<< Previous | Displaying results 201-250 of 6720 for "" | Next >>
-
Boleslaw Brodecki
ID CardRaised by religious Jewish parents, Boleslaw and his older sister grew up in an apartment complex in a Jewish section of Warsaw. His father worked as an accountant. When Boleslaw was 8 years old, his mother died, and an aunt moved in to help raise him and his sister. Boleslaw loved electronics. When he was 10 years old, he succeeded in building a portable radio. 1933-39: The Germans attacked Warsaw on September 8, 1939. The bombing was relentless. Boleslaw's father wouldn't leave his ill relatives but…

-
Cecilie Klein-Pollack
ID CardCecilie was the youngest of six children born to a religious Jewish family in the Czechoslovakian town of Yasinya. Her father, who was from Poland, taught private lessons in math and German. The family owned a small grocery store, which Cecilie's mother managed. 1933-39: Cecilie's father died in 1934 when she was 9. In March 1939 Hungary, which was sympathetic to Nazi Germany, annexed the area of Czechoslovakia where they lived. One day, Cecilie arrived home to find her mother and sister had been arrested…

-
Elizabeth Kaufmann
ID CardElizabeth's father was a journalist who covered financial and political subjects. In 1930, because of the economic crisis in Austria, her father relocated his family from Vienna to Berlin. 1933-39: In 1933 the Nazis blacklisted Elizabeth's father as an anti-fascist writer, so her family returned to Vienna. With fascism rising there, her father left, eventually making it to Paris. They were to join him, but the Reich's borders were closed to Jews. Finally, Elizabeth's mother used her jewelry to get French…

-
Emanuel (Manny) Mandel
ID CardManny was born to a religious Jewish family in the port city of Riga, Latvia. Shortly after Manny's birth, his father accepted a post as one of the four chief cantors in Budapest and the family returned to Hungary, where they had lived before 1933. Manny's father was based at the renowned Rombach Street synagogue. Between the wars, Budapest was an important Jewish center in Europe. 1933-39: Manny's father wouldn't let him have a bicycle. He thought someone might take it away from him because he was…

-
Ezra Zelig Szabasson
ID CardEzra Zelig, who was called Zelig by family and friends, worked in the lumber business in Kozienice, a village by the Kozienice birch forest. He was married and the father of six children. A prominent member of the community, Zelig served on Kozienice's city council, and was also president of the local Zionist organization. 1933-39: In 1937 Zelig tried to obtain visas for his family to immigrate to Palestine [the Yishuv], at that time a British protectorate, but was unsuccessful because of the…

-
Chaya Szabasson Rubinstein
ID CardIn 1930 Chaya married Mordecai Rubinstein, a businessman, and moved with him from her hometown of Kozienice to the nearby city of Radom. Chaya had been raised in a religious, Yiddish-speaking Jewish family, and her father owned a lumber mill near the Kozienice birch forest. In Radom, Chaya's husband operated a small bus line. 1933-39: Chaya gave birth to a daughter, Gila, in 1933. In the mid 1930s the Rubinsteins moved back to Kozienice. There, they were trapped when German troops invaded [Poland] in…

-
Mordecai Pinchas Szabasson
ID CardMordecai, known in Yiddish as Motl, was born to a religious Jewish family with six children. His hometown of Kozienice, located near a birch forest, had an important lumber industry. After graduating from secondary school, Mordecai entered the lumber business. His small, successful company bought and sold lumber. 1933-39: A few months after the Germans invaded Poland in September 1939, Mordecai's father was warned to leave because, as a prominent member of the community, it was likely that the Germans…

-
Lewek Szabasson
ID CardLewek and his five brothers and sisters were born to religious Jewish parents in the town of Kozienice, situated in east central Poland near a birch forest. Lewek's father owned a sawmill, and when Lewek and his brothers were grown, they helped their father manage the family business. 1933-39: When Lewek was 15 he attended an agricultural school near Kozienice, because he wanted to immigrate to Palestine [Aliyah] to work the land. But after the Nazis rose to power in Germany in 1933, immigration…

-
Chaya Medalion
ID CardChaya and her brother and two sisters were raised in a religious, Yiddish-speaking home in the town of Kozienice, situated in east central Poland near a large birch forest. As a child, Chaya learned Hebrew. She attended Polish public schools and graduated at 14. Her father owned a factory that produced handmade shoes. 1933-39: Chaya was active in the Zionist movement, through which she met her boyfriend, Lewek Szabasson. Chaya and Lewek would stroll on Kozienice's main promenade which was at the…

-
Vita Rivkina
ID CardBecause both of her parents had died by the time Vita was 5 years old, she went to live with her cousins. At the age of 18, Vita married Iosif Rivkin, and the couple moved to Minsk where they raised three daughters--Hacia, Dora and Berta. 1933-39: By the early 1930s, the Rivkin family lived on Novomesnitskaya Street in central Minsk, near the Svisloch River. In the 1930s the girls attended Soviet state schools and were members of the Soviet youth organization, Young Pioneers. By the late 1930s Minsk was…

-
Isak Saleschutz
ID CardIsak was one of seven children born to devout Hasidic Jewish parents living in Dubas. By 1900, all of his siblings had immigrated to America; Isak remained in Poland due to his strong religious convictions. Through an arranged marriage, he was wed to Ester Berl when he was 18. They settled in Kolbuszowa, a small town near Dubas, where Isak ran a successful wholesale general store. 1933-39: On September 9, 1939, the German army occupied Dubas. They hanged two Jews to demonstrate the consequences of not…

-
Urszula Kaczmarek
ID CardUrszula was one of four children born to Franciszek and Jadwiga Kaczmarek, who lived in the industrial city of Poznan in western Poland. The family lived at 11 Smolnej Street. Like their parents, the Kaczmarek children were baptized in the Roman Catholic faith. 1933-39: As one of the older children in the family, Urszula helped her mother with the housework. She was 10 years old when the Germans invaded Poland on Friday, September 1, 1939. German planes bombed Poznan that same day, and German troops…

-
Israel Milkow
ID CardIsrael was born to a religious Jewish family living in the town of Slonim. He was called Yisroel by his Yiddish-speaking parents. Israel's father, Lazar Milkow, was a baker who supported his family on a meager income. 1937-39: Israel's grandparents and many of his mother's relatives lived in a nearby village called Kaslovchina. Each summer one of the Milkow boys was invited to stay in Kaslovchina with their Uncle Herschel who worked as a farmer and horse trader. In September 1939 Slonim became part of the…

-
Karl-Heinz Kusserow
ID CardKarl-Heinz was born during World War I, while his father was in the German army. After the war, his Lutheran parents became Jehovah's Witnesses and gave their children daily Bible lessons. When Karl-Heinz was 13, the family moved to the rustic Westphalian town of Bad Lippspringe. Their home became the headquarters of a new Jehovah's Witness congregation. 1933-39: Because of the Jehovah's Witnesses' missionary work, and because their sole allegiance was to God and His commandments, their activities were…

-
Joseph von Hoppen Waldhorn
ID CardJoseph was the youngest of three children born to immigrant Jewish parents. His Polish-born father was a former officer in the Austro-Hungarian army who had met and married Joseph's Hungarian-born mother during World War I. Joseph was raised in a religious household and grew up speaking French. 1933-39: Joseph's mother says it's better here in Paris than in the poor village where she grew up. Unlike his mother, who speaks broken French, Joseph and his older sisters have grown up speaking French fluently.…

-
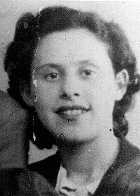
-
Aaron Lejzerowicz
ID CardAaron was one of four children born to a Jewish family in the northeastern Polish town of Zdzieciol. His father was a shoemaker and, along with a business partner, he also ran a shoe store in the town. Aaron attended a private Jewish school, where he studied the Polish language and history as well as Jewish history and Hebrew. 1933-39: On September 1, 1939, Germany invaded Poland. Three weeks later, Poland was partitioned between Germany and the Soviet Union [under the German-Soviet Pact]. Aaron and his…

-
Paula Wajcman
ID CardPaula was raised in a religious Jewish family in Kielce, a city in the southeast of Poland. Her family lived in a modern two-story apartment complex. Paula's father owned the only trucking company in the district. Her older brother, Herman, attended religious school, while Paula attended public kindergarten in the morning and religious school in the afternoon. 1933-39: Paula's school uniform was a navy blazer with a white blouse and pleated skirt. At age 9, she did the "Krakowiak" dance at school. Boys…
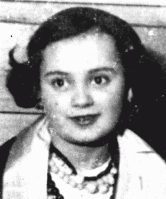
-
Chaim Frenkiel
ID CardChaim was the third of seven boys born to religious Jewish parents. They lived in a town near Warsaw called Gabin, where Chaim's father worked as a cap maker. Gabin had one of Poland's oldest synagogues, built of wood in 1710. Like most of Gabin's Jews, Chaim's family lived close to the synagogue. The family of nine occupied a one-room apartment on the top floor of a three-story building. 1933-39: In September 1939, two months before Chaim was 12, Germany invaded Poland. In Gabin 10 people were shot in…

-
Jakob Frenkiel
ID CardJakob was one of seven boys in a religious Jewish family. They lived in a town 50 miles west of Warsaw called Gabin, where Jakob's father worked as a cap maker. Gabin had one of Poland's oldest synagogues, built of wood in 1710. Like most of Gabin's Jews, Jakob's family lived close to the synagogue. The family of nine occupied a one-room apartment on the top floor of a three-story building. 1933-39: On September 1, 1939, just a few months before Jakob turned 10, the Germans started a war with Poland.…

-
Inge Scheer
ID CardInge grew up in Vienna's Leopoldstadt, a large Jewish district located between the banks of the Danube Canal and the Danube River. The Scheers loved music, and Inge grew up listening to family members singing selections from popular operettas. 1933-39: Inge was 8 years old when the Germans annexed Austria in 1938 and her parents decided they'd better flee. They were smuggled illegally, via the Netherlands, to Brussels where the Jewish community helped to hide illegal refugees like Inge and her family.…
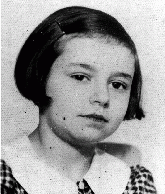
-
Laura Ellenbogen
ID CardLaura was one of five children born to a Jewish family in the southeastern Polish town of Rozwadow. Jews comprised almost two-thirds of the town's population. Laura's father worked as a wholesaler, providing families in the area with grain, potatoes and other produce. Laura attended one of the town's public schools. 1933-39: Germany and the Soviet Union partitioned Poland [as a result of the Nazi-Soviet Pact] in September 1939. Laura's town lay on the demarcation line. On September 24 the Germans reached…
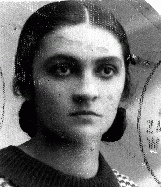
-
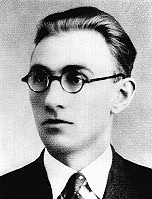
Abraham Roman Ellenbogen
ID CardAbraham was the oldest of five children born to a Jewish family in the central Polish town of Rozwadow, where his father was a produce wholesaler. Abraham attended secondary school in the nearby town of Rzeszow and then went on to complete an undergraduate degree at the University of Cracow. 1933-39: Abraham was accepted to law school, despite quotas restricting the number of Jews allowed to enter, and in 1937 he set up a practice in Rozwadow. Two years later, on September 1, 1939, Germany invaded Poland.…
-
Hanna Ellenbogen
ID CardHanna was one of three children born to a Jewish family in the central Polish town of Rozwadow. Hanna's father was a produce wholesaler. As a young girl, Hanna was active in Benei Akiva, a Zionist youth organization. She attended public school in Rozwadow, and then went on to business school. 1933-39: After finishing business school, Hanna took classes in childhood education. She and a friend then set up a nursery school in Rozwadow a few blocks from Hanna's home. The nursery had been open only a few…

-
Maurits Wijnberg
ID CardMaurits was one of four children born to religious Jewish parents living in the town of Leek. When he was 12, the Wijnbergs moved to the town of Zwolle, where they ran a kosher hotel. That same year, Maurits became ill with meningitis. After he recovered, he worked hard to compensate for missed school and became an exceptional student. 1933-39: Along with his younger sister, Maurits was active in the local Zionist organization. One of the group's activities was raising money for Palestine [Yishuv]. Every…

-
Marthijn Wijnberg
ID CardWhen Marthijn was 10, his religious Jewish family moved from Groningen to the town of Zwolle. There, his parents ran the only kosher hotel in the region. The Wijnbergs had two other sons and a daughter. All of the children attended Dutch public schools, and four afternoons a week they also went to religious school to study Jewish history, Hebrew and the Bible. 1933-39: Marthijn could play almost any instrument, including piano, saxophone and accordion. Sometimes each of his brothers would pick up an…

-
Abraham Wijnberg
ID CardAbraham, or "Braham" as he was nicknamed, was the oldest of four children. When Braham was 14, his Jewish parents moved to the town of Zwolle, where they built a kosher hotel. Braham attended Dutch public schools. Monday through Thursday afternoons he also went to religious school where he learned Hebrew, Jewish history and the Bible. 1933-39: Abraham felt that it was a shame that he had to forfeit a scholarship to college in Groningen, but he had to stay in Zwolle to help his parents with the hotel.…

-
Edith Goldman Bielawski
ID CardEdith's parents owned a cotton factory in the town of Wegrow [in Poland]. The Goldmans were a religious family, and raised Edith, her brother and three sisters to strictly observe the Sabbath, Jewish holidays and the dietary laws. 1933-39: Edith attended public school, and also studied at the Beis Yakov religious school for girls where she learned Hebrew, the Bible and Jewish history. Her favorite hobby was knitting, and after finishing secondary school she learned the quilt-making trade. In the…

-
Ludmilla Schatz
ID CardLudmilla was one of four children born to Jewish parents in a small industrial city in southwestern Ukraine when the area was part of Tsarist Russia. Ludmilla grew up in Odessa, but she and her mother left in 1919 when Ludmilla's father was killed during the Russian civil war. Ludmilla and her mother emigrated to France and settled near Paris. Ludmilla married, and gave birth to a daughter in 1930. 1933-39: With her knowledge of Russian, French and German, Ludmilla felt comfortable in cosmopolitan Paris.…
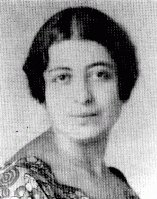
-
Tonie Frederika Kaufmann Soep
ID CardTonie's parents came to the Netherlands from Germany in the 1880s, and their six children were born in Amsterdam. As a child, Tonie studied the piano, and she excelled in French. When she married Abraham Soep, a diamond manufacturer, Tonie adopted her husband's observant Jewish practices. Their three children were born in 1919, 1923, and 1924. 1933-39: Tonie's husband served for many years as the president of the Amsterdam Jewish community. The Soeps had a large and comfortable home. Tonie and Abraham…

-
Abraham Soep
ID CardAbraham, known as "Bram," was born to a religious Jewish family in Amsterdam. After graduating from high school, Bram went into the diamond business with his father. By 1924 he and his wife, Tonie, had three children. Bram served as president of the Amsterdam Jewish community. 1933-39: The Soeps had a large and comfortable home. Bram and his wife often traveled abroad, and each summer the family rented a home near the seashore in Zandvoort. In 1937 Bram's son Benno joined him in the diamond…

-
Catharina Soep
ID CardCatharina, called "Ina" by her family and friends, grew up in a religious Jewish household in Amsterdam. Ina's father, a successful diamond manufacturer, was president of the Amsterdam Jewish community. Ina had one brother, Benno, and a sister, Josette. 1933-39: On Sunday mornings and on Wednesdays after her classes at an Amsterdam Montessori school, Ina went to a private Jewish school where she studied Jewish history and Hebrew. Ina and her friends loved to meet in the evenings after they finished their…

-
Raszka (Roza) Galek
ID CardRoza was born to a Jewish family in a predominately Catholic village near Warsaw. Her father owned a prosperous pearl button factory that employed some 100 people. They shared a large home with Roza's grandmother who ran a general store and bakery in the village. Roza and her three sisters attended Polish schools and took Hebrew lessons at the towns' synagogue. 1933-39: Roza's father frequently did business in Warsaw so the family moved there in 1934. They loved the city, and often went to concerts and…

-
Moshe Galek
ID CardMoshe was one of eight children born to Jewish parents in Sochocin, a predominantly Catholic village near Warsaw. Moshe was a self-made man, having founded a successful pearl-button factory in the village. While in his thirties, he married Fela Perznianko, the daughter of a prominent attorney from nearby Zakroczym. He brought his new wife to Sochocin, where they raised four daughters. 1933-39: In 1936 the Galeks moved to Warsaw, attracted by the city's cultural life. When Germany invaded Poland on…

-
Peter Somogyi
ID CardPeter and his twin brother, Thomas, were the youngest of three children born to an observant Jewish family. They lived in Pecs, an industrial center where goods such as bricks and ceramics were produced. Peter's father owned a prosperous business selling accessories and parts for cars, motorcycles and bicycles. He was also a regional sales representative for Ford automobiles. 1933-39: A German nanny took care of Peter, Thomas, and their older sister. She taught them German and they became quite fluent.…

-
Rachel Lejzerowicz Rechnitz
ID CardRachel, or Ruchla as she was called, was raised by Jewish parents in the small southwestern Polish town of Bedzin. In 1930 she moved with her husband, Bernard, to the nearby city of Katowice, where Bernard had a wholesale leather business. The couple lived with their two children, Moses and Genia, in a three-bedroom, upper-floor apartment on Jordana Street. 1933-39: Ruchla was active in Hadassah, a women's Zionist organization, and in 1939 she and her husband prepared to immigrate to Palestine [Aliyah…
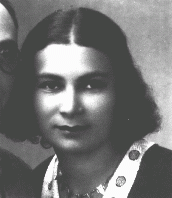
-
Saul Ingber
ID CardSaul was born to a Jewish family in the small northern Transylvanian town of Moisei, famous for its 18th-century monastery, to which many Christians came on pilgrimage. Saul's family was religious. His father transported lumber to several mills in the area. 1933-39: Saul and his brothers attended a Jewish school held at their neighbor's home. A rabbi led them in prayers and they learned quotations from holy texts. After his schooling he needed to learn a trade, so he decided to become a tailor. Jews were…

-
Fischel (Philip) Goldstein
ID CardFischel was the youngest of five children. He came from a Jewish family of artisans; his father was a tailor, his uncles were furriers, and his sister was a dressmaker. Fischel started his education at a Jewish parochial school at age 3, where he studied Hebrew and Yiddish. He continued his education at Jewish private schools until age 10, when he entered Polish public schools. 1933-39: After graduating from the Polish public school system at age 14, Fischel started an apprenticeship in his father's…

-
Feige Schwarzfink
ID CardFeige was born to a religious Jewish family in the small village of Szydlowiec [in Poland]. She lived with her parents, six brothers and sisters, and elderly grandparents in a small house which, like many homes in the village, had no running water, indoor plumbing, or electricity. Feige's father was a shoemaker. 1933-39: In the afternoons after public school Feige studied at a Jewish religious school. Although her parents didn't know it, she attended meetings of the Bund, the Jewish Socialist party. Feige…

-
Albert Gani
ID CardAlbert and his family lived in Preveza, a town with a Jewish population of 300 that was located on the Ionian seashore. Albert's father had a small textile shop. The Ganis were of Romaniot descent, Jews whose ancestors had lived in Greece and the Balkans for more than a thousand years. 1933-39: After graduating from high school, Albert assisted his father in the family textile shop. A quiet and reserved young man, Albert enjoyed spending time at home with his family. Albert loved taking excursions with…

-
Joseph Gani
ID CardJoseph and his family lived in Preveza, a town with a Jewish population of 300 that was located on the Ionian seashore. Joseph's father had a small textile shop. The Ganis were of Romaniot descent, Jews whose ancestors had lived in Greece and the Balkans for more than a thousand years. 1933-39: Joseph attended Greek public school in Preveza. He also received a religious education; the local rabbi would come to the public school for several hours a week to give religious instruction to the Jewish students.…
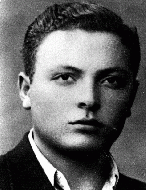
-
Rena Gani
ID CardRena and her family were Romaniot Jews, a group that had lived in Greek cities and the Balkans for more than 1,100 years. The town of Preveza, located on the Ionian seashore, had 300 Jews. Rena's father had a small textile shop and her mother stayed at home to care for Rena, her sister and her three brothers. 1933-39: When Rena's family moved to the nearby town of Ioannina, she completed Jewish primary school there. The school was sponsored by the French organization Alliance Israelite Universelle, and…

-
Claude Brunswic
ID CardClaude was one of five children born to Jewish parents in the university city of Heidelberg. His father, a physician specializing in internal medicine, had his practice on the first floor of the apartment building in which the family lived. Claude was an avid swimmer until November 1932, when local Nazi party edicts forbad Jews to use the city pool where he swam. 1933-39: In January 1933, just after Hitler became chancellor of Germany, hoodlums attacked Jewish-owned businesses in Heidelberg. They broke…

-
Helena Manaster
ID CardHelena was the eighth of 10 children born to a Jewish family in the town of Lesko. Her father was a landowner. When Helena was a young girl the family moved to nearby Orelec, where they had a summer home. As there were no schools in Orelec, Helena and her siblings continued attending school in Lesko. Later, Helena traveled three hours by train daily to attend the nearest high school, which was in Przemysl. 1933-39: The German army invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. By the beginning of October the…
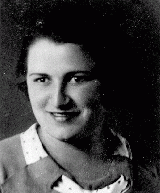
-
Amalie Petranker
ID CardAmalie was one of three daughters born to Jewish parents. The family lived in Stanislav [Stanislawow], Poland. Her father was an ardent supporter of resettlement in Palestine, and dreamed of moving his family there to help build the Jewish homeland. Amalie and her sisters attended private Hebrew primary and secondary schools to help prepare them for their eventual immigration to Palestine. 1933-39: In September 1939 Stanislav [Stanislawow] was occupied by the Soviet army. Amalie's father lost his job in…

-
Celia Petranker
ID CardCelia was the youngest of three daughters born to Jewish parents living in Stanislav [Stanislawow], Poland. Her father was an ardent Zionist, and dreamed of moving his family to Palestine to help build a Jewish homeland. Celia and her sisters attended private Hebrew primary and secondary schools to help prepare them for their eventual immigration to Palestine. 1933-39: Celia's oldest sister, Pepka, left for Palestine one week after the Germans invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. Pepka's departure was…
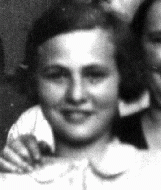
-
Faiga Grynbaum
ID CardFaiga was one of nine children born to religious Jewish parents in Starachowice, a town in east-central Poland. Their small one-story house served as both the family's residence and their tailor shop. Faiga worked in the shop sewing women's clothes; the tailoring was often done in exchange for goods such as firewood or a sack of potatoes. 1933-39: In 1935 Faiga married Haskel Ochervitch. She moved to Kielce, a larger town some 25 miles southwest of Starachowice, where her husband worked selling meat to…

-
Baruch Aaron Szabasson
ID CardBaruch was known by his family and friends as Buzek. He came from the east central Polish town of Kozienice. Kozienice was a popular vacation spot situated near lakes and a birch forest. Baruch's father worked in the lumber business. 1933-39: Baruch attended public school, and in the afternoons he also went to Jewish religious school. On Friday nights for the sabbath, Baruch would go to his grandparents' house, where his relatives would gather to visit with one another. Baruch would run to his grandfather…

-
Samson Reichstein
ID CardSamson was raised by Jewish parents in Tarnopol. His father died when Samson was 13, and Samson went to work to help support his mother and four brothers and sisters. In October 1918 Samson married Kaethe Ert, and the couple moved to Hanover, Germany, where Samson worked as a traveling salesman. Their son Herbert was born in 1920. 1933-39: In 1938 Samson and Kaethe got their son an exit visa on America's Polish quota (since they were Polish citizens). Later that year, the Gestapo came to their door with…

-
Welwel Kisielnicki
ID CardWelwel lived with his wife, Feiga, and their three children in the small, predominantly Jewish town of Kaluszyn, which was 35 miles east of Warsaw. The Kisielnickis were religious and spoke Yiddish in their home. Welwel was a merchant and often traveled, by horse and wagon, to Warsaw on business. 1933-39: The Kisielnicki family's hopes that the war wouldn't reach Kaluszyn have been shattered. Last week, a German plane flew over their town and dropped a bomb on people waiting in line outside a bakery.…

