You searched for: 外贸谷歌竞价【TG飞机:@bapingseo】北京赛车1390x【TG电报:@bapingseo】廣東谷歌推廣產品哪家強【Telegram:@bapingseo】梦之城网站王者荣耀下注官网亚博网址版足猜彩怎样可以做到稳定盈利?7BtkWY/266272.html
<< Previous | Displaying results 201-250 of 280 for "外贸谷歌竞价【TG飞机:@bapingseo】北京赛车1390x【TG电报:@bapingseo】廣東谷歌推廣產品哪家強【Telegram:@bapingseo】梦之城网站王者荣耀下注官网亚博网址版足猜彩怎样可以做到稳定盈利?7BtkWY/266272.html" | Next >>
-
Blimcia Lische
ID CardBlimcia's parents were religious Jews. Her father, Shaya David, and her mother, Malcia Saleschtz, had settled in Kolbuszowa, where Blimcia's mother had been raised. There, Malcia's father bought the newlyweds a home and started his new son-in-law in the wholesale flour business. 1933-39: Blimcia was born in 1938, and was raised among many aunts, uncles and cousins. Around Blimcia's first birthday, Germany invaded Poland and soon reached Kolbuszowa. Polish soldiers on horses tried to fight against the…

-
Yves Oppert
ID CardYves' mother died when he was 7, and he grew up in the home of his grandfather, who was the chief Ashkenazi rabbi of Paris. Yves became a successful businessman, owning a chain of department stores. He was an avid mountain climber and liked to play tennis and to race cars and motorcycles. As a young man, Yves did his military service in France's alpine corps. 1933-39: In 1934 Yves married Paulette Weill, and the couple had two daughters, Nadine in 1935 and Francelyn in 1939. He was called up by the French…

-
Magdalena Kusserow
ID CardOne of 11 children, Magdalena was raised as a Jehovah's Witness. When she was 7, her family moved to the small town of Bad Lippspringe. Her father was a retired postal official and her mother was a teacher. Their home was known as "The Golden Age" because it was the headquarters of the local Jehovah's Witness congregation. By age 8 Magdalena could recite many Bible verses by heart. 1933-39: The Kusserow's loyalty was to Jehovah, so the Nazis marked them as enemies. At 12 Magdalena joined her parents and…

-
Thomas Pfeffer
ID CardThomas' father, Heinz, was a German-Jewish refugee who had married Henriette De Leeuw, a Dutch-Jewish woman. Frightened by the Nazi dictatorship and the murder of Heinz's uncle in a concentration camp, they immigrated to the Netherlands when Henriette was nine months pregnant with Thomas' older brother. They settled in Amsterdam. 1933-39: Thomas, also known as Tommy, was born 18 months after his older brother, Jan-Peter. In 1939 the parents and brother of Tommy's father joined them in the Netherlands as…

-
Nazi Racism
ArticleNazi racism and racial antisemitism ultimately led to mass murder and genocide. Learn more about Nazi racial ideology.

-
Barbara Nemeth Balint
ID CardBarbara was born to a middle-class Jewish family in southeast Hungary. Her father had a store that carried grocery and hardware items. Barbara had a sister named Margit and a brother named Desider. In 1928 Barbara married Istvan Geroe and moved to the town of Torokszentmiklos. Her son, Janos, was born there a year later. 1933-39: In 1933 Barbara divorced and returned with 3-year-old Janos to her parents' home in the town of Szentes. She helped run her parents' store, which was located on a busy inter-city…

-
Janos Geroe
ID CardJanos was the only child born to a Jewish family in the small agricultural city of Torokszentmiklos, about 65 miles southeast of Budapest. His father, who had a degree in pharmacology, joined his family's grain exporting business. 1933-39: In 1933, when Janos was 4 years old, his parents divorced. According to Hungarian law, Janos was to live with his mother until he was 7 and then return to his father. Janos moved with his mother to her hometown of Szentes, where he began studying at a religious primary…

-
Shaye Rothkopf
ID CardShaye's town in the province of Lodz had a Jewish community that comprised almost one-third of the town's population. Shaye was very young when his father died during World War I. Afterwards, his grandparents helped to support his family. When Shaye was a teenager, his mother died. He and his siblings then lived with their grandparents. 1933-39: Swimming was Shaye's favorite pastime and he'd go with his friends to the banks of the Vistula River on every possible occasion. He worked in Lodz for a company…

-
Rifka Fass
ID CardRifka was the oldest of three children born to a Jewish family in the Polish town of Ulanow. Ulanow's Jewish community had many of its own organizations and maintained a large library. From the age of 3, Rifka attended a private religious school for girls where she learned Jewish history and Hebrew. At 7 she started public school. Rifka's father worked as a tailor. 1933-39: In 1935 Rifka's father went to America to find a job so his family could later join him. While waiting for immigration papers,…

-
Johanna Falkenstein Heumann
ID CardThe oldest of five children, Johanna was born to Jewish parents living in a small town near Cologne. Her father owned a cigar factory. After Johanna graduated from high school, she worked in a bank in Cologne. At 22 she married Carl Heumann and the couple settled in the village of Hellenthal near the Belgian border. There they owned a general store. The couple had two daughters, Margot and Lore. 1933-39: A year ago Johanna's family moved to nearby Bielefeld, and she enrolled Margot and Lore in the city's…

-
Edek Blonder
ID CardThe Blonder family lived in a two-room apartment in the back of a store. Edek was the third of eight children. His father eked out a meager living by tutoring students in Jewish subjects, and beginning in 1930 he worked distributing food vouchers to the poor. 1933-39: After graduating from secondary school, Edek was invited to play soccer professionally on the local Club Maccabi team, which was part of a Jewish soccer league. Club Maccabi arranged for him to attend trade school to learn cabinet making at…

-
Leon Kusmirek
ID CardLeon was the oldest of two boys born to a Jewish family in Zgierz, a central Polish town in the heart of Poland's textile producing region. The family lived at 15 Konstantynowska Street. Leon's father worked at a textile factory. At age 7, Leon began attending public school in the morning and religious school in the afternoon. 1933-39: On Friday, September 1, 1939, Leon's mother had just returned from the market when the family saw German planes. On Sunday they flew over again, lower, panicking the city.…

-
Moses Rechnitz
ID CardThe younger of two children, Moses was born to Jewish parents living in the southwestern Polish town of Bedzin. When he was 7, his family moved to the nearby city of Katowice where his father had a wholesale leather business. The Rechnitzes lived in a three-bedroom, upper-floor apartment on Jordana Street. Moses attended a Polish elementary school and also received religious instruction. 1933-39: In secondary school, Moses was one of the only Jewish pupils. He first encountered antisemitism when a teacher…

-
Adela Low
ID CardAdela, known as Udl to her family, was one of four children born to a Jewish family in the Polish town of Ulanow. Her father was a landowner and cattle merchant, transporting calves from the Ulanow area for sale in other towns in the region. From the age of 3, Adela attended a private religious school for girls where she learned Jewish history and Hebrew. At age 7 she began public school. 1933-39: Adela came from a charitable family; when her mother baked challah, a special bread for the Jewish Sabbath,…

-
Herschel Low
ID CardHerschel was the oldest of four children born to a Jewish family in the Polish town of Ulanow. His father was a landowner and cattle merchant who transported calves from the Ulanow area for sale in other towns. Herschel attended a religious school from the age of 3, and started public school at age 7. 1933-39: Since Herschel was skilled with his hands, his father got him a job weaving reed baskets after he graduated from high school. Herschel was also a member of a Jewish youth organization, Benei Akiva,…

-
Mieczyslaw (Marek) Madejski
ID CardMieczyslaw was the eldest of three sons born to well-to-do Roman Catholic parents in Poland's capital of Warsaw. His father was a real estate developer and his mother was a housewife. Mieczyslaw, or Mieteck as he was nicknamed, began attending public elementary school in 1930 when he was 7 years old. 1933-39: Mieczyslaw's father urged him to study either German or Russian because he thought it was likely that there would be a German or Soviet invasion. Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. During…

-
Refugees Today
ArticleAs of mid-2022, there were about 27 million refugees. Learn more about these refugees, the violence they face, and the global impact of the refugee crisis.

-
Dismissal letter from the Berlin transit authority
DocumentA letter written by the Berlin transit authority (Berliner Verkehrs Aktiengesellschaft) to Viktor Stern, informing him of his dismissal from his post with their agency as of September 20, 1933. This action was taken to comply with provisions of the Law for the Restoration of the Professional Civil Service. On April 7, the German government issued the Law for the Restoration of the Professional Civil Service (Gesetz zur Wiederherstellung des Berufsbeamtentums), which excluded Jews and political opponents…

-
Roosevelt announces aid for Britain
FilmAlthough constrained by powerful isolationist sentiment in the United States, President Roosevelt was determined to help democratic Great Britain continue the war against Nazi Germany. Even as he promised to keep the United States neutral in the European war, Roosevelt ordered the expansion of military construction and pledged--as shown in this footage--that the United States would serve as the "great arsenal of democracy." In March 1941, Congress approved Lend-Lease aid for Britain. Britain ultimately…

-
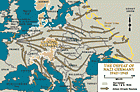
Defeat of Nazi Germany, 1942-1945
MapBeginning in 1938, the Nazis increased their territorial control outside of Germany. By 1942, three years into World War II, Nazi Germany reached the peak of its expansion. At the height of its power, Germany had incorporated, seized, or occupied most of the continent. However, also in 1942, the Allied Powers started to systematically bomb Germany. They would continue to do so until Germany's surrender in 1945, weakening the war effort and demolishing cities. Slowly, the Allied Powers began pushing…
-
Elie Wiesel Timeline and World Events: 1928–1951
ArticleSurvivor Elie Wiesel devoted his life to educating the world about the Holocaust. Learn about key events in the world and his life from 1928–1951.

-
Auschwitz: Key Dates
ArticleExplore a timeline of key events in the history of the Auschwitz camp complex in German-occupied Poland.

-
Fürstengrube
ArticleLearn about Fürstengrube subcamp of Auschwitz, including its establishment, administration, prisoner population, and forced labor and conditions in the camp.
-
World War I: Treaties and Reparations
ArticleAfter the devastation of WWI, the victorious western powers imposed a series of treaties upon the defeated nations. Learn about the treaties and their impact.

-
Theresienstadt: Key Dates
ArticleExplore key dates in the history of the Theresienstadt camp/ghetto, which served multiple purposes during its existence from 1941-45.

-
Tehran Children
ArticleLearn about the “Tehran Children,” a group of Polish-Jewish refugees. In 1942, they were resettled from the Soviet Union to Palestine via Iran.

-
Hajj Amin al-Husayni: Key Dates
ArticleKey dates associated with Hajj Amin al-Husayni, former Mufti of Jerusalem who participated in a pro-Axis coup in Iraq in 1941. Explore further

-
Adolf Hitler: 1930-1933
ArticleUnder Adolf Hitler's leadership, the Nazi regime was responsible for the mass murder of 6 million Jews and millions of other victims. Learn about Hitler in the years 1930-1933.

-
Julien Bryan
ArticleUS filmmaker and photographer Julien Bryan was one of the few western photographers left in Warsaw upon the German invasion of Poland in September 1939.

-
Anti-Jewish Legislation in Prewar Germany
ArticleNazi anti-Jewish laws began stripping Jews of rights and property from the start of Hitler’s dictatorship. Learn about antisemitic laws in prewar Germany.

-
Blechhammer
ArticleThe Germans established the Blechhammer camp as a subcamp of Auschwitz in April 1941. Learn about the camp's history and conditions there.
-
University Student Groups in Nazi Germany
ArticleNazi student groups played a key role in aligning German universities with Nazi ideology and in solidifying Nazi power.

-
The Harrison Report
ArticleThe Harrison Report criticized conditions in the DP camps, called for changes in the treatment of Jewish DPs, and recommended allowing them to emigrate to the US and Palestine.

-
Children's Aid Society (Oeuvre de Secours aux Enfants)
ArticleDuring WWII, the Children’s Aid Society (OSE) operated 14 children's homes throughout France to save Jewish children from internment and deportation to killing centers.

-
Warsaw Uprising
ArticleThe 1944 Warsaw uprising was the single largest military effort undertaken by resistance forces to oppose German occupation during World War II.

-
Nazi Party Platform
ArticleThe Nazi Party Platform was a 25-point program for the creation of a Nazi state and society. Hitler presented it at the Hofbräuhaus Beerhall in Munich in February 1920.

-
Melk
ArticleLearn about the establishment of and conditions in Melk, a subcamp of the Mauthausen camp system in Austria.

-
Gleichschaltung: Coordinating the Nazi State
ArticleGleichschaltung is the German term applied to the Nazification of all aspects of German society following the Nazi rise to power in 1933.

-
Aryan
ArticleAdolf Hitler and the Nazi Party adapted, manipulated, and radicalized the unfounded belief in the existence of an "Aryan race." Learn about the term Aryan.

-
The Nazification of the German Police, 1933–1939
ArticleThe Nazis utilized the German police for mass repression and genocide. Learn more about the Nazification of the police force from 1933-1939.

-
Rudolf (Rezső) Kasztner
ArticleLearn more about Rudolf (Rezső) Kasztner (1906-1957) during World War II and his controversial efforts to help refugees escape Hungary in 1944.

-
The Vélodrome d'Hiver (Vél d'Hiv) Roundup
ArticleThe Vélodrome d'Hiver (or Vél d'Hiv) roundup was the largest French deportation of Jews during the Holocaust. It took place in Paris on July 16–17, 1942.

-
Earl G. Harrison: Biography
ArticleEarl G. Harrison, Commissioner for Immigration and Naturalization under FDR, is known for a report harshly criticizing the US and British treatment of Jewish DPs.

-
Subsequent Nuremberg Proceedings, Case #9, The Einsatzgruppen Case
ArticleThe Einsatzgruppen Case was Case #9 of 12 Subsequent Nuremberg Proceedings against leading German industrialists, military figures, SS perpetrators, and others.

-
US Troops Capture Ludendorff Railroad Bridge at Remagen
Timeline EventMarch 7, 1945. On this date, the US 9th Armored Division captured the Ludendorff Railroad Bridge at Remagen, between Koblenz and Bonn, Germany.

-
The 45th Infantry Division during World War II
ArticleThe 45th Infantry Division participated in major WWII campaigns and is recognized for liberating the Dachau concentration camp in 1945.
-
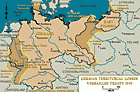
Treaty of Versailles
ArticleLearn about the provisions and impact of the 1919 Treaty of Versailles, including the "War Guilt Clause" which held Germany responsible for starting World War I.
-
Timeline of the German Military and the Nazi Regime
ArticleKey dates illustrating the relationship between Germany’s professional military elite and the Nazi state, and the German military’s role in the Holocaust.

-
The United States and the Nazi Threat: 1933–37
ArticleLearn about responses in the United States to reports about Nazi anti-Jewish policies and violence against Jews from 1933–37.

-
Selma (Wijnberg) Engel describes forced labor sorting the clothing and possessions of people deported to Sobibor
Oral HistorySelma was the youngest of four children born to Jewish parents. When she was 7, Selma and her family moved to the town of Zwolle where her parents ran a small hotel. When the Germans invaded the Netherlands in 1940, they confiscated the hotel. The family had to live in a poor Jewish section of the town. Selma went into hiding but was betrayed and then sent to the Westerbork camp. In April 1943 she was deported to Sobibor, where she worked in the clothes sorting area. There, the prisoners tried to pocket…

