You searched for: 荷兰加勒比区国外灰产【TG飞机:@bapingseo】北京app推廣兼職【TG电报:@bapingseo】外貿新產品推廣信【Telegram:@bapingseo】彩库宝典下载40版本安卓免费版凤凰app软件下载金沙电玩城手机版官网?dD4scE/606982.html
<< Previous | Displaying results 51-100 of 105 for "荷兰加勒比区国外灰产【TG飞机:@bapingseo】北京app推廣兼職【TG电报:@bapingseo】外貿新產品推廣信【Telegram:@bapingseo】彩库宝典下载40版本安卓免费版凤凰app软件下载金沙电玩城手机版官网?dD4scE/606982.html" | Next >>
-
Johanna Gerechter Neumann describes her family's arrival in Bologna and aid received from Italian students before emigrating to Albania
Oral HistoryAmid intensifying anti-Jewish measures and the 1938 Kristallnacht ("Night of Broken Glass") pogrom, Johanna's family decided to leave Germany. They obtained visas for Albania, crossed into Italy, and sailed in 1939. They remained in Albania under the Italian occupation and, after Italy surrendered in 1943, under German occupation. The family was liberated after a battle between the Germans and Albanian partisans in December 1944.

-
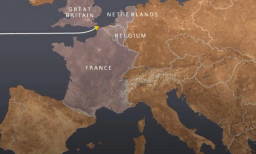
The Voyage of the St. Louis
Animated MapView an animated map describing the voyage of the St. Louis and the fate of its passengers, Jewish refugees from Nazi Germany in May-June, 1939.
-
Martin Niemöller: Biography
ArticleProtestant pastor Martin Niemöller emerged as an opponent of Adolf Hitler and was imprisoned in camps for 7 years. Learn about the complexities surrounding his beliefs.

-
Voyage of the St. Louis
ArticleIn May 1939, the German transatlantic liner St. Louis sailed from Germany to Cuba. Most of the passengers were Jews fleeing Nazi Germany. Learn more about the voyage.

-
1942: Key Dates
ArticleExplore a timeline of key events during 1942 in the history of Nazi Germany, World War II, and the Holocaust.

-
Halle
ArticleHalle an der Saale was a satellite camp of Buchenwald concentration camp. It was established by the Nazis in Saxony, Germany in 1941.
-
Maria Schimek Dicker
ID CardMaria's Jewish family lived in a Slovakian manufacturing town. When her father's match factory failed, the family of seven moved to Budapest. In her early twenties, Maria opened a flower shop, but she gave it up when she married and moved to Ujpest, outside Budapest. Maria then stayed at home to raise her five children. Her husband owned a large furniture store, and she often gave him business advice. 1933-39: Maria loves having all her grown children gathered around her at the dinner table, enjoying her…

-
Feliks Bruks
ID CardFeliks was the only child of Catholic parents living in Czarnkow, a town close to the German border, some 40 miles north of Poznan. Czarnkow was situated on the Notec River. Feliks' parents owned a mineral water, soda and beer factory. They delivered their goods by horse and wagon to towns throughout the area. His parents also owned a restaurant and 120 acres of farmland. 1933-39: In 1937 Feliks entered the University of Poznan to study pharmacy. His education was cut short when the German army invaded…

-
Moishe Menyuk
ID CardMoishe was born to a Jewish family in the village of Komarovo, which until 1918 was part of the Russian Empire. At 18, he was drafted into the Russian army and fought in World War I. He was captured by the Germans, and while a POW, learned German. After the war he returned to Komarovo, which by then was part of Poland. He supported his family by farming and managing an estate for a Pole from Warsaw. 1933-39: The few Jews of Komarovo got along well with the Ukrainians. Moishe even played the fiddle at…

-
Pola Nussbaum
ID CardPola was born to a Jewish family in a small town [in Poland] about three miles from the German border. Her family had lived there for generations. Pola's father exported geese and other goods to Germany; her mother owned a fabric store. They lived with Pola's grandmother in a large, single-level, gray stucco house. Raczki had a small Jewish community with a Hebrew school that Pola attended. 1933-39: In 1937 Pola began secondary school in the town of Suwalki. She excelled in math, and hoped to study…
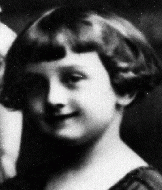
-
Elsa (Eliska) Skutezka Kulkova
ID CardElsa was the eldest of three children born to Jewish parents in Brno, the capital of Moravia, where her father ran a successful shipping company. In 1920 she graduated from a German-language secondary school. She married and moved to Bratislava, but the marriage was unsuccessful and Elsa returned to Brno in 1926, where she opened a millinery business. 1933-39: On May 24, 1933, Elsa married Robert Kulka and the couple settled in Robert's hometown of Olomouc. Their son, Tomas, was born a year and a day…
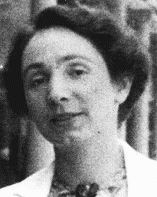
-
Ethel Stern
ID CardEthel was born to a Jewish family living in Warsaw. When she was 9, her family moved to the town of Mogielnica, about 40 miles southwest of Warsaw. Ethel's father spent much of his time studying religious texts. His wife managed the family liquor store. Ethel attended public school during the day and was tutored in religious studies in the evening. 1933-39: Ethel had always wanted to be a teacher. At age 14, after attending religious school in Lodz, she began to teach in the town of Kalisz, where her…

-
Wilek Loew
ID CardWilek was the son of Jewish parents living in Lvov, a large city in southeastern Poland. His family owned and operated a honeywine winery. Although they lived amongst Poles and Ukrainians, Wilek's family spoke Hebrew, German and Polish at home and were among Lvov's Jewish intelligentsia. When Wilek was 4, his father died of a heart attack. 1933-39: Jews were often discriminated against in Poland. They found it hard to gain access to schools and jobs. In 1939 Wilek managed to pass the entrance exam and…

-
Ben Stern
ID CardBen was born to Jewish parents in Warsaw. When Ben was 7, his family moved to Mogielnica, about 40 miles from Warsaw. Ben's father spent much of his time studying religious texts. His wife managed the family liquor store. Ben attended public school during the day and was tutored in religious studies in the evening. 1933-39: After attending school in Warsaw, Ben returned home to help in the family's liquor store. One day, there was a mass demonstration in town. People chanted, "Don't buy from the Jews!"…

-
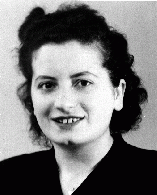
Henia Ring
ID CardThe youngest of two children, Henia was born to a Jewish family in the town of Krzepice. By the early 1930s, the Jewish population of Krzepice comprised more than 40 percent of the town's inhabitants. Henia's father made his living trading cattle in the area. Henia attended a public elementary school. 1933-39: On September 1, 1939, the Germans invaded Poland; a day later, they entered Henia's town. Her family tried to escape to Warsaw but the German forces quickly overtook them and ordered them back to…
-
Ilse Luise Citroen Ledermann
ID CardIlse was one of four children born to a Dutch-Jewish father and a German-Jewish mother. In 1924 she married Franz Ledermann, a successful lawyer who was 15 years her senior. The couple made their home in Berlin, where they raised two daughters, Barbara and Susanne. 1933-39: The Nazis came to power in January 1933. While the Ledermanns were vacationing in Holland that summer, Ilse's Dutch cousin advised her not to return to Germany. Franz was reluctant to remain in Holland without a job, but when the Nazis…

-
Dorotka Goldstein
ID CardDorotka was the youngest of three children in a Jewish family. Her father was the director of the Jewish Telegraphic Agency in Warsaw and worked for a popular newspaper. An avid Zionist, he had traveled to Palestine. 1933-39: Dorotka's father established a soup kitchen in Warsaw for Jewish refugees who had fled from Germany. In September 1939 Dorotka was supposed to begin first grade when war broke out. Her father escaped to Vilna with other Jewish leaders. People were suffering, but she didn't understand…
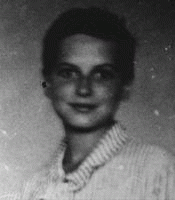
-
Refugees Today
ArticleAs of mid-2022, there were about 27 million refugees. Learn more about these refugees, the violence they face, and the global impact of the refugee crisis.

-
Bernburg T4 Facility
ArticleBernburg was the fifth of six centralized killing centers established by German authorities within the context of the Nazi “euthanasia,” or T4, program.

-
Edward Adler describes forced labor and conditions in the Sachsenhausen camp
Oral HistoryEdward was born to a Jewish family in Hamburg. In 1935, the Nuremberg Laws prohibited marriage or sexual relations between German non-Jews and Jews. Edward was then in his mid-twenties. Edward was arrested for dating a non-Jewish woman. Classified as a habitual offender, he was later deported to the Sachsenhausen concentration camp, near Berlin. He was forced to perform hard labor in construction projects. Edward had married shortly before his imprisonment, and his wife made arrangements for their…

-
Vladka (Fagele) Peltel Meed describes clandestine cultural activities in the Warsaw ghetto
Oral HistoryVladka belonged to the Zukunft youth movement of the Bund (the Jewish Socialist party). She was active in the Warsaw ghetto underground as a member of the Jewish Fighting Organization (ZOB). In December 1942, she was smuggled out to the Aryan, Polish side of Warsaw to try to obtain arms and to find hiding places for children and adults. She became an active courier for the Jewish underground and for Jews in camps, forests, and other ghettos.

-
William Denson describes postwar trials of concentration camp personnel
Oral HistoryWilliam Denson graduated from the US Military Academy at West Point in 1934 and attended Harvard Law School. He returned to West Point to teach law from 1942 until 1945. In January 1945, Denson accepted the position of Judge Advocate General (JAG) in Europe and was assigned to US Third Army headquarters in Germany. He took part in more than 90 trials against Germans who had committed atrocities against downed American pilots. In August 1945, Denson became chief prosecutor for the US government at the…

-
Le Chambon-sur-Lignon
ArticleFrom 1940 to 1944, Le Chambon-sur-Lignon and neighboring villages provided shelter to some 5,000 people, among them Jews fleeing persecution.

-
Kovno
ArticleKovno had a rich and varied Jewish culture. Learn about the Soviet and German occupations of Kovno, ghettoization, secret archives, and resistance in Kovno during WWII and the Holocaust.

-
Ravensbrück
ArticleLearn about conditions and the treatment of prisoners in Ravensbrück, the largest concentration camp for women in the German Reich.

-
Refuge in Latin America
ArticleBetween 1933-1945, Latin American governments officially permitted approx. 84,000 Jewish refugees. Learn more about Latin America refugee policy.

-
American Jewish Joint Distribution Committee and Refugee Aid
ArticleA relief organization, the American Jewish Joint Distribution Committee (JDC or Joint) was established in 1914. Learn about its activities before, during, and after WWII.

-
Herzogenbusch Subcamps
ArticleLearn about the subcamps of the SS-established Herzogenbusch concentration camp in the Netherlands, including Amersfoort, Arnheim, Eindhoven, and others.
-
Berlin-Marzahn (camp for Roma)
ArticleThe Berlin-Marzahn camp was established a few miles from Berlin's city center, for the detention of Roma, on the eve of the 1936 summer Olympics.

-
Melk
ArticleLearn about the establishment of and conditions in Melk, a subcamp of the Mauthausen camp system in Austria.

-
Communism
ArticleCommunist ideas spread rapidly in Europe during the 19th and 20th centuries, offering an alternative to both capitalism and far-right fascism and setting the stage for a political conflict with global repercussions.

-
The Armenian Genocide (1915-16): In Depth
ArticleLearn more about the Armenian Genocide, which was the physical annihilation of ethnic Armenian Christians living in the Ottoman Empire between 1915-1916.

-
Gerda Blachmann Wilchfort describes the mood of passengers on the "St. Louis" after they were denied entry into Cuba
Oral HistoryGerda and her parents obtained visas to sail to Cuba on the "St. Louis" in May 1939. When the ship arrived in Havana harbor, most of the refugees were denied entry and the ship had to return to Europe. Gerda and her parents disembarked in Belgium. In May 1940, Germany attacked Belgium. Gerda and her mother escaped to Switzerland. After the war, they were told that Gerda's father had died during deportation.

-
The United States and the Holocaust, 1942–45
ArticleWhy did the United States go to war? What did Americans know about the “Final Solution”? How did Americans respond to news about the Holocaust? Learn more.

-
Kristallnacht
ArticleOn November 9–10, 1938, the Nazi regime coordinated a wave of antisemitic violence. This became known as Kristallnacht or the "Night of Broken Glass." Learn more

-
Benjamin (Beryl) Ferencz describes early war crimes investigations
Oral HistoryBen was born in a small village in the Carpathian Mountains of Transylvania in Romania. When he was an infant, his family moved to the United States. Ben attended Harvard University, where he studied criminal law. Ben graduated from Harvard University Law School in 1943. He joined a US anti-aircraft artillery battalion that was training in preparation for an Allied invasion of western Europe. At the end of World War II in Europe, Ben was transferred to the war crimes investigation branch of the US Army. He…

-
Edward Adler recalls forced labor and conditions in the Sachsenhausen camp
Oral HistorySeveral of the IMT defendants were charged with exploiting concentration camp inmates for forced labor under harsh conditions, like those described here by Holocaust survivor Edward Adler. Edward was born to a Jewish family in Hamburg. In 1935, the Nuremberg Laws prohibited marriage or sexual relations between German non-Jews and Jews. Edward was then in his mid-twenties. Edward was arrested for dating a non-Jewish woman. Classified as a habitual offender, he was later deported to the Sachsenhausen…

-
Gerda Haas describes postwar reunion with her father in the United States
Oral HistoryGerda was raised in a religious family in the small town of Ansbach, Germany, where her father was the Jewish butcher. She attended German schools until 1936, and then moved to Berlin to attend a Jewish school. She returned to her hometown after Kristallnacht in November 1938. Her family was then ordered to move to Munich, and in July 1939 her father left for England and then the United States. He was unable to arrange for the rest of his family to join him. Gerda moved to Berlin in 1939 to study nursing.…

-
Art and Survival: György Beifeld's Visual Memoir from the Russian Front, 1942–1943
ArticleGyörgy Beifeld, a Jewish conscript in the Hungarian army, created a visual memoir of his experiences on the eastern front in 1942–1943 as a member of a forced-labor battalion .

-
The Holocaust in Macedonia: Deportation of Monastir Jewry
ArticleIn March 1943, Bulgarian authorities transported the entire Jewish community of Monastir to a transit camp from which they were deported to Treblinka.

-
Belzec
ArticleBelzec was the first of three killing centers in Operation Reinhard, the SS plan to murder almost two million Jews living in the German-administered territory of occupied Poland.

-
Sobibor
ArticleTo carry out the mass murder of Europe's Jews, the Nazis established killing centers that used assembly-line methods of murder. Sobibor was among these facilities.

-
Mannschafts-Stammlager (Stalag) IX B
ArticleIn 1939, the Nazis established the Mannschafts-Stammlager (Stalag) IX B camp in Germany. Learn more about the camp’s history, prisoners, and liberation.
-
Charles E. Coughlin
ArticleCharles Coughlin, Catholic priest and populist leader, promoted antisemitic and pro-fascist views. In the 1930s, he was one of the most influential public figures in the US.

-
Japanese American Relocation
ArticleLearn more about the forcible relocation of some 120,000 people of Japanese descent living in the US to “relocation centers.”

-
Elie Wiesel
ArticleElie Wiesel was a human rights activist, author, and teacher who reflected on his experience during the Holocaust in more than 40 books. Learn more.

-
Deceiving the Public
ArticleThe Nazis frequently used propaganda to disguise their political aims and deceive the German and international public. Learn more.

-
Börgermoor Camp
ArticleBörgermoor was part of the Nazi regime’s early system of concentration camps. It was located in the Emsland region of Prussia.
-
Hodonín U Kunštátu (Hodonín bei Kunstadt) (Roma camp)
ArticleIn March 1942, the Hodonin camp was classified as a camp for Roma. It was a transfer station during deportation to Auschwitz-Birkenau. Learn about the camp and its history.

-
The United States and the Refugee Crisis, 1938–41
ArticleNazi Germany’s territorial expansion and the radicalization of Nazi anti-Jewish policies triggered a mass exodus. Learn about the US and the refugee crisis of 1938–41.

