You searched for: 谷歌优化神器app【TG飞机:@bapingseo】代googleseo优化投放专业【TG电报:@bapingseo】投資理財盤網站源碼【Telegram:@bapingseo】彩票注册送50元彩金凤凰彩票争8邀请码注册九五至尊网址?h6B20B/i0PEux.html
<< Previous | Displaying results 201-250 of 367 for "谷歌优化神器app【TG飞机:@bapingseo】代googleseo优化投放专业【TG电报:@bapingseo】投資理財盤網站源碼【Telegram:@bapingseo】彩票注册送50元彩金凤凰彩票争8邀请码注册九五至尊网址?h6B20B/i0PEux.html" | Next >>
-
Death Marches
ArticleAs Allied forces approached Nazi camps in the last months of WWII, the SS organized brutal “death marches” (forced evacuations) of concentration camp inmates.

-
Tarnow
ArticleLearn about the prewar Jewish community of Tarnow, German occupation, deportations and killings of the Jewish population, ghettoization, and resistance.

-
Riga
ArticleGerman forces occupied Riga, Latvia in July 1941. Learn more about the establishment of the Riga ghetto, mass shootings of Jews, and Jewish resistance.

-
Life in the Ghettos
ArticleDuring the Holocaust, Jews were forced into ghettos with terrible living conditions, overcrowding, and starvation. Learn more about life in the Lodz ghetto.

-
Nuremberg Trials
ArticleTrials of top surviving German leaders for Nazi Germany’s crimes began in Nuremberg after World War II. Read about the Nuremberg trials.

-
1945: Key Dates
ArticleExplore a timeline of key events during 1945 in the history of Nazi Germany, World War II, the Holocaust, and liberation and the aftermath of the Holocaust.

-
Flossenbürg: Key Dates
ArticleExplore a timeline of the history of the Flossenbürg camp in the Nazi camp system from its establishment in 1938 until liberation in 1945.

-
The Biological State: Nazi Racial Hygiene, 1933–1939
ArticleBetween 1933-1939, Nazi eugenics and racial hygiene led to policies like mass sterilization and criminalizing marriage between Jews and non-Jews.

-
The Movement to Boycott the Berlin Olympics of 1936
ArticleSoon after Hitler came to power, debates began outside Germany about taking part in Olympics hosted by the Nazi regime. Learn more about calls to boycott the Games.

-
Althammer
ArticleThe Germans established the Althammer camp in September 1944. It was a subcamp of Auschwitz. Read more about the camp's history and conditions there.
-
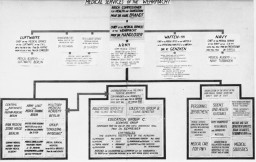
The Nuremberg Code
ArticleLeading German physicians and administrators were put on trial for their role during the Holocaust. The resulting Nuremberg Code was a landmark document on medical ethics. Learn more
-
King Christian X of Denmark
ArticleDid King Christian X of Denmark wear a yellow star in support of the Danish Jews? Read more about the historical truth behind the legend.
-
George Kadish
ArticleAt great risk, George Kadish secretly documented life in the Kovno ghetto in Lithuania, creating a key photographic record of ghetto life during the Holocaust.
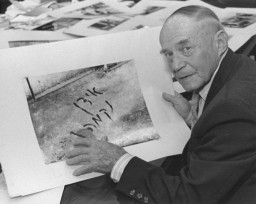
-
Soviet and US Troops Meet at Torgau
Timeline EventApril 25, 1945. On this date, Soviet and American troops met at Torgau, Germany.

-
Jakob Frenkiel
ID CardJakob was one of seven boys in a religious Jewish family. They lived in a town 50 miles west of Warsaw called Gabin, where Jakob's father worked as a cap maker. Gabin had one of Poland's oldest synagogues, built of wood in 1710. Like most of Gabin's Jews, Jakob's family lived close to the synagogue. The family of nine occupied a one-room apartment on the top floor of a three-story building. 1933-39: On September 1, 1939, just a few months before Jakob turned 10, the Germans started a war with Poland.…

-
Welwel Kisielnicki
ID CardWelwel lived with his wife, Feiga, and their three children in the small, predominantly Jewish town of Kaluszyn, which was 35 miles east of Warsaw. The Kisielnickis were religious and spoke Yiddish in their home. Welwel was a merchant and often traveled, by horse and wagon, to Warsaw on business. 1933-39: The Kisielnicki family's hopes that the war wouldn't reach Kaluszyn have been shattered. Last week, a German plane flew over their town and dropped a bomb on people waiting in line outside a bakery.…

-
Rojske Kisielnicki Sadowsky
ID CardThe second of three children, Rojske was born to Jewish parents living 35 miles east of Warsaw in the small predominantly Jewish town of Kaluszyn. Rojske's mother was a housewife and her father was a merchant who often traveled, by horse and wagon, to Warsaw on business. When Rojske was in her twenties, she married Welwel Sadowsky, a fruit dealer. 1933-39: After war broke out last week, German forces fought Polish troops in a battle right here in Kaluszyn. Half the town has been flattened by shelling, and…
-
Johannes M. Lublink
ID CardJohannes was born to Christian parents and had three brothers and three sisters. His father sold coal for heating systems. By 1933, Johannes was also a coal distributor. Like many other Dutch citizens, Johannes did not approve of Hitler's policies. He especially objected to Hitler's persecution of Jews and Jehovah's Witnesses. 1933-39: Hitler's coming to power in Germany was a threat to all of them. In 1936, Johannes became a Jehovah's Witness. His mother was also a Witness and, by 1938, one brother and…

-
Shulamit Perlmutter (Charlene Schiff)
ID CardShulamit, known as Musia, was the youngest of two daughters born to a Jewish family in the town of Horochow, 50 miles northeast of Lvov. Her father was a philosophy professor who taught at the university in Lvov, and both of her parents were civic leaders in Horochow. Shulamit began her education with private tutors at the age of 4. 1933-39: In September 1939 Germany invaded Poland, and three weeks later the Soviet Union occupied eastern Poland, where Shulamit's town was located. Hordes of refugees…

-
Miso Vogel
ID CardMiso came from a religious family in a small village in Slovakia, where his father was a cattle dealer. He was the eldest of five children. When Miso was 6 his family moved to Topol'cany, where the children could attend a Jewish school. Antisemitism was prevalent in Topol'cany. When Miso played soccer, it was always the Catholics versus the Jews. 1933-39: In 1936 Miso had his bar mitzvah and was considered a man. His grandparents traveled 50 miles for it; he was so happy they were all together. In March…

-
Preben Munch-Nielsen
ID CardPreben was born to a Protestant family in the small Danish fishing village of Snekkersten. He was raised by his grandmother, who was also responsible for raising five other grandchildren. Every day Preben commuted to school in the Danish capital of Copenhagen, about 25 miles south of Snekkersten. 1933-39: There were very few Jews in Preben's elementary school, but he didn't think of them as Jews; they were just his classmates and pals. In Denmark they didn't distinguish between Jews and non-Jews, they…
-
Agnes Mandl
ID CardWhen Agnes was a teenager, she attended Budapest's prestigious Baar Madas private school, run by the Hungarian Reformed Church. Although she was the only Jewish student there, Agnes' parents believed that the superior education at the school was important for their daughter. Agnes' father, a textile importer, encouraged his daughter to think for herself. 1933-39: In 1936 Agnes studied educational techniques with Signora Maria Montessori in Italy and earned a diploma so she could teach. Hoping to improve…

-
Zofia Yamaika
ID CardZofia was raised in a well-to-do, prominent Hasidic Jewish family in Warsaw. Uneasy with the constant tension between the Polish people and the Jewish minority, Zofia joined the communist student club Spartacus when she was a teenager. Spartacus actively campaigned against the growing fascist movement in Europe. 1933-39: When Warsaw surrendered to the Germans on September 28, 1939, Zofia was 14 years old. She stopped going to school. Though the Nazis banned Spartacus, she secretly helped to revive the…

-
Tchiya Perlmutter
ID CardTchiya was the eldest of two daughters born to a Jewish family in the town of Horochow, 50 miles northeast of Lvov. Her father was a philosophy professor who taught at the university in Lvov, and both of her parents were civic leaders in Horochow. 1933-39: In September 1939 Germany invaded western Poland, and three weeks later the Soviet Union occupied eastern Poland [as a result of the German-Soviet Pact], where Horochow was located. Hordes of refugees fleeing the Germans streamed through the town.…
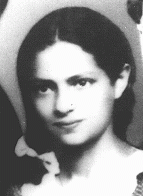
-
Manon Marliac
ID CardManon's Christian parents lived in Paris. Roger Marliac, her father, originally from a wealthy family, supported his family by selling produce at small marketplaces. Margarit, her mother (called Maguy by her friends), had a university degree in science. The family lived in a large apartment in a fashionable neighborhood near the Eiffel Tower. 1933-39: Manon, the Marliacs' second child, was born in 1937. She was 2 years old when her father was drafted into the French army as the country mobilized for a…

-
Morris Kornberg
ID CardMorris was the youngest of six children born to a religious Jewish family in Przedborz, a south central Polish town with a large Jewish population. Morris' family owned a business that supplied nearby factories with raw metal materials. 1933-39: When Germany invaded Poland in early September 1939 Morris and his family fled to the woods. They returned a few days later; most of the town had been burned down. The Nazis set up a ghetto and ordered everyone age 13 to 50 to report for work details. His family…

-
Gucia Grosfeld Frydmacher
ID CardGucia was born to middle-class Jewish parents in Radom, an industrial city known for its armaments factory, in which Jews were not allowed to work, and for a leather industry, in which many Jews were employed. Radom had a large and active Jewish community, and at home Gucia's family spoke both Polish and Yiddish. Gucia completed her schooling in Radom. 1933-39: As a young woman, Gucia was introduced to Benjamin Frydmacher, a young Jewish tanner from Lublin who occasionally came to Radom to visit his…

-
Bernburg T4 Facility
ArticleBernburg was the fifth of six centralized killing centers established by German authorities within the context of the Nazi “euthanasia,” or T4, program.

-
Vladka (Fagele) Peltel Meed describes clandestine cultural activities in the Warsaw ghetto
Oral HistoryVladka belonged to the Zukunft youth movement of the Bund (the Jewish Socialist party). She was active in the Warsaw ghetto underground as a member of the Jewish Fighting Organization (ZOB). In December 1942, she was smuggled out to the Aryan, Polish side of Warsaw to try to obtain arms and to find hiding places for children and adults. She became an active courier for the Jewish underground and for Jews in camps, forests, and other ghettos.

-
Morris Kornberg describes forced labor beginning after the German invasion of Poland
Oral HistoryMorris grew up in a very religious Jewish household and was active in a Zionist sports league. When the Germans invaded Poland in September 1939, Morris's town was severely damaged. Morris's family was forced to live in a ghetto, and Morris was assigned to forced labor. After a period of imprisonment in Konskie, a town about 30 miles from Przedborz, Morris was deported to the Auschwitz camp. He was assigned to the Jawischowitz subcamp of Auschwitz. In January 1945, Morris was forced on a death march and…

-
Belle Mayer Zeck describes research about IG Farben for the postwar trial
Oral HistoryBelle Mayer trained as a lawyer and worked for the General Counsel of the US Treasury, Foreign Funds Control Bureau. This bureau worked to enforce the Trading With the Enemy Act passed by Congress. In this capacity, Mayer became familiar with the German I. G. Farben chemical company, a large conglomerate that used slave labor during World War II. In 1945, Mayer was sent as a Department of Treasury representative to the postwar London Conference. She was present as representatives from the Allied nations…

-
Historian Peter Black describes the legislation used to deal with Nazi offenders living in the United States
Oral HistoryIn the 1980s and 1990s, historian Peter Black worked for the US Department of Justice Office of Special Investigations, as part of a team tracking and prosecuting suspected war criminals. Black later served as the Senior Historian at the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum.

-
Belle Mayer Zeck reflects upon people who have dedicated their lives to the cause of human rights
Oral HistoryBelle Mayer trained as a lawyer and worked for the General Counsel of the US Treasury, Foreign Funds Control Bureau. This bureau worked to enforce the Trading With the Enemy Act passed by Congress. In this capacity, Mayer became familiar with the German I. G. Farben chemical company, a large conglomerate that used slave labor during World War II. In 1945, Mayer was sent as a Department of Treasury representative to the postwar London Conference. She was present as representatives from the Allied nations…

-
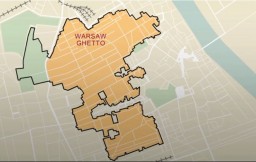
The Warsaw Ghetto
Animated MapView an animated map showing key events in the history of the Warsaw ghetto, the largest ghetto established by the Germans in occupied Europe.
-
Treblinka: Key Dates
ArticleExplore a timeline of key events during the history of the Treblinka killing center in German-occupied Poland.

-
Theresienstadt: "Retirement Settlement" for German and Austrian Jews
ArticleIn 1942, German authorities began to deport German and Austrian Jews to Theresienstadt. Learn about the administration of the camp-ghetto and Jews’ experiences.

-
The Bielski Partisans
ArticleUnder the protection of the Bielski partisan group, founded by brothers Tuvia, Asael, and Zus, over 1,200 Jews survived after fleeing into forests in western Belarus.

-
Supreme Court Decision on the Nuremberg Race Laws
ArticleLearn more about the 1936 German Supreme Court decision on the Nuremberg Race Laws.

-
Sachsenhausen
ArticleIn July 1936, the SS opened the Sachsenhausen concentration camp as the principal concentration camp for the Berlin area.

-
Collections Highlight: Selma Schwarzwald and her Bear, "Refugee"
ArticleWhile living under an assumed identity after escaping from the Lvov ghetto, Selma Schwarzwald received a toy bear that she kept with her for many years. Read about Refugee the bear.

-
Immigration to the United States 1933–41
ArticlePotential immigrants to the US from Nazi-occupied territory faced many obstacles, including restrictive quotas and complicated requirements for obtaining visas.

-
The Police in the Weimar Republic
ArticleThe Weimar Republic existed in Germany from 1918-1933. Learn more about German police during that time.

-
Blood Libel
ArticleBlood libels were false allegations that Jews used the blood of non-Jewish children in rituals. Nazi propagandists used this false charge in their antisemitic propaganda.

-
Ben Ferencz and the Fight for International Justice
ArticleBen Ferencz investigated and prosecuted Nazi crimes and devoted his career to creating an international system of justice. Learn about his activities and impact.

-
Spanish Civil War
ArticleThe Spanish Civil War (1936–39) was the bloodiest conflict western Europe had experienced since the end of WWI in 1918. It was a breeding ground for mass atrocities.

-
Liberation of Mauthausen
Timeline EventMay 5, 1945. On this date, US troops liberated Mauthausen concentration camp. Days before, a group of prisoners took control of Mauthausen.

-
The Armenian Genocide (1915-16): In Depth
ArticleLearn more about the Armenian Genocide, which was the physical annihilation of ethnic Armenian Christians living in the Ottoman Empire between 1915-1916.

-
The 45th Infantry Division during World War II
ArticleThe 45th Infantry Division participated in major WWII campaigns and is recognized for liberating the Dachau concentration camp in 1945.
-
Gerda Blachmann Wilchfort describes the mood of passengers on the "St. Louis" after they were denied entry into Cuba
Oral HistoryGerda and her parents obtained visas to sail to Cuba on the "St. Louis" in May 1939. When the ship arrived in Havana harbor, most of the refugees were denied entry and the ship had to return to Europe. Gerda and her parents disembarked in Belgium. In May 1940, Germany attacked Belgium. Gerda and her mother escaped to Switzerland. After the war, they were told that Gerda's father had died during deportation.

-
The United States and the Holocaust, 1942–45
ArticleWhy did the United States go to war? What did Americans know about the “Final Solution”? How did Americans respond to news about the Holocaust? Learn more.

