist Church. Johan grew up in Collonges, France, where his father served as a pastor. After attending French public schools, Johan graduated from the Seventh-Day Adventist Seminary in Collonges, and went on to study law and business at the universities of Geneva and Paris. 1933-39: After completing his studies in 1935, Johan opened an import/export textile business in Paris. Business prospered…

-
Danuta Justyna
ID CardDanuta was born to Roman Catholic parents in the small industrial town of Piotrkow Trybunalski in central Poland. Her father and mother were school teachers. She and her younger sister, Maria, became friends with two Jewish girls, Sabina and Helena Szwarc. Although their houses were more than a mile apart, the girls often played together. 1933-39: Danuta was planning on attending college in September 1939, but on September 1 Germany invaded Poland. Four days later, German soldiers streamed into Danuta's…
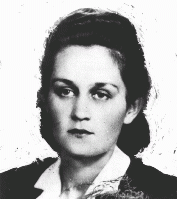
-
Kazimiera Banach Justynowa
ID CardKazimiera was born to Roman Catholic parents in the town of Mierzen. After graduating from a teacher's college in Staniatki, she married Wincenty Justyna, a secondary school teacher. The couple settled in the small industrial city of Piotrkow Trybunalski and raised three children, Jerzy (a boy), Danuta and Maria. Kazimiera worked as a school teacher. 1933-39: With their combined incomes the Justynas were able to buy a plot of land and build a house. The Germans invaded Poland on September 1, 1939, and…

-
Maria Justyna
ID CardMaria was born to Roman Catholic parents in the industrial town of Piotrkow Trybunalski in central Poland. Her father and mother were school teachers. Maria attended grade school and secondary school in Piotrkow. She and her older sister, Danuta, became friends with two Jewish girls, Sabina and Helena Szwarc. Although their houses were more than a mile apart, the girls often played together. 1933-39: The Germans invaded Poland on September 1, 1939, and occupied Piotrkow four days later. Most schooling for…

-
Stefania (Fusia) Podgorska
ID CardStefania was born to a Catholic family in a village near Przemysl. They lived on a large farm and cultivated several different crops. While her father worked with the farmhands in the fields, Stefania's mother, a trained midwife, managed the house and cared for her eight children. 1933-39: Stefania's father died in 1938 after an illness. With her mother's approval, she joined her sister in Przemysl in 1939. At 14 she worked in a grocery store owned by the Diamants, a Jewish family. They treated her like…
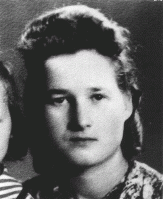
-
Simone Weil
ID CardSimone was the oldest of two children born to a Jewish family in the small village of Ringendorf. When she was 3 her family moved to Strasbourg. Her father made his living breeding sheep. Simone and her younger brother were both active in a Jewish scouting organization, Les Eclaireurs Israelites de France (EIF). Simone attended a public secondary school in Strasbourg. 1933-39: In addition to attending secondary school for five days of the week, Simone also went to a Jewish religious school on the other…

-
Manya Moszkowicz
ID CardManya was born in Chmielnik, a small Polish town that had a Jewish community dating back to the 16th century. Her father owned a furniture shop and her mother took care of the home. Manya had two younger brothers, David and Mordechai, and was surrounded by many close relatives. She attended both public and Hebrew schools and had many friends. 1933–39: In 1938 Manya's family moved to Sosnowiec, a larger city located near the German border. There she had her first experience with antisemitism. Signs…

-
Welek Luksenburg
ID CardWelek grew up in Dabrowa Gornicza, an industrial town in western Poland. His father, Simcha, was a wholesale meat merchant and his mother, Rozalia, served as president of the local chapter of the Women's International Zionist Organization. Welek's older brother, Szlomo, was a dentist. The Luksenburgs were among the several thousand Jews who lived in Dabrowa Gornicza. 1933–39: Like many other children in the town, Welek attended public school. Because his family was very religious, he did not attend…

-
Abraham Malnik
ID CardAbraham was born to a Jewish family in Kovno, a city picturesquely situated at the confluence of two rivers. With an opera company, chic stores and lively nightclubs, it was often called "Little Paris." The city had a large Jewish community of 38,000 and was known for its extensive Hebrew school system. Abraham's father was a barber, and his mother was a beautician. 1933-39: When Abraham was a kid his family used to go to his grandparents' house for Sunday dinner. In the winter they would take a…

-
Kalman Kernweiss
ID CardKalman was the oldest of ten children born to poor, devout Jewish parents in a small village in south central Poland. His father supported the family by buying chickens, eggs and vegetables from the peasants and selling them at the Kolbuszowa market a few miles away. Kalman walked to Kolbuszowa each day to attend public school in the morning and religious school in the afternoon. 1933-39: In 1933 Kalman was accepted to study at a renowned rabbinical institute in Lublin. When there was time, he taught…

-
Abraham Bergman
ID CardAbraham was born to a Jewish family in Krasnik, a town in the Lublin district of Poland. The town had a large Jewish population. Abraham's father was a tailor. When Abraham was 2, his mother died and he was raised by his grandmother. At the age of 7, Abraham started public school. 1933-39: Abraham liked school but found it difficult. The Christian children often yelled at the Jews, "You killed our God." One year, on the day before Christmas break, some kids brought ropes tied to iron weights to school.…

-
Eugeniusz Rozenblum
ID CardEugeniusz's parents married in 1922 in the Soviet Union, where his father owned a textile mill. Fearing arrest by the Soviets for being "bourgeois," Eugeniusz's parents fled to Poland, where Eugeniusz was born. 1933-39: Eugeniusz was a secondary school student and was preparing to enter university, either in Poland or at the Hebrew University in Palestine. The German occupation of Lodz in September 1939 interrupted his schooling. One month after the occupation, a German soldier came to his family's door…

-
Walter Szczeniak
ID CardWalter was the oldest of eight children born to Polish-Catholic immigrant parents in a town near Boston, Massachusetts. The family moved back to Poland when Walter was a child, and lived on a family farm near Ostroleka in northern Poland that Walter's mother had inherited. Because his father's American nickname was "Stetson," Walter was mistakenly registered as "Charles Stetson" on his American birth certificate. 1933-39: After Walter completed secondary school, his father sent him to the University of…

-
Yitzhak (Irving) Balsam
ID CardYitzhak was the second of four children born to religious Jewish parents. The family lived on the Polish-German border in Praszka, a small town where Yitzhak's father worked as a tailor. His work was not steady, and the family struggled to make ends meet. Yitzhak attended Polish public school in the mornings and Hebrew school in the afternoons. 1933-39: At 4 a.m. on September 1, 1939, the Balsams were awakened by an explosion. The Polish army had blown up the bridge over the Prosna River to impede the…

-
David Bayer
ID CardDavid was the second of four children born to religious Jewish parents in Kozienice, a town in southeastern Poland. His father, Manes, owned a shoe factory that supplied stores throughout the country. His mother, Sarah, took care of the home and children, and helped in the factory. Kozienice had a thriving Jewish community that constituted over half of the town's population. 1933–39: For most of the 1930s, David spent his days going to school, playing sports, and working in his father's shoe factory.…

-
Ruth Elisabeth Dahl
ID CardRuth was born into an orthodox Jewish family in Geilenkirchen, a rural German town near the Dutch border. Her father, Isidor, was a respected cattle dealer in the area and her mother, Sophia, took care of the home. Ruth had two older siblings, Edith and Carl. 1933–39: When the Nazis came to power in Germany, life changed in Geilenkirchen. The townspeople supported the new regime and nobody helped their Jewish neighbors. Excluded from public institutions, Ruth attended a private Catholic school. In 1938,…

-
Inge Berg
ID CardInge lived with her parents, grandparents, uncle, and younger sister, Gisella, in Lechenich, a small village outside Cologne. The Bergs were an observant Jewish family. Inge's grandfather was the president of the local synagogue association and her uncle was the cantor. Her father, Josef was a respected cattle dealer, who had many business and personal contacts with their Jewish and non-Jewish neighbors. 1933–39: In 1935, two years after the Nazis came to power, Inge was forced to leave public school in…

-
Werner Katzenstein
ID CardWerner was raised in the rural German town of Herleshausen, where his family owned a farming supply business. His father sold seeds to local farmers and purchased their grain, while his mother ran the office. After several years of public schooling in Herleshausen, Werner began attending a high school in Eisenach, some 12 miles from their home. The Katzensteins were one of about two dozen Jewish families living in the area. 1933–39: When the Nazis came to power in January 1933, the Katzensteins' lives…

-
Kato Fried
ID CardKato was born to Jewish parents in Smolnik, a small village in eastern Czechoslovakia. While still a young child, she moved with her parents and brother Theodore to Sighet, Romania. There in the Carpathian mountains, her father ran a lumber business that exported wood to Germany and Czechoslovakia. 1933–39: In the 1930s, the popular appeal of antisemitism and fascism increased in Romania. Leaders of the Iron Guard, the militant and violent Romanian fascist party, publicly proclaimed their support for…

-
Hinda Chilewicz
ID CardHinda was the eldest of three children in a comfortable middle class Jewish family. Her father owned a textile business in Sosnowiec and her mother attended to the home. Sosnowiec in southwestern Poland had a growing Jewish community of almost 30,000 people. There was a Jewish hospital as well as religious schools. 1933–39: Hinda was just 13 years old when German troops invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. Three days later, they occupied Sosnowiec and terrorized the Jewish community, killing over a…

-
Gisella Renate Berg
ID CardGisella lived with her parents, grandparents, uncle, and older sister, Inge, in Lechenich, a small village outside of Cologne. The Bergs were an observant Jewish family. Gisella's grandfather was the president of the local synagogue association and her uncle was the cantor. Her father, Josef was a respected cattle dealer, who had many business and personal contacts with their Jewish and non-Jewish neighbors. 1933–39: Gisella was born several months after the Nazis came to power. Her parents feared for…

-
Kurt Pauly
ID CardKurt was born to Jewish parents in the city of Aachen, where his mother's family had resided since the 18th century. His father, though trained as a chef, worked as a butcher and also managed several stores for his father-in-law. The Paulys lived over one of those shops in the nearby suburb of Eilendorf. Kurt enjoyed large family gatherings, where he would play with his cousins, Anne and Margot Frank. 1933–39: When the Nazis came to power in 1933, the situation drastically changed for the Paulys.…

-
Peter Philipps
ID CardPete grew up in Essen, a major industrial city on Germany's Ruhr River. His father worked as a cattle hide dealer for an international trading company in nearby Muehlheim. His mother was a designer for a fashionable women's dress shop. Pete, his younger twin brothers, and parents lived together in an apartment. 1933–39: Pete had barely passed his first birthday when the Nazis came to power. His father realized the danger that now faced Jews in Germany, and the family left for Prague, Czechoslovakia, in…

-
György (George) Pick
ID CardGyörgy was the only child of middle class Jewish parents living in the Hungarian capital of Budapest. His father, Istvan, was an engineer responsible for producing hydraulic grape presses for wineries. His mother, Margit, worked as a legal secretary. 1933–39: In 1938 and 1939, Hungary’s authoritarian government passed the first in a series of major anti-Jewish laws. The legislation severely restricted the participation of Jews in the economy and defined them in racial terms, much like the Nuremberg…

-
Moniek Rozen
ID CardOne of 12 children, Moniek grew up in Dabrowa Gornicza, an industrial town in western Poland. His father, Jacob, owned a general store, which he was forced to close in 1938 as the result of a boycott by local antisemites. Moniek attended both public and Jewish schools, and his father hoped that one day he would become a rabbi. 1933–39: On September 1, 1939, Moniek was awakened by the sounds of airplanes flying overhead as German forces invaded Poland. As the war drew closer, Moniek fled eastward, but…

-
Tania Marcus
ID CardTania grew up in Smorgonie, a Polish town where Jews constituted more than half of the population. Her father was a successful businessman who sold farming equipment and purchased flax for export. Her grandfather, an affluent merchant, traveled frequently and brought the first truck to Smorgonie. The Marcuses took part in the town's vibrant Jewish culture, attended the theater, and hosted discussions about art in their home. 1933–39: On September 1, 1939, German troops invaded Poland, triggering World…

-
Hans (John) Sachs
ID CardHans was born to a Jewish family in the Sudetenland, a region of Czechoslovakia that had a large German population. In 1922 the Sachs family moved to Vienna, Austria, where they purchased a dry goods store. Hans attended public school and had many non-Jewish friends. 1933–39: By 1936 many of Hans' friends and their families supported the Nazi movement. In March 1938, German troops entered Austria and incorporated it into the Reich. Hans watched as large crowds in Vienna cheered Hitler when he visited…

-
Regina Gutman
ID CardRegina was born in Radom, a city that had 120,000 inhabitants. Her father worked as a leather cutter for a large shoe manufacturer and her mother took care of their six children. The Gutmans were very religious and Regina attended Hebrew school in the afternoons. Radom had a vibrant Jewish community of some 30,000 people, several Yiddish daily newspapers, and beautiful synagogues. 1933–39: On September 1, 1939, the German army invaded Poland, and seven days later, Radom was occupied. Soon afterward, the…

-
Sam Spiegel
ID CardSam was the eldest of five children born to Jewish parents in Kozienice, a town in east central Poland. His father owned a shoe factory and his mother cared for the children and the home. Kozienice had a thriving Jewish community that made up about half of the town's population. 1933–39: On September 1, 1939, German troops invaded Poland. That morning the Spiegels heard an air raid siren blaring and quickly left their house. Fifteen minutes later a bomb struck the building. Sam was just 17 years old.…

-
Elzbieta Lusthaus
ID CardElzbieta grew up in Iwonicz, a resort town in southwestern Poland noted for its mineral water. Her father, Edmund, was a respected physician and Helena, her mother, had studied pharmacology. At home, they spoke Polish and were among the few Jewish families who lived in Iwonicz. 1933–39: When German troops invaded Poland on September 1, 1939, Elzbieta's father was drafted into the Polish army. Seventeen days later, the Soviet army drove in from the east and Edmund was captured. He was transported to a…

-
Susan Strauss
ID CardSusan grew up in Vacha, a small Thuringian town where her family had lived for more than 400 years. Her father, Herman, owned a general store and her mother, Bertha, took care of the home and children. Susan had a younger sister Brunhilde. The Strausses were one of about 25–30 Jewish families living in Vacha. 1933–39: Soon after the Nazis took power, many of Susan's friends stopped playing with her. In 1938 she was forced to leave the public school. That November, the Nazis unleashed a wave of pogroms…

-
Susi Hilsenrath
ID CardThe Hilsenraths lived in Bad Kreuznach, a city in western Germany with a Jewish community that dated back to the 13th century. Susi was the eldest of three children. Her father owned a thriving linen store, and her mother took care of Susi and her two brothers. 1933–39: After the Nazis came to power, the Hilsenraths, like other Jewish families, began to feel the effects of increased antisemitism. Susi was forced to leave the public school, along with the other Jewish children. Even walking on the…

-
Gerd Jacob Zwienicki
ID CardGerd was the eldest of four children. His father, Josef, had left Ukraine in 1913 and opened a bicycle sales and repair shop in Bremen. His mother, Selma, was descended from a distinguished Jewish family and had been a kindergarten teacher and a bookkeeper for a large firm. As a child, Gerd experienced the hardships of the Depression and witnessed the violent street fights between the Nazis and their political opponents, the Communists and Socialists. 1933–39: When the Nazis came to power in 1933, Gerd…

-
Martin Weiss
ID CardMartin was one of nine children born to orthodox Jewish parents in Veľká Poľana, a rural village in the Carpathian Mountains. His father owned a farm and a meat business, and his mother attended to the children and the home. Everyone in the family helped take care of the horses and cows. 1933–39: Martin attended the village's Czechoslovak schools, which were quite progressive. Like many of the other children, he looked forward to leaving the provincial life in Veľká Poľana. In 1938–1939, his…

-
Lisa Nussbaum
ID CardLisa was born to a Jewish family who lived in a town about three miles from the German border. Her family had lived there for generations. Lisa's father exported geese to Germany, and her mother owned a fabric store. The family lived with Lisa's grandmother in a large, single-level, gray stucco house. Lisa attended a small Hebrew school in Raczki. 1933-39: In 1937 Lisa transferred to a public school. One day, in fifth grade during recess, some boys grabbed her long blonde hair. Others joined in and pinned…

-
Barbara Ledermann
ID CardBarbara was the older of two daughters born to Jewish parents in Germany's capital, Berlin. Barbara's father was a successful lawyer. As soon as Barbara was old enough to walk, he would take her around Berlin to see the sights and tour the city's art museums. Barbara liked to go horseback riding and dreamed of becoming a dancer. 1933-39: After the Nazis came to power in January 1933, it was illegal for Barbara's father to have non-Jewish clients. His law practice quickly folded. Later that year when…

-
Barbara Marton
ID CardThe Martons were one of 35 Jewish families in the small northern Transylvanian town of Beliu. Barbara's father owned a grocery, and her mother helped out in the store. The Martons lived in a comfortable home with a flower garden, and enjoyed friendly relations with the townspeople. As a child, Barbara learned Hebrew on Sunday mornings at the home of Beliu's rabbi. 1933-39: Barbara's father's business began to fall off when another grocery opened nearby in Beliu. By 1937 business was so bad that they sold…

-
Bella Jakubowicz
ID CardBella was the oldest of four children born to a Jewish family in the small city of Sosnowiec, in Polish Silesia. Her father owned a successful knitting factory. In 1938, when she was 12, Bella began attending a private secondary school. 1933-39: When Bella's family returned from vacation in late August 1939, there were rumors of war. Her mother tried to stock up on food but the stores were already out of staples. The Germans took Sosnowiec on September 4; two weeks later they interned all the Jewish men…

-
Beno Helmer
ID CardBeno was the oldest of three children in a Jewish family. His mother, originally from Austria, came to Czechoslovakia after World War I. Beno's father, a Swedish Jew, arrived there in search of work and became a successful merchant. The German-speaking Helmer home was frequently full of guests. Every day some students from the local rabbinical academy were invited to join the family for a meal. 1933-39: Beno's parents sent him to Budapest to attend high school. Later, because of his talent with languages,…

