You searched for: used%E4%BA%A4%E6%98%93%E7%A8%8B%E5%BA%8F%E5%BE%8C%E8%87%BA%E6%BA%90%E7%A2%BC%E3%80%90tg%EF%BF%BD%EF%BF%BD%EF%BF%BD%EF%BF%BD%EF%BF%BD%EF%BF%BD%EF%BF%BD%EF%BF%BD%EF%BF%BD%40ek7676%E3%80%91%E5%B9%B3%E5%8F%B0%E5%8C%85%E7%BD%91%E6%90%AD%E5%BB%BAusd%E4%BA%A4%E6%98%93%E7%A8%8B%E5%BA%8F%E5%BE%8C%E8%87%BA%E6%BA%90%E7%A2%BC%E3%80%90tg%EF%BF%BD%EF%BF%BD%EF%BF%BD%EF%BF%BD%EF%BF%BD%EF%BF%BD%EF%BF%BD%EF%BF%BD%EF%BF%BD%40ek7676%E3%80%91%E5%B9%B3%E5%8F%B0%E5%8C%85%E7%BD%91%E6%90%AD%E5%BB%BAivkcss1pgu
<< Previous | Displaying results 1601-1650 of 1832 for "used%E4%BA%A4%E6%98%93%E7%A8%8B%E5%BA%8F%E5%BE%8C%E8%87%BA%E6%BA%90%E7%A2%BC%E3%80%90tg%EF%BF%BD%EF%BF%BD%EF%BF%BD%EF%BF%BD%EF%BF%BD%EF%BF%BD%EF%BF%BD%EF%BF%BD%EF%BF%BD%40ek7676%E3%80%91%E5%B9%B3%E5%8F%B0%E5%8C%85%E7%BD%91%E6%90%AD%E5%BB%BAusd%E4%BA%A4%E6%98%93%E7%A8%8B%E5%BA%8F%E5%BE%8C%E8%87%BA%E6%BA%90%E7%A2%BC%E3%80%90tg%EF%BF%BD%EF%BF%BD%EF%BF%BD%EF%BF%BD%EF%BF%BD%EF%BF%BD%EF%BF%BD%EF%BF%BD%EF%BF%BD%40ek7676%E3%80%91%E5%B9%B3%E5%8F%B0%E5%8C%85%E7%BD%91%E6%90%AD%E5%BB%BAivkcss1pgu" | Next >>
-
Karl Gorath
ID CardKarl was born in the small town of Bad Zwishenahn in northern Germany. When he was 2, his family moved to the port of Bremerhaven. His father was a sailor and his mother became a nurse in a local hospital. After his father died, Karl continued to live with his mother. Karl was 20 when he began training as a deacon at his parish church. 1933-39: Karl was 26 when his jealous lover denounced him and he was arrested at his house under paragraph 175 of the criminal code, which defined homosexuality as an…

-
Liane Reif
ID CardLiane's Polish-born Jewish parents were married in Vienna, where they lived in a 14-room apartment in a middle-class neighborhood near the Danube River. Liane's father, a dentist, had his office in their home. 1933-39: After Germany annexed Austria in 1938, Liane's father was found dead, a probable suicide. In May 1939, four months before war broke out, her mother booked passage on the St. Louis, a ship bound for Cuba. But Cuban authorities turned the ship back. Along with some other refugees from the…

-
Yennj Baehr
ID CardYennj and her husband Heinrich were two of a few Jewish residents in Ruchheim, a small town in the Rhine River valley. Yennj helped Heinrich run their dry goods store that was on the first floor of their house. In the summer she liked working in the garden out back. Their son, Kurt, had immigrated to America after World War I. Ida, their daughter, helped them in the store until she married. 1933-39: The Nazis have come to power, and many Jews have decided to leave Germany. Yennj and Heinrich's niece,…

-
Heinrich Baehr
ID CardA Jewish merchant, Heinrich ran a dry goods business with his wife, Yennj, in Ruchheim, a small town in the Rhine River valley. Their son, Kurt, had immigrated to America after World War I. Their daughter, Ida, had helped them in the business until she married. The Baehrs' store took up the first floor of their comfortable two-story brick house. In the summer, they enjoyed their garden in the back. 1933-39: The Nazis have come to power, and many Jews have decided to leave Germany. Heinrich and Yennj's…

-
Ivo Herzer
ID CardIvo was an only child born to a Jewish family in the city of Zagreb. His father worked in an insurance company. Though blatant antisemitism was considered uncommon in Yugoslavia, Jews were barred from government and university positions unless they converted to Christianity. 1933-39: In Zagreb Ivo studied at a public secondary school. The curriculum was fixed and included three languages as well as religion. His school was highly selective but he enjoyed studying and did well. Though he didn't personally…

-
Martin Hans Munzer
ID CardHans was born to Jewish parents in a town in northwestern Germany. The family moved to Berlin when Hans' father obtained a post there as a history teacher in a secondary school. After graduating from university, Hans married and settled with his wife Margaret in an apartment in Berlin. In 1920 their child Wolfgang was born. Hans worked as foreign representative for a sewing notions company. 1933-39: When the Nazis won the election a few weeks ago, Hans was afraid for people like himself who are active…

-
Renee Schwalb
ID CardVienna, home to some 175,000 Jews before World War II, was a major center of European Jewry. Vienna was also the intellectual heart of the Palestine resettlement movement. Most of the city's Jews lived in two large districts on the east side of the Danube Canal. Renee's father owned a prosperous men's clothing store in the city. 1933-39: German forces occupied Austria in March 1938. Anti-Jewish measures were quickly imposed. Renee's father was prohibited from doing business and his store was seized. He…

-
Judith Margareth Konijn
ID CardJudith was the younger of two children born to religious, middle-class Jewish parents. Judith's mother, Clara, was Sephardic, a descendant of Jews who had been expelled from Spain in 1492. Her father, Lodewijk, was a traveling representative for a firm based in Amsterdam. The family lived in an apartment in a new section of Amsterdam on the southern outskirts. 1933-39: Judith attended grade school with her cousin Hetty who was the same age. Judith loved to study. Her mother taught piano to students who…
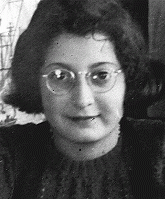
-
Golda (Olga) Bancic
ID CardOlga was born to a large Jewish family living in the Bessarabia province when it was still part of the Russian Empire. In 1918 the province was annexed by Romania. When Olga was 12 years old, she was arrested for the first time for having participated in a strike at the mattress factory where she worked. Despite her youth, she was put in prison and beaten. 1933-39: Olga was an active and vocal member of the local workers' organization. She had been arrested and imprisoned so often that she simply…

-
Betty Leiter Lauchheimer
ID CardBetty was one of 14 children born to a religious Jewish family in Aufhausen, a village in southwestern Germany. Her father was a successful cattle dealer in the area. On May 8, 1903, at age 20, Betty married Max Lauchheimer, a cattle merchant and kosher butcher. They lived in a large house by an orchard in the village of Jebenhausen. Betty and Max had two children, Regina and Karl. 1933-39: In late 1938 Betty and Max were visiting their daughter in Kippenheim when police arrested Max and their son-in-law.…

-
Nazi Racism
ArticleNazi racism and racial antisemitism ultimately led to mass murder and genocide. Learn more about Nazi racial ideology.

-
Lila Lam
ID CardLila was born to a Jewish family in the largely Jewish city of Stanislawow. The Lam family owned an oil field and refinery, and Lila's father, who was trained as a lawyer, helped to manage the business. When it came time for Lila to begin first grade, her parents decided to have her tutored privately at home rather than have her attend an elementary school. 1933-39: The Jewish holidays were always special times. Although Lila's family wasn't religious, the holidays were wonderful opportunities for her…

-
Jeno Gabor Braun
ID CardThe son of a rabbi, Jeno was raised in the town of Sighet in Transylvania. The region was multi-ethnic, and Jeno grew up in a family that knew Yiddish, Hungarian, Romanian, German and Hebrew. During World War I, when Sighet was near the front, Jeno's family fled to Hungary. There Jeno met Eszter Mendel, whom he married after the war. The couple settled in the town of Cristuru-Secuiesc in Romania. 1933-39: As a jeweler, Jeno is one of only two watchmakers in Cristuru-Secuiesc; the other is a German who…

-
Juliana Nemeth
ID CardJuliana, who was born to a Jewish merchant family, lived in Szentes, a town in southeasten Hungary which was about 30 miles from the city of Szeged. She and her husband, Jeno, had three children—two married daughters, Barbara and Margit, and a son, Desider, who was a dentist in Szentes. Juliana and her husband owned a hardware and grocery store located on a busy inter-city roadway. 1933-39: Juliana and Jeno work hard in their store. The Depression of the 1930s was devastating, but things are starting to…

-
Bernard (Green) Greenspan
ID CardBernard was one of five children born to a Jewish family in the southern Polish town of Rozwadow. His father, a World War I veteran incapacitated as a result of the war, supported his family on his military pension. In the early 1930s Bernard completed high school and worked on the family farm. 1933-39: In 1934 Bernard was recruited into the Polish army and stationed in Lvov, where he ran a canteen. After three years there he returned to his family's farm outside Rozwadow to work. On September 24, 1939,…

-
Masza Tenenbaum
ID CardThe youngest of three children, Masza was born to Jewish parents living 35 miles east of Warsaw in the small predominantly Jewish town of Kaluszyn. Her father owned a shop where he sold cosmetics and non-prescription medicines. Masza was close friends with a group of Jewish teenagers who went to the same public school and who spent much of their free time and vacations together. 1933-39: Majlich, Sara, and the rest of Masza's group have always liked discussing politics as they strolled down the main…

-
Felicia Karo
ID CardFelicia grew up in a Jewish family living in a predominantly Catholic neighborhood in the large, industrial city of Lodz. Her father's side of the family had lived in Poland for 400 years. He was the principal of a Jewish secondary school for boys. Known affectionately by family and friends as Lusia, Felicia attended a bilingual Jewish school in which both Hebraic and Polish subjects were taught. 1933-39: When Felicia was 12 she heard a lot of bad things about the Nazis. A Polish-born German Jewish…

-
Selma Schwarzwald
ID CardBoth of Selma's Jewish parents, Daniel Schwarzwald and Laura Litwak, had been raised in the industrial city of Lvov. As many different nationalities lived in Lvov, Selma's mother and father could speak many languages--Polish, Russian, German and Yiddish. In running his successful lumber business, Daniel also occasionally used English. 1933-39: Selma's parents married in April 1935 and she was born two years later. Her father was afraid that there might be a war and wanted to move the family to safety in…
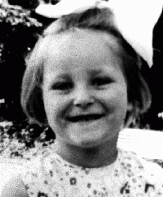
-
Ezra BenGershom
ID CardEzra was born to a Jewish family in the Bavarian city of Wurzburg. In the summer of 1929, his father, a third-generation rabbi, accepted a position as a district rabbi, guiding 12 congregations in Upper Silesia. In primary school, Ezra, who showed a keen interest in chemistry, was often harassed by his schoolmates for being Jewish. 1933-39: Because of his "Nordic" features, Ezra was able to frequent places where Jews couldn't go. In 1938, one year after he entered a Jewish secondary school in Berlin, the…

-
Margot Heumann
ID CardThe older of two girls, Margot was born to Jewish parents living in a village close to the Belgian border. The Heumanns lived above their general store. Across the street lived Margot's grandfather, who kept horses and cows in his large barn. When Margot was 4, her family moved to the city of Lippstadt. As a young girl, she learned to swim in the Lippe River, which flowed behind their garden. 1933-39: When Margot was 9, her family moved to the nearby city of Bielefeld, where she was enrolled in public…

-
Charles (Karel) Bruml
ID CardCharles was born to a Jewish family in Prague, the capital of Czechoslovakia. His father owned several shoe factories there. Prague's Jewish minority enjoyed a great deal of cultural freedom because of the new democratic Republic. Though antisemitism still existed in Czechoslovakia, Prague was a relatively tolerant city. 1933-39: Charles' father's business thrived in Prague, and they lived well. Charles enjoyed painting as a child and decided to study at an art school in the city. On the morning of March…

-
Fritz Silten
ID CardFritz was the youngest of two sons born to a Jewish family in the German capital of Berlin. In the late 1920s he earned a doctorate in chemistry and pharmacy. In 1931 he married Ilse Teppich, and in 1933 the couple had a daughter, Gabriele. 1933-39: Fritz worked in his father's pharmacy until 1938, when the Nazis forced them to sell the business for a fraction of its value to an "Aryan" German [Aryanization]. Leaving his parents behind was agonizing, but concern for the safety of his wife and daughter…

-
Jeno Brieger
ID CardJeno was born into a large, religious Jewish family in the village of Nagyhalasz in northeastern Hungary. The Briegers spoke Yiddish and Hungarian. After Jeno's mother died, his father remarried and the family moved to the town of Nyiregyhaza where his father owned and operated a hardware store. Nyiregyhaza had a Jewish population of 5,000. 1933-39: Jeno was the oldest son in a household of seven children. Nyiregyhaza was a rural town in which people still used horses and buggies. Jeno attended a…

-
Gyula (Gyuszi) Brieger
ID CardGyula was also known as Gyuszi. He was born into a large religious Jewish family in the village of Nagyhalasz in northeastern Hungary. The Briegers spoke both Yiddish and Hungarian. After Gyula's mother died, his father remarried and the family moved to the town of Nyiregyhaza, where his father owned and operated a hardware store. Nyiregyhaza had a Jewish population of 5,000. 1933-39: Gyula was the second oldest son in a household of seven children. Nyiregyhaza was a rural town in which people still used…

-
Bernard Krakauer
ID CardBernard was one of seven children born to a German-speaking, Jewish family in the small Moravian town of Mikulov in the central part of Czechoslovakia. The family later moved to the town of Hodonin where Bernard opened a dry-goods and clothing store. In 1899 he married Berta Koselova, and the couple had six children. During World War I Bernard served in the Austro-Hungarian army. 1933-39: In 1938 Bernard retired, and since none of his sons wanted to take over the business, Bernard sold it. He, his wife,…

-
Eva Miodelska
ID CardEva was the oldest of four children born to a Jewish family in the central Polish town of Lipsko, about 30 miles southeast of Radom. The family lived at #12 Casimirska Street and Eva attended a private Jewish primary school. Eva's father owned a factory that produced shoes made from leather and cork. 1933-39: In the early 1930s Eva began secondary school in Zwolen, a town about 20 miles to the north. In 1936 her father left for Argentina to settle the estate of his deceased sister. For the two years he…

-
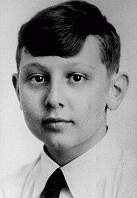
Peter Winternitz
ID CardPeter was the oldest of two children born to a Jewish family in the Czechoslovakian capital of Prague, a city with a Jewish community that dated back to the eleventh century. His family lived on Karlova Street in the city's Karlin district. Peter's father owned a wholesale business that sold floor coverings. 1933-39: As a boy, Peter was active in a Zionist sports organization, Maccabi Ha-Zair. The group also helped prepare youth to immigrate to Palestine [Aliyah Bet] by training them in agricultural work.…
-
Bernburg T4 Facility
ArticleBernburg was the fifth of six centralized killing centers established by German authorities within the context of the Nazi “euthanasia,” or T4, program.

-
Martin Niemöller: "First they came for..."
ArticleLearn about the origins and legacy of Pastor Martin Niemöller's famous postwar words, “First they came for the socialists, and I did not speak out…”

-
A notice sent by the American Consulate General in Berlin regarding immigration visas
DocumentA notice sent by the American Consulate General in Berlin to Arthur Lewy and family, instructing them to report to the consulate on July 26, 1939, with all the required documents, in order to receive their American visas. German Jews attempting to immigrate to the United States in the late 1930s faced overwhelming bureaucratic hurdles. It was difficult to get the necessary papers to leave Germany, and US immigration visas were difficult to obtain. The process could take years.

-
A chart detailing physical characteristics of a Romani (Gypsy) individual
DocumentA chart detailing physical characteristics of a Romani (Gypsy) individual, c. 1938. Dr. Robert Ritter and his team created extensive family trees and genealogical charts in order to identify, register, and classify all Romani people living in Nazi Germany. During the Nazi era, Dr. Robert Ritter was a leading authority on the racial classification of people pejoratively labeled “Zigeuner” (“Gypsies”). Ritter’s research was in a field called eugenics, or what the Nazis called “racial…

-
German invasion of Norway: Narvik
FilmGermany invaded Norway on April 9, 1940, simultaneously attacking Norway's coastal cities from Narvik in the far north to Oslo in the south. Narvik was the scene of fierce battles between German forces and the Allies, who landed troops by sea in support of the Norwegians. Narvik changed hands several times. However, British, French, and Polish forces were finally withdrawn in June 1940 due to the success of the German campaign in western Europe. German victory in Norway secured access to the North Atlantic…

-
Telford Taylor during Justice Case
FilmIn the Justice Case of the Subsequent Nuremberg Proceedings, nine officials from the German Ministry of Justice and seven members of the Nazi-era People's and Special Courts were charged with “judicial murder and other atrocities, which they committed by destroying law and justice in Germany, and then utilizing the emptied forms of legal process for the persecution, enslavement and extermination on a large scale.” In this footage from the trial, US prosecutor Telford Taylor describes the nature…

-
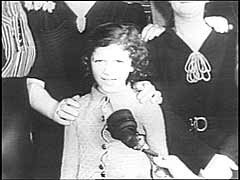
Air raid shelter in London during the Blitz
FilmAfter the defeat of France in June 1940, Germany moved to gain air superiority over Great Britain as a prelude to an invasion of Britain. During almost nightly German air raids (known as "the Blitz") on London, the civilian population of the city sought refuge--as shown in this footage--in air raid shelters and in London's subway system (called the "Underground" or the "Tube"). Despite months of air attacks, Germany was not able to destroy Britain's Royal Air Force (RAF). In the fall of 1940, the invasion…
-
Ruth Moser Borsos describes roll call (Appell) in Bergen-Belsen
Oral HistoryRuth moved to the Netherlands after Kristallnacht (the "Night of Broken Glass") in 1938. She and her father had permits to sail to the United States, but Germany invaded the Netherlands in May 1940 and they could not leave. Ruth was deported to the Westerbork camp in 1943 and to the Bergen-Belsen camp in Germany in 1944. After an exchange agreement with the Allies broke down, Ruth was interned near the Swiss border until liberation by French forces in 1945.

-
Tomasz (Toivi) Blatt describes the Izbica Jewish council (Judenrat) and German attacks (Aktionen) there
Oral HistoryAfter war began in September 1939, the Germans established a ghetto and Jewish council in Izbica. Tomasz's work in a garage initially protected him from roundups in the ghetto. In 1942 he tried to escape to Hungary, using false papers. He was caught but managed to return to Izbica. In April 1943 he and his family were deported to the Sobibor killing center. Tomasz escaped during the Sobibor uprising. He went into hiding, and worked as a courier in the Polish underground.

-
Hanne Hirsch Liebmann describes conditions in the Gurs camp
Oral HistoryHanne's family owned a photographic studio. In October 1940, she and other family members were deported to the Gurs camp in southern France. In September 1941, the Children's Aid Society (OSE) rescued Hanne and she hid in a children's home in Le Chambon-sur-Lignon. Her mother perished in Auschwitz. In 1943, Hanne obtained false papers and crossed into Switzerland. She married in Geneva in 1945 and had a daughter in 1946. In 1948, she arrived in the United States..

-
David (Dudi) Bergman recalls the importance of work for survival in the Plaszow labor camp
Oral HistoryThe Germans occupied David's town, previously annexed by Hungary, in 1944. David was deported to Auschwitz and, with his father, transported to Plaszow. David was sent to the Gross-Rosen camp and to Reichenbach. He was then among three of 150 in a cattle car who survived transportation to Dachau. He was liberated after a death march from Innsbruck toward the front line of combat between US and German troops.

-
Robert Wagemann describes secret Jehovah's Witness prayer meetings in Nazi Germany
Oral HistoryRobert and his family were Jehovah's Witnesses. The Nazis regarded Jehovah's Witnesses as enemies of the state for their refusal to take an oath of loyalty to Adolf Hitler, or to serve in the German army. Robert's family continued its religious activities despite Nazi persecution. Shortly before Robert's birth, his mother was imprisoned briefly for distributing religious materials. Robert's hip was injured during delivery, leaving him with a disability. When Robert was five years, he was ordered to report…

-
David Stoliar describes how he survived the sinking of the Struma
Oral HistoryIn 1936, David moved to Bucharest to live with his father. As Romania came under German influence, Romanian authorities introduced increasingly harsh measures against Jews. Antisemitic agitation increased and Jews came under attack in the streets of Bucharest and in other public places. David's father decided David should leave the country and arranged passage for him to Palestine. In December 1941, David left Romania from Constanta, a port city on the Black Sea, on the Struma, an old cattle boat. The…

-
Vladka (Fagele) Peltel Meed describes clandestine cultural activities in the Warsaw ghetto
Oral HistoryVladka belonged to the Zukunft youth movement of the Bund (the Jewish Socialist party). She was active in the Warsaw ghetto underground as a member of the Jewish Fighting Organization (ZOB). In December 1942, she was smuggled out to the Aryan, Polish side of Warsaw to try to obtain arms and to find hiding places for children and adults. She became an active courier for the Jewish underground and for Jews in camps, forests, and other ghettos.

-
Jerry von Halle describes hiding in Amsterdam
Oral HistoryIn 1933 Jerry's family moved from Hamburg to Amsterdam. The Germans invaded the Netherlands in 1940. In 1941, Jerry's brother perished in Mauthausen. Jerry and his parents went into hiding first in Amsterdam and then in a farmhouse in the south. The Gestapo (German Secret State Police) arrested Jerry's father in 1942, but Jerry and his mother managed to return to their first hiding place. They were liberated in Amsterdam by Canadian and Jewish Brigade troops.

-
Carla Heijmans Lessing describes the fear her family felt while in hiding
Oral HistoryAfter invading the Netherlands in 1940, the Germans imposed anti-Jewish measures. With the aid of a Catholic priest who helped Jews find hiding places, Carla, her mother, and her brother went into hiding in August 1942 to avoid deportation to work camps. They had to leave the hiding place after three months and with the priest's help found shelter in Delft with a Catholic family which had seven children. They remained in hiding there for 30 months, until liberation in May 1945.

-
Alisa (Lisa) Nussbaum Derman describes joining the Nekama (Revenge) Jewish partisan unit led by Josef Glazman in the Naroch Forest
Oral HistoryLisa was one of three children born to a religious Jewish family. Following the German occupation of her hometown in 1939, Lisa and her family moved first to Augustow and then to Slonim (in Soviet-occupied eastern Poland). German troops captured Slonim in June 1941, during the invasion of the Soviet Union. In Slonim, the Germans established a ghetto which existed from 1941 to 1942. Lisa eventually escaped from Slonim, and went first to Grodno and then to Vilna, where she joined the resistance movement. She…

-
Leo Schneiderman describes routine at the Ebensee camp
Oral HistoryThe Germans invaded Poland in September 1939. Leo and his family were confined to a ghetto in Lodz. Leo was forced to work as a tailor in a uniform factory. The Lodz ghetto was liquidated in 1944, and Leo was deported to Auschwitz. He was then sent to the Gross-Rosen camp system for forced labor. As the Soviet army advanced, the prisoners were transferred to the Ebensee camp in Austria. The Ebensee camp was liberated in 1945.

-
Abraham Lewent describes conditions in the Warsaw ghetto
Oral HistoryLike other Jews, the Lewents were confined to the Warsaw ghetto. In 1942, as Abraham hid in a crawl space, the Germans seized his mother and sisters in a raid. They perished. He was deployed for forced labor nearby, but escaped to return to his father in the ghetto. In 1943, the two were deported to Majdanek, where Abraham's father died. Abraham later was sent to Skarzysko, Buchenwald, Schlieben, Bisingen, and Dachau. US troops liberated Abraham as the Germans evacuated prisoners.

-
Ruth Berkowicz Segal describes deciding to leave Warsaw shortly after the outbreak of war
Oral HistoryWhen German forces invaded Poland in September 1939, Ruth's father fled to eastern Poland. Upon the Soviet occupation of eastern Poland, he fled to Lithuania. Ruth left Warsaw with two friends to find her father and later joined him in Vilna. After Soviet forces occupied Lithuania, Ruth and her father obtained transit visas for Japan, but only Ruth obtained a Soviet exit visa. Her father insisted she leave and not wait for him. Ruth traveled by the Trans-Siberian Railroad across the Soviet Union to…

-
Yonia Fain describes leaving Warsaw after the German invasion of Poland
Oral HistoryAfter World War I, Yonia's family moved to Vilna. Yonia studied painting and graduated from the Academy of Fine Arts in Vilna. When Germany invaded Poland in September 1939, Yonia was living with his wife in Warsaw. They fled to Brest-Litovsk in eastern Poland, occupied by Soviet forces in mid-September 1939. Then Yonia and his wife escaped to Vilna. After the Soviets occupied Vilna in June 1940, Yonia and his wife forged Japanese transit visas and left for Japan. In Japan, they were unable to obtain valid…

-
Johanna Gerechter Neumann describes how her family obtained visas to emigrate to Albania
Oral HistoryAmid intensifying anti-Jewish measures and the 1938 Kristallnacht ("Night of Broken Glass") pogrom, Johanna's family decided to leave Germany. They obtained visas for Albania, crossed into Italy, and sailed in 1939. They remained in Albania under the Italian occupation and, after Italy surrendered in 1943, under German occupation. The family was liberated after a battle between the Germans and Albanian partisans in December 1944.

-
Tomasz (Toivi) Blatt describes the Sobibor uprising
Oral HistoryTomasz was born to a Jewish family in Izbica. After the war began in September 1939, the Germans established a ghetto in Izbica. Tomasz's work in a garage initially protected him from roundups in the ghetto. In 1942 he tried to escape to Hungary, using false papers. He was caught but managed to return to Izbica. In April 1943 he and his family were deported to the Sobibor killing center. Tomasz escaped during the Sobibor uprising. He went into hiding and worked as a courier in the Polish underground.

