You searched for: 柬埔寨短信通道【TG飞机:@bapingseo】阿塞拜疆谷歌霸屏【TG电报:@bapingseo】烏茲別克斯坦谷歌留痕推廣【Telegram:@bapingseo】彩51网站下载飞艇计划微信讲解1分快3走势图怎么看懂?202207063iXbCk.html
<< Previous | Displaying results 501-550 of 829 for "柬埔寨短信通道【TG飞机:@bapingseo】阿塞拜疆谷歌霸屏【TG电报:@bapingseo】烏茲別克斯坦谷歌留痕推廣【Telegram:@bapingseo】彩51网站下载飞艇计划微信讲解1分快3走势图怎么看懂?202207063iXbCk.html" | Next >>
-
Szlamach Radoszynski
ID CardSzlamach was one of six children born to Yiddish-speaking, religious Jewish parents. Szlamach's father was a peddler, and the Radoszynski family lived in a modest apartment in Warsaw's Praga section on the east bank of the Vistula River. After completing his schooling at the age of 16, Szlamach apprenticed to become a furrier. 1933-39: During the 1930s Szlamach owned a fur business. Despite the Depression, he was hoping the economy would turn around so that he could make enough money to move into his own…

-
Irena Elzbieta Wos
ID CardIrena was the second of four children born to religious Roman Catholic parents in Poland's capital of Warsaw. Irena's father owned a successful textile business. When Irena was 10, her family moved to a comfortable apartment near the Royal Castle and the Vistula River. In 1930 Irena entered a private grade school. 1933-39: At 14 Irena began secondary school. She was a good student and wanted to be a doctor. On September 1, 1939, the day she was supposed to begin the new school year, the Germans attacked…
-
Mieczyslaw (Marek) Madejski
ID CardMieczyslaw was the eldest of three sons born to well-to-do Roman Catholic parents in Poland's capital of Warsaw. His father was a real estate developer and his mother was a housewife. Mieczyslaw, or Mieteck as he was nicknamed, began attending public elementary school in 1930 when he was 7 years old. 1933-39: Mieczyslaw's father urged him to study either German or Russian because he thought it was likely that there would be a German or Soviet invasion. Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. During…

-
Martin Niemöller: "First they came for..."
ArticleLearn about the origins and legacy of Pastor Martin Niemöller's famous postwar words, “First they came for the socialists, and I did not speak out…”

-
Mass Shootings at Babyn Yar (Babi Yar)
ArticleAt Babyn Yar in late September 1941, SS and German police units and their auxiliaries perpetrated one of the largest massacres of World War II.

-
Treblinka: Key Dates
ArticleExplore a timeline of key events during the history of the Treblinka killing center in German-occupied Poland.

-
Genocide Timeline
ArticleKey dates in the use of the term genocide as part of the political, legal, and ethical vocabulary of responding to widespread threats of violence against groups.

-
Warsaw
ArticleIn October 1940, Nazi authorities established the Warsaw ghetto. Learn more about life in the ghetto, deportations, armed resistance, and liberation.

-
Trial of Ion Antonescu
FilmIon Antonescu governed Romania from 1940 until 1944. Antonescu aligned Romania with the Axis powers in November 1940, and became one of Nazi Germany's closest allies. Romania joined in the German invasion of the Soviet Union in 1941. It also implemented harsh anti-Jewish policies against Jews in Romania. While Antonescu ultimately refused to hand Jews over to the Germans, Romanian forces brutally killed hundreds of thousands of Jews, mainly residents of Bessarabia, Bukovina, and the western Ukraine. As the…

-
The Olympic stadium in Berlin
PhotoView of the Olympic Stadium, centerpiece of Berlin's Reich Sports Field. Berlin, Germany, 1936. The Nazis made elaborate preparations for the August 1–16 Summer Olympic Games. A huge sports complex was constructed, including the new stadium and state-of-the art Olympic village for housing the athletes. Olympic flags and swastikas bedecked the monuments and houses of a festive, crowded Berlin. Most tourists were unaware that the Nazi regime had temporarily removed anti-Jewish signs, nor would…

-
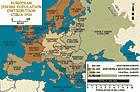
European Jewish population distribution, ca. 1933
MapJews have lived in Europe for more than two thousand years. The American Jewish Yearbook placed the total Jewish population of Europe at about 9.5 million in 1933. This number represented more than 60 percent of the world's Jewish population, which was estimated at 15.3 million. Most European Jews resided in eastern Europe, with about 5 1/2 million Jews living in Poland and the Soviet Union. Before the Nazi takeover of power in 1933, Europe had a dynamic and highly developed Jewish culture. In little more…
-
Richard Baer at a ceremony
PhotoSeptember 1, 1944, Richard Baer ceremonially accepts a copy of the construction plans from the Chief of the Central Construction Directorate of the Waffen SS, SS-Sturmbannführer Karl Bischoff, celebrating the opening of an SS military hospital (SS-Lazarette). Baer was the last commandant of the Auschwitz camp. From Karl Höcker's photograph album, which includes both documentation of official visits and ceremonies at Auschwitz as well as more personal photographs depicting the many social…

-
Heinrich Himmler: Key Dates
ArticleHeinrich Himmler was the leader of the dreaded SS of the Nazi Party from 1929 until 1945. Learn more about key dates in the life of Heinrich Himmler.

-
Theresienstadt: Transit Camp for Czech Jews
ArticleLearn more about Theresienstadt’s function as a transit camp and the deportation of Czech Jews during World War II.

-
The Aftermath of the Holocaust: Effects on Survivors
ArticleSurvivors of the Holocaust faced huge obstacles in rebuilding their lives. Learn about the challenges they faced in the aftermath of the Holocaust.

-
Law for the Imposition and Implementation of the Death Penalty
ArticleLearn more about the Law for the Imposition and Implementation of the Death Penalty, which the Nazis enacted after the Reichstag Fire Decree in 1933.

-
Gross-Rosen
ArticleLearn about the Gross-Rosen camp, including its establishment, prisoner population, subcamps, forced labor, and liberation.

-
Jewish Community of Munkacs: An Overview
ArticleLearn about the Jewish community of Munkacs, famous for its Hasidic activity as well as its innovations in Zionism and modern Jewish education.

-
Ravensbrück: Key Dates
ArticleExplore a timeline of the history of the Ravensbrück camp in the Nazi camp system from its establishment in 1938 until the last of the Ravensbrück trials in 1966.

-
1940: Key Dates
ArticleExplore a timeline of key events during 1940 in the history of Nazi Germany, World War II, and the Holocaust.

-
Ravensbrück: Liberation and Postwar Trials
ArticleRavensbrück was the largest concentration camp for women in the German Reich. Learn about the last months of the Ravensbrück camp and the postwar trials of camp staff.

-
Featured Artifact: Model of the Lodz Ghetto
ArticleLeon Jakubowicz began constructing a model of the Lodz ghetto in the spring of 1940, after the ghetto was sealed. Explore the artifact and Leon's story.

-
Coining a Word and Championing a Cause: The Story of Raphael Lemkin
ArticlePolish-Jewish lawyer Raphael Lemkin introduced the word genocide in 1944 and lobbied tirelessly for its addition as a crime in international law.

-
Youth Camps
ArticleMoringen, Uckermark, and Litzmannstadt were reform camps established to confine young people who were deemed to have strayed from Nazi norms and ideals. Learn more

-
Wannsee Protocol
ArticleThe Wannsee Protocol documents the 1942 Wannsee Conference participants and indicates their agreement to collaborate on a continental scale in the Final Solution.

-
Edward R. Murrow
ArticleUS radio and TV journalist Edward R. Murrow reported live from London during the Blitz; he also broadcast the first eyewitness account of the liberation of Buchenwald.
-
Chère Odette
Timeline EventMarch 21, 1942. On this date, while in prison for resistance activities, Charlotte Delbo wrote to her sister. Later deported to Auschwitz, Charlotte would write about her experiences after the war.

-
First Conviction for Genocide
Timeline EventSeptember 2, 1998. On this date, the International Criminal Tribunal for Rwanda found Jean-Paul Akayesu guily of genocide and crimes against humanity.

-
Munich Agreement
Timeline EventSeptember 29-30, 1938. On this date, Germany, Italy, Great Britain, and France signed the Munich agreement, giving Germany the Sudetenland.

-
Drancy Camp Established
Timeline EventAugust 20, 1941. On this date, German authorities opened the Drancy internment and transit camp in France.

-
The Armenian Genocide (1915-16): Overview
ArticleThe Armenian genocide (1915–1916) is sometimes called the first genocide of the twentieth century.

-
German and Soviet forces partition Poland
FilmThe German-Soviet Pact of August 1939 included a nonaggression pact whereby Germany and the Soviet Union promised not to attack one another for 10 years. Germany was thus able to invade Poland on September 1, 1939, without fear of Soviet intervention. In accordance with secret provisions of the pact, Poland was partitioned between Germany and the Soviet Union. Soviet forces occupied eastern Poland. In this footage, German and Soviet forces meet along the Bug River in central Poland. Less than two years…

-
Börgermoor Camp
ArticleBörgermoor was part of the Nazi regime’s early system of concentration camps. It was located in the Emsland region of Prussia.
-
“Give Me Your Children”: Voices from the Lodz Ghetto
ArticleThe Jewish children of Lodz suffered harsh conditions after the German invasion of Poland. Read excerpts from diaries where they recorded their experiences.

-
United States Immigration and Refugee Law, 1921–1980
ArticleUS immigration and refugee laws and policies evolved in response to World War I, the 1918 influenza pandemic, and World War II and the Holocaust. Learn more.

-
The United States and the Nazi Threat: 1933–37
ArticleLearn about responses in the United States to reports about Nazi anti-Jewish policies and violence against Jews from 1933–37.

-
München-Schwabing
ArticleLearn about the establishment and history of the Dachau subcamp München-Schwabing, and the role of Eleonore Baur (also known as Schwester Pia or Sister Pia).
-
Wagner-Rogers Bill
ArticleThe Wagner-Rogers Bill proposed admitting 20,000 refugee children to the US from the Greater German Reich in 1939–40, but did not become law. Learn more

-
Kurt Gerstein
ArticleSS officer Kurt Gerstein was horrified by what he witnessed at the Belzec killing center. Learn about how he recorded what he witnessed and about his postwar fate.
-
Simone Weil
ID CardSimone was the oldest of two children born to a Jewish family in the small village of Ringendorf. When she was 3 her family moved to Strasbourg. Her father made his living breeding sheep. Simone and her younger brother were both active in a Jewish scouting organization, Les Eclaireurs Israelites de France (EIF). Simone attended a public secondary school in Strasbourg. 1933-39: In addition to attending secondary school for five days of the week, Simone also went to a Jewish religious school on the other…

-
Welek Luksenburg
ID CardWelek grew up in Dabrowa Gornicza, an industrial town in western Poland. His father, Simcha, was a wholesale meat merchant and his mother, Rozalia, served as president of the local chapter of the Women's International Zionist Organization. Welek's older brother, Szlomo, was a dentist. The Luksenburgs were among the several thousand Jews who lived in Dabrowa Gornicza. 1933–39: Like many other children in the town, Welek attended public school. Because his family was very religious, he did not attend…

-
Abraham Bergman
ID CardAbraham was born to a Jewish family in Krasnik, a town in the Lublin district of Poland. The town had a large Jewish population. Abraham's father was a tailor. When Abraham was 2, his mother died and he was raised by his grandmother. At the age of 7, Abraham started public school. 1933-39: Abraham liked school but found it difficult. The Christian children often yelled at the Jews, "You killed our God." One year, on the day before Christmas break, some kids brought ropes tied to iron weights to school.…

-
Fischel (Philip) Goldstein
ID CardFischel was the youngest of five children. He came from a Jewish family of artisans; his father was a tailor, his uncles were furriers, and his sister was a dressmaker. Fischel started his education at a Jewish parochial school at age 3, where he studied Hebrew and Yiddish. He continued his education at Jewish private schools until age 10, when he entered Polish public schools. 1933-39: After graduating from the Polish public school system at age 14, Fischel started an apprenticeship in his father's…

-
Milica Popovic Kuhn
ID CardMilica was the fourth of nine children born to Serbian Orthodox landowners in the Croatian part of Yugoslavia. In 1922 Milica married Milan Kuhn, a Catholic Serb, in a Serbian Orthodox ceremony, and the couple moved to the Macedonian part of Yugoslavia, where Milan was working on hydroelectric projects. In 1932 the couple returned with their young daughter to live in northern Yugoslavia. 1933-39: The Kuhns lived in the city of Zrenjanin in the Vojvodina region where Milan worked as a hydroengineer…

-
Walther Hamann
ID CardWalther was born in the state of Thuringia in east central Germany. Though his parents were Lutheran, Walther became a Jehovah's Witness in 1923. After becoming a master baker and confectioner in 1924, Walther worked in various coffeehouses in Plauen, Magdeburg and Duesseldorf. In 1928 he graduated from a professional school. He married and had two sons. 1933-39: In 1933 Walther became a pastry-making manager at the Cafe Weitz on Duesseldorf's Koenigsallee. The Gestapo arrested him at the cafe in 1937…

-
Marcus Fass
ID CardMarcus, known to his family as Moniek, was one of three children born to a Jewish family in the Polish town of Ulanow. His father worked as a tailor. Ulanow's Jewish community had many of its own organizations and maintained a large library. From the age of 3, Moniek attended a religious school. He started public school when he was 7. 1933-39: In 1935 Moniek's father left for America to find a job so that his family could later join him. He sent money to them while they waited for their emigration papers.…

-
Zigmond Adler
ID CardZigmond's parents were Czechoslovakian Jews who had emigrated to Belgium. His mother, Rivka, was a shirtmaker. She had come to Belgium as a young woman to find a steady job, following her older brother, Jermie, who had moved his family to Liege several years earlier. In Liege, Rivka met and married Otto Adler, a businessman. The couple looked forward to raising a family. 1933-39: Zigmond was born to the Adlers in 1936, but his mother died one year later. His father remarried, but the marriage didn't last.…

-
Henoch Kornfeld
ID CardHenoch's religious Jewish parents married in 1937. His father, Moishe Kornfeld, and his mother, Liba Saleschutz, had settled in Kolbuszowa, where Henoch's mother was raised. There, Liba's father bought the newlyweds a home and started his new son-in-law in the wholesale textile business. 1938-39: Henoch was born in late 1938, and was raised among many aunts, uncles and cousins. Around Henoch's first birthday, Germany invaded Poland and soon reached Kolbuszowa. Polish soldiers on horses tried to fight…

-
Smiljka Ljoljic Visnjevac
ID CardSmiljka was one of three daughters born to Serbian Orthodox parents in the town of Mostar in the central Yugoslav region of Herzegovina. Smiljka's mother died when Smiljka was 3, and the three girls were raised by their father. A tomboy in her youth, at 17 Smiljka won the Miss Makarska Riviera beauty pageant and left for Germany to become a fashion model. 1933-39: Smiljka had a successful modeling career in Berlin. With her tall, slim figure, high cheekbones, and almond-shaped, grey-blue eyes, she was…

-
Claude J. Letulle
ID CardOne of five children, Claude grew up in a Catholic family in Paris. His father, a physician, owned a prosperous general medicine practice and medical laboratory. Claude's father encouraged him to study medicine and to join his practice, but Claude was more interested in becoming a lawyer. 1933-39: Claude continued his studies, and in 1936 he entered the university to study law. By mid-1939, Germany's threat against France had escalated, and on September 3, 1939, France declared war on Germany. Claude knew…

